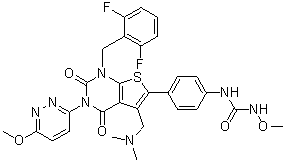
Relugolix (formerly TAK-385; TAK385; trade names: Orgovyx and Relumina) is a non-peptidyl and orally bioactive antagonist of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) approved in 2020 for use in the treatment of prostate cancer in men and uterine fibroids in women. It is also being developed as an endometriosis treatment. Relugolix inhibits GnRH in the presence of 40% fetal bovine serum with an IC50 of 0.33 nM. When compared to TAK-013, it has a stronger antagonistic activity and a higher affinity. While TAK-385 regulates the effects of LH and FSH on the ovary and lowers blood levels of estrogen, which are known to be linked to the development of endometriosis and uterine fibroids, Relugolix inhibits LH-RH from binding with the LH-RH receptor in the anterior pituitary gland and suppresses the secretion of luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle stimulation hormone (FSH) from the anterior pituitary gland.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C29H27F2N7O5S |
| Molecular Weight | 623.630391359329 |
| Exact Mass | 623.18 |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 55.85; H, 4.36; F, 6.09; N, 15.72; O, 12.83; S, 5.14 |
| CAS # | 737789-87-6 |
| Related CAS # | Relugolix-d6 |
| PubChem CID | 10348973 |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid powder |
| LogP | 3.966 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 11 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 9 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 44 |
| Complexity | 1010 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| SMILES | O=C(NOC)NC1=CC=C(C(S2)=C(CN(C)C)C(C(N3C4=NN=C(OC)C=C4)=O)=C2N(CC5=C(F)C=CC=C5F)C3=O)C=C1 |
| InChi Key | AOMXMOCNKJTRQP-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C29H27F2N7O5S/c1-36(2)14-19-24-26(39)38(22-12-13-23(42-3)34-33-22)29(41)37(15-18-20(30)6-5-7-21(18)31)27(24)44-25(19)16-8-10-17(11-9-16)32-28(40)35-43-4/h5-13H,14-15H2,1-4H3,(H2,32,35,40) |
| Chemical Name | 1-[4-[1-[(2,6-difluorophenyl)methyl]-5-[(dimethylamino)methyl]-3-(6-methoxypyridazin-3-yl)-2,4-dioxothieno[2,3-d]pyrimidin-6-yl]phenyl]-3-methoxyurea |
| Synonyms | TAK 385; TAK385; TAK-385; trade names: Orgovyx; Relumina |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | human GnRH ( IC50 = 0.33 nM ); monkey GnRH ( IC50 = 0.32 nM ) |
| ln Vitro | Relugolix shows a 30000-fold decrease for the rat receptor (IC50=9800 nM) but a strong binding affinity (IC50=0.32 nM) for the monkey receptor, which is comparable to that of the human receptor (IC50=0.33 nM). In the presence of 40% serum, TAK-385's antagonistic in vitro activity against the human receptor (IC90=18 nM) was 95 times greater than that against the monkey receptor (IC90=1700 nM)[1]. |
| ln Vivo |
Relugolix (oral administration; 1-3 mg/kg; single dose for pharmacokinetic study) shows clear suppression of circulating LH levels in monkeys at a dose of 1 mg/kg and a good pharmacokinetic profile. Male cynomolgus monkeys show a pharmacokinetic profile with Cmax, Tmax, and AUCo values of 16.0 ng/mL, 2.7 h, and 90.1 ng, respectively[1]. Relugolix (oral administration; 3, 10, or 30 mg/kg; twice daily; 4 weeks) dramatically lowers the weight of the testicles, lowers the weight of the ventral prostate (3 mg/kg), and lowers the weight of the prostate to castrate levels (10 mg/kg) in male hGNRHR-knock-in mice[2]. Relugolix (oral administration; 30, 100, or 200 mg/kg; twice daily; 4 weeks) causes all mice to enter a constant diestrous phase during the first week at 100 mg/kg, and after 4 weeks in female hGNRHR-knock-in mice, this dose significantly reduces the weights of the uteri and ovaries[2]. |
| Animal Protocol |
Male hGNRHR-knock-in mice 3, 10 or 30 mg/kg Oral administration; 3, 10 or 30 mg/kg; twice daily; 4 weeks |
| ADME/Pharmacokinetics |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion The Cmax and AUC of orally-administered relugolix increase proportionally following single doses - in contrast, with repeat dosing the AUC remains proportional to the dose while the Cmax increases greater than proportionally to the dose. Following the administration of 120mg once daily, the steady-state AUC and Cmax of relugolix were 407 (± 168) ng.hr/mL and 70 (± 65) ng/mL, respectively. The absolute oral bioavailability of relugolix is approximately 12% and the median Tmax following oral administration is 2.25 hours. Approximately 81% of an orally administered dose was recovered in the feces, of which 4.2% was unchanged parent drug, while 4.1% of the dose was recovered in the urine, of which 2.2% remained unchanged. The average renal clearance of relugolix is 8 L/h with a total clearance of 26.4 L/h. Metabolism / Metabolites Relugolix is metabolized mainly by the CYP3A subfamily of P450 enzymes, with a smaller contribution by CYP2C8. Biological Half-Life The average effective half-life of relugolix is 25 hours, while the average terminal elimination half-life is 60.8 hours. |
| Toxicity/Toxicokinetics |
Hepatotoxicity Relugolix therapy has been associated with serum aminotransferase elevations above 3 times the upper limit of normal (ULN) in 1% to 3% of patients and in similar proportions of patients receiving comparator agents such as leuprolide or degarelix. The serum enzyme elevations are generally mild and self-limited, resolving even without dose adjustment. ALT values above 5 times the ULN occur in less than 1% of patients, and episodes of ALT elevations with symptoms or jaundice were not observed in preregistration clinical trials of relugolix alone or in combination with estradiol and norethindrone. Since its approval and more widescale use, there have been no published reports of clinically apparent liver injury attributed to relugolix. Likelihood score: E (unlikely cause of clinically apparent liver injury). Protein Binding Relugolix is 68-71% protein-bound in plasma, primarily to albumin and, to a lesser extent, α1-acid glycoprotein. |
| References |
[1]. Discovery of 1-{4-[1-(2,6-Difluorobenzyl)-5-[(dimethylamino)methyl]-3-(6-methoxypyridazin-3-yl)-2,4-dioxo-1,2,3,4-tetrahydrothieno[2,3-d]pyrimidin-6-yl]phenyl}-3-methoxyurea (TAK-385) as a Potent, Orally Active, Non-Peptide Antagonist of the Human Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone Receptor. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 14, 4998–5012 [2]. Suppression of the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis by TAK-385 (relugolix), a novel, investigational, orally active, small molecule gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) antagonist: studies in human GnRH receptor knock-in mice. Eur J Pharmacol . 2014 Jan 15:723:167-74. |
| Additional Infomation |
Pharmacodynamics Approximately 56% of patients achieved castrate-level testosterone concentrations (<50 ng/dL) by day 4 of therapy and 97% of patients maintain these levels through 48 weeks of therapy. Relugolix requires once-daily oral administration to maintain the desired testosterone concentrations. Androgen deprivation therapies may prolong the QTc interval and should therefore be used with caution in patients having a high baseline risk of QTc prolongation, such as those with electrolyte abnormalities, congestive heart failure, or using other medications known to prolong the QTc interval. Based on its mechanism of action and data from animal studies, relugolix may result in fetal harm if administered to pregnant females - male patients with female partners should be advised to use effective contraception throughout therapy and for 2 weeks following cessation of therapy to prevent inadvertent fetal exposure. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | DMSO: 61~100 mg/mL (97.8~160.4 mM) |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 0.83 mg/mL (1.33 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 8.3 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL of PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL of Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL of normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 0.83 mg/mL (1.33 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 8.3 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 0.83 mg/mL (1.33 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 8.3 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.6035 mL | 8.0176 mL | 16.0351 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3207 mL | 1.6035 mL | 3.2070 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1604 mL | 0.8018 mL | 1.6035 mL |