Terbutaline is a potent and selective β2-adrenergic receptor agonist with IC50 of 53 NM, it has little or no effect on alpha-adrenergic receptors. The medication preferentially affects β2-adrenergic receptors, but it stimulates beta-adrenergic receptors less selectively than beta2-agonists, which are more selectively stimulating. The clinical efficacy of terbutaline in the treatment of allergic asthma is attributed to its inhibition of antigen-induced histamine release from human lung tissue that has been passively sensitized.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C12H19NO3 |
| Molecular Weight | 225.288 |
| Exact Mass | 225.136 |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 63.98; H, 8.50; N, 6.22; O, 21.30 |
| CAS # | 23031-25-6 |
| Related CAS # | Terbutaline sulfate; 23031-32-5; Terbutaline-d9; 1189658-09-0; Terbutaline-d3 |
| PubChem CID | 5403 |
| Appearance | White to off-white crystalline powder |
| Density | 1.171 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 419.2ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 204-208ºC |
| Flash Point | 165.3ºC |
| Vapour Pressure | 3.42E-07mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.4596 (estimate) |
| LogP | 1.91 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 16 |
| Complexity | 205 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
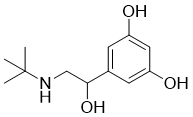
| SMILES | CC(C)(C)NCC(C1=CC(=CC(=C1)O)O)O |
| InChi Key | XWTYSIMOBUGWOL-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C12H19NO3/c1-12(2,3)13-7-11(16)8-4-9(14)6-10(15)5-8/h4-6,11,13-16H,7H2,1-3H3 |
| Chemical Name | 5-[2-(tert-butylamino)-1-hydroxyethyl]benzene-1,3-diol |
| Synonyms | Bricaril; Bricyn; KWD 2019; KWD-2019; KWD2019; Terbutaline |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | Beta-2 adrenergic receptor |
| ln Vitro | Terbutaline (0–10 μM, 1 h) increases the expression of MKP-1 in mouse macrophages that have been activated[3]. |
| ln Vivo | Terbutaline (intraperitoneal injection; 0.5 mg/kg; twice a day; 20 days) treatment can alleviate allodynia in ob/ob mice[4]. |
| Cell Assay |
Cell Line: J774 macrophages Concentration: 0-10 μM Incubation Time: 1 hour Result: Enhanced MKP-1 expression in J774 macrophages in a dose-dependent manner. |
| Animal Protocol |
Adult male ob/ob mice 0.5 mg/kg Intraperitoneal injection; 0.5 mg/kg; twice a day; 20 days |
| ADME/Pharmacokinetics |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion A 0.5 mg subcutaneous dose of terbutaline reaches a mean Cmax of 9.6 ± ng/mL, with a median Tmax of 0.5 hours, and a mean AUC of 29.4 ± 14.2 h\*ng/mL. A 5 mg oral terbutaline tablet reaches a mean Cmax of 8.3 ± 3.9 ng/mL with a median Tmax of 2 hours, and a mean AUC of 54.6 ± 26.8 h\*ng/mL. A 5 mg oral terbutaline solution reaches a mean Cmax of 8.6 ± 3.6 ng/mL, with a median Tmax of 1.5 hours, and a mean AUC of 53.1 ± 23.5 h\*ng/mL. Oral terbutaline has an oral bioavailability of 14-15%. An oral dose of terbutaline is 40% eliminated in the urine after 72 hours. The major metabolite in the urine was the sulphate conjugated form of terbutaline. Parenteral doses of terbutaline are 90% eliminated in the urine, with approximately 2/3 as the unchanged parent drug. Less than 1% of a dose of terbutaline is eliminated in the feces. Terbutaline has a mean volume of distribution of 1.6 L/kg. The average clearance of terbutaline is 3.0 mL/min/kg. Metabolism / Metabolites Terbutaline is sulphated or glucuronidated prior to elimination. Biological Half-Life An oral dose of terbutaline has an elimination half life of 3.4 hours, while a subcutaneous dose has an elimination half life of 2.9 hours. |
| Toxicity/Toxicokinetics |
Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation ◉ Summary of Use during Lactation Maternal use of oral or inhaled terbutaline is unlikely to affect a breastfed infant. The authors of several reviews and expert guidelines agree that use of inhaled bronchodilators is acceptable during breastfeeding because of the low bioavailability and maternal serum levels after use. Terbutaline use as a tocolytic agent might decrease the duration of breastfeeding. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Two papers have reported a total of 4 infants aged 3 to 8 weeks who were breastfed during maternal use of oral terbutaline 2.5 or 5 mg three times daily. None of the infants had any signs of sympathetic stimulation and all were developing normally. These cases were also summarized in a third publication. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk A small retrospective survey from Serbia found that mothers who received a beta agonist pharmacologically similar to terbutaline (fenoterol or hexoprenaline) as a tocolytic breastfed for a shorter period of time than those who received no tocolytic (4.5 vs 9.5 months). It is not known if terbutaline has a similar effect. A study in an Australian hospital compared breastfeeding outcomes in women who received a cesarean section during 2 time periods. During the first time period women did not receive terbutaline before a category one or two cesarean section (n = 423). In the second period, all women receiving a category one or two cesarean section received terbutaline 250 mcg subcutaneously as a tocolytic agent unless there was a contraindication at the time a decision was made to perform a cesarean section (n = 253). The breastfeeding rates at the time of discharge were 95% in the first period and 99% in the second period. The difference was statistically significant. Protein Binding Terbutaline is not highly bound to protein in plasma. |
| References |
[1]. Nifedipine versus terbutaline for tocolysis in external cephalic version. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2008 Sep;102(3):263-6. [2]. The interaction of a β2 adrenoceptor agonist drug with biomimetic cell membrane models: The case of terbutaline sulphate. Life Sci. 2021 Nov 15;285:119992. [3]. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of β2-Receptor Agonists Salbutamol and Terbutaline Are Mediated by MKP-1. PLoS One. 2016 Feb 5;11(2):e0148144. [4]. The antiallodynic action of nortriptyline and terbutaline is mediated by β(2) adrenoceptors and δ opioid receptors in the ob/ob model of diabetic polyneuropathy. Brain Res. 2014 Feb 10;1546:18-26. |
| Additional Infomation |
Terbutaline is a member of the class of phenylethanolamines that is catechol substituted at position 5 by a 2-(tert-butylamino)-1-hydroxyethyl group. It has a role as a beta-adrenergic agonist, an EC 3.1.1.7 (acetylcholinesterase) inhibitor, an anti-asthmatic drug, a bronchodilator agent, a sympathomimetic agent, a tocolytic agent and a hypoglycemic agent. It is a member of phenylethanolamines and a member of resorcinols. Terbutaline was first synthesized in 1966 and described in the literature in the late 1960s and early 1970s. It is a selective beta-2 adrenergic agonist used as a bronchodilator in asthmatic patients. Terbutaline was granted FDA approval on 25 March 1974. Terbutaline is an ethanolamine derivative with bronchodilating and tocolytic activities. Terbutaline selectively binds to and activates beta-2 adrenergic receptors, leading to intracellular adenyl cyclase activation via a trimeric G protein and subsequent increase in cyclic AMP (cAMP) production. Increased cAMP levels result in relaxation of bronchial and vascular smooth muscle mediated through the activation of protein kinase A (PKA), which phosphorylates proteins in control of muscle tone. cAMP also inhibits calcium ion release from intracellular stores, reduces calcium entry into cells and induces the sequestration of intracellular calcium all of which aids in the relaxation of airway muscles. Terbutaline also increases mucociliary clearance and reduces release of inflammatory cell mediators. A selective beta-2 adrenergic agonist used as a bronchodilator and tocolytic. See also: Terbutaline Sulfate (has salt form). Drug Indication Terbutaline is indicated for prevention and reversal of bronchospasm in patients at least 12 years old, with asthma and reversible bronchospasm associated with bronchitis and emphysema. Mechanism of Action Terbutaline is a selective beta-2 adrenergic receptor agonist. Agonism of these receptors in bronchioles activates adenylyl cyclase, increasing intracellular cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP). Increased cAMP decreases intracellular calcium, activating protein kinase A, inactivating myosin light-chain kinase, activating myosin light-chain phosphatase, and finally relaxing smooth muscle in the bronchiole. Pharmacodynamics Terbutaline is a beta-2 adrenergic receptor agonist indicated to treat reversibly bronchospasm in asthmatic patients with bronchitis and emphysema. It has a short duration as the inhaled form is taken up to three times daily, and the therapeutic window is wide. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | DMSO: ~250 mg/mL (~1109.7 mM) |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Note: Listed below are some common formulations that may be used to formulate products with low water solubility (e.g. < 1 mg/mL), you may test these formulations using a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples. Injection Formulations (e.g. IP/IV/IM/SC) Injection Formulation 1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO stock solution → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline) *Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH ₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) Example: Take the Injection Formulation 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) as an example, if 1 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can take 100 μL 25 mg/mL DMSO stock solution and add to 900 μL corn oil, mix well to obtain a clear or suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Injection Formulation 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in saline = 10 : 90 [i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in saline)] *Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 5: 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin : Saline = 50 : 50 (i.e. 500 μL 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin → 500 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 6: DMSO : PEG300 : castor oil : Saline = 5 : 10 : 20 : 65 (i.e. 50 μL DMSO → 100 μLPEG300 → 200 μL castor oil → 650 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 7: Ethanol : Cremophor : Saline = 10: 10 : 80 (i.e. 100 μL Ethanol → 100 μL Cremophor → 800 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 8: Dissolve in Cremophor/Ethanol (50 : 50), then diluted by Saline Injection Formulation 9: EtOH : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 900 μL Corn oil) Injection Formulation 10: EtOH : PEG300:Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Oral Formulations Oral Formulation 1: Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na (carboxymethylcellulose sodium) Oral Formulation 2: Suspend in 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Example: Take the Oral Formulation 1 (Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na) as an example, if 100 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can first prepare 0.5% CMC Na solution by measuring 0.5 g CMC Na and dissolve it in 100 mL ddH2O to obtain a clear solution; then add 250 mg of the product to 100 mL 0.5% CMC Na solution, to make the suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Oral Formulation 3: Dissolved in PEG400 Oral Formulation 4: Suspend in 0.2% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 5: Dissolve in 0.25% Tween 80 and 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 6: Mixing with food powders Note: Please be aware that the above formulations are for reference only. InvivoChem strongly recommends customers to read literature methods/protocols carefully before determining which formulation you should use for in vivo studies, as different compounds have different solubility properties and have to be formulated differently. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.4387 mL | 22.1936 mL | 44.3872 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.8877 mL | 4.4387 mL | 8.8774 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.4439 mL | 2.2194 mL | 4.4387 mL |