Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C15H12O6 |
| Molecular Weight | 288.252 |
| Exact Mass | 288.063 |
| CAS # | 56486-94-3 |
| PubChem CID | 10356745 |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid powder |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 631.1±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Flash Point | 244.2±25.0 °C |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.9 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.725 |
| LogP | 2.47 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 6 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 1 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 21 |
| Complexity | 400 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
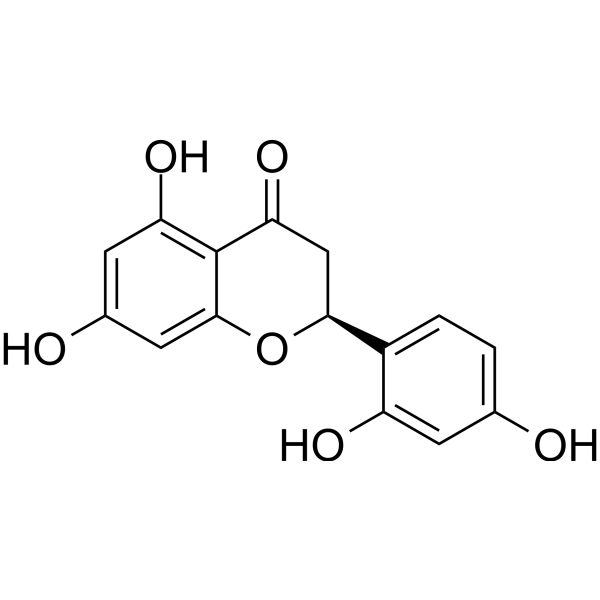
| SMILES | O=C1C[C@@H](C2=CC=C(O)C=C2O)OC3=CC(O)=CC(O)=C13 |
| InChi Key | QBLQLKNOKUHRCH-ZDUSSCGKSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C15H12O6/c16-7-1-2-9(10(18)3-7)13-6-12(20)15-11(19)4-8(17)5-14(15)21-13/h1-5,13,16-19H,6H2/t13-/m0/s1 |
| Chemical Name | (2S)-2-(2,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-5,7-dihydroxy-2,3-dihydrochromen-4-one |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| ln Vitro | Under hypoxic conditions, steppogenin (0-10 μM, 24 h) suppresses in a dose-dependent manner the activity of HIF-1α and VEGF-induced DLL4 expression in vascular endothelium (EC) in HEK293T cells [1]. μM, 6 h) suppresses the hypoxia regulation-induced mRNA expression of HIF-1α target genes (VEGF, GLUT1, CXCR4, and CA9) [1]. Steppogenin (0-3 μM, 24 h) suppresses hypoxia-induced vascular EC proliferation and migration as well as VEGF-induced EC spheroid sprouting [1]. It also inhibits the levels of the proteins VEGF, CXCR4, and CA9. |
| ln Vivo | Steppogenin (2 mg/kg, intraperitoneal injection, once) suppresses tumor development and angiogenesis [1]. Steppogenin (2 mg/kg, intraperitoneal injection, once) has the largest distribution in the liver and liver (25.5-fold and 9.74-fold, respectively) Pharmacokinetic characteristics of Steppogenin in male C57BL/6 J mice AUC), T1/ 2 is significantly greater [1]. Cmax (ng/mL) Tmax (h) T1/2 (h) AUC8h (ng/mL*h) AUC∞ (ng/mL*h) AUC Ratio Plasma 448 ± 113 0.25 0.49 ± 0.14 283 ± 98.9 284 ± 97.8 1 Tumor 635 ± 114 0.3 ± 0.1 1.87 ± 0.87 1078 ± 494 1252 ± 547 4.58 Liver 4319 ± 1063 0.25 1.72 ± 0.26 6733 ± 1300 6967 ± 1200 25.5 Lung 521 ± 181 0.2 5 0.36 ± 0.12 261 ± 96.1 280 ± 106 1.02 Heart 285 ± 15.2 0.25 0.2 107 ± 44.3 176.9 0.65 Kidney 1225 ± 463 0.25 0.33 ± 0.01 628 ± 234 624.7 ± 238 2.35 Spleen 6110 ± 2954 0.25 0.47 ± 0.01 2443 ± 11 55 2663 ± 1289 9.74 Brain 309 ± 95.7 0.25 1.36 ± 0.46 191 ± 67 241 ± 75.4 0.88 |
| Cell Assay |
RT-PCR[1] Cell Types: A549 Cell Tested Concentrations: 0, 0.3, 1, 3 μM Incubation Duration: 6 h Experimental Results: The mRNA expression of HIF-1α target genes (VEGF, GLUT1, CXCR4 and CA9) was inhibited under hypoxic conditions. Western Blot Analysis[1] Cell Types: HEK293T, A549, ARPE19 Cell Tested Concentrations: 0, 0.3, 1, 3 μM Incubation Duration: 16 hrs (hours) Experimental Results: Dramatically inhibited HIF-1α protein levels in a dose-dependent manner. Nuclear expression of HIF-1α is diminished under hypoxic conditions. The protein levels of VEGF, CXCR4, and CA9 were suppressed compared with the levels detected in the vehicle control group. Inhibits VEGF-induced DLL4 protein expression. |
| Animal Protocol |
Animal/Disease Models: C57BL/6 J mouse (6 weeks old, male, Lewis lung cancer (LLC) allograft tumor model) [1] Doses: 2 mg/kg Route of Administration: IP, primary Experimental Results: significant Inhibit tumor growth. Animal/Disease Models: C57BL/6 J mouse (6 weeks old, male, Lewis lung cancer (LLC) allograft tumor model) [1] Doses: 2 mg/kg Route of Administration: IP, once (pharmacokinetic/PK/PK analysis ) Experimental Results: demonstrated the highest distribution to the liver and spleen (AUC ratios of 25.5x and 9.74x, respectively), with Dramatically higher T1/2. Steppogenin may not accumulate after repeated administration even in highly distributed tissues. |
| References |
[1]. Steppogenin suppresses tumor growth and sprouting angiogenesis through inhibition of HIF-1α in tumors and DLL4 activity in the endothelium. Phytomedicine. 2023 Jan;108:154513. |
| Additional Infomation |
(2S)-5,7,2',4'-tetrahydroxyflavanone has been reported in Morus lhou, Maclura pomifera, and other organisms with data available. See also: Steppogenin (annotation moved to). |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Note: Listed below are some common formulations that may be used to formulate products with low water solubility (e.g. < 1 mg/mL), you may test these formulations using a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples. Injection Formulations (e.g. IP/IV/IM/SC) Injection Formulation 1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO stock solution → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline) *Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH ₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) Example: Take the Injection Formulation 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) as an example, if 1 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can take 100 μL 25 mg/mL DMSO stock solution and add to 900 μL corn oil, mix well to obtain a clear or suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Injection Formulation 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in saline = 10 : 90 [i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in saline)] *Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 5: 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin : Saline = 50 : 50 (i.e. 500 μL 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin → 500 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 6: DMSO : PEG300 : castor oil : Saline = 5 : 10 : 20 : 65 (i.e. 50 μL DMSO → 100 μLPEG300 → 200 μL castor oil → 650 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 7: Ethanol : Cremophor : Saline = 10: 10 : 80 (i.e. 100 μL Ethanol → 100 μL Cremophor → 800 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 8: Dissolve in Cremophor/Ethanol (50 : 50), then diluted by Saline Injection Formulation 9: EtOH : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 900 μL Corn oil) Injection Formulation 10: EtOH : PEG300:Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Oral Formulations Oral Formulation 1: Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na (carboxymethylcellulose sodium) Oral Formulation 2: Suspend in 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Example: Take the Oral Formulation 1 (Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na) as an example, if 100 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can first prepare 0.5% CMC Na solution by measuring 0.5 g CMC Na and dissolve it in 100 mL ddH2O to obtain a clear solution; then add 250 mg of the product to 100 mL 0.5% CMC Na solution, to make the suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Oral Formulation 3: Dissolved in PEG400 Oral Formulation 4: Suspend in 0.2% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 5: Dissolve in 0.25% Tween 80 and 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 6: Mixing with food powders Note: Please be aware that the above formulations are for reference only. InvivoChem strongly recommends customers to read literature methods/protocols carefully before determining which formulation you should use for in vivo studies, as different compounds have different solubility properties and have to be formulated differently. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.4692 mL | 17.3461 mL | 34.6921 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.6938 mL | 3.4692 mL | 6.9384 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3469 mL | 1.7346 mL | 3.4692 mL |