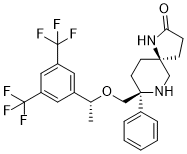
Rolapitant (formerly SCH-619734; SCH619734; trade name: Varubi) is a selective, CNS penetrant and orally bioactive neurokinin (NK1) receptor antagonist (Ki = 0.66 nM) with antiemetic activity. It has been approved in 2015 for use along with other medications (eg, dexamethasone) to prevent delayed nausea and vomiting associated with cancer chemotherapy. It functions by obstructing the brain's signals that trigger nausea and vomiting.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C25H26F6N2O2 | |
| Molecular Weight | 500.49 | |
| Exact Mass | 500.189 | |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 60.00; H, 5.24; F, 22.78; N, 5.60; O, 6.39 | |
| CAS # | 552292-08-7 | |
| Related CAS # | Rolapitant hydrochloride; 858102-79-1; Rolapitant hydrochloride hydrate; 914462-92-3 | |
| PubChem CID | 10311306 | |
| Appearance | Solid powder | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | |
| Boiling Point | 523.5±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Flash Point | 270.4±30.1 °C | |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.4 mmHg at 25°C | |
| Index of Refraction | 1.542 | |
| LogP | 4.01 | |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 | |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 9 | |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 5 | |
| Heavy Atom Count | 35 | |
| Complexity | 731 | |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 3 | |
| SMILES | C[C@@](C1=CC(C(F)(F)F)=CC(C(F)(F)F)=C1)([H])OC[C@@]2(C3=CC=CC=C3)CC[C@@](CCC4=O)(N4)CN2 |
|
| InChi Key | FIVSJYGQAIEMOC-ZGNKEGEESA-N | |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C25H26F6N2O2/c1-16(17-11-19(24(26,27)28)13-20(12-17)25(29,30)31)35-15-23(18-5-3-2-4-6-18)10-9-22(14-32-23)8-7-21(34)33-22/h2-6,11-13,16,32H,7-10,14-15H2,1H3,(H,33,34)/t16-,22-,23-/m1/s1 | |
| Chemical Name | (5S,8S)-8-[[(1R)-1-[3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]ethoxy]methyl]-8-phenyl-1,9-diazaspiro[4.5]decan-2-one | |
| Synonyms |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 | |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | human NK1 ( Ki = 0.66 ); gerbil NK1 ( Ki = 0.13 ); guinea pig NK1 ( Ki = 0.72 ); monkey NK1 ( Ki = 2.5 ); rabbit NK1 ( Ki = 31.7 ); rat NK1 ( Ki = 78.6 ); mouse NK1 ( Ki = 60.4 ) |
| ln Vitro |
Rolapitant has high selectivity over the human NK2 and NK3 subtypes of more than 1000-fold, as well as preferential affinity for human, guinea pig, gerbil and monkey NK1 receptors over rat, mouse and rabbit[1]. 1–1000 nM) inhibits the GR-73632 (an NK1 receptor agonist)–induced calcium efflux in a concentration-dependent and competitive manner in CHO cells expressing the human NK1 receptor[1]. |
| ln Vivo |
Rolapitant (0.03-1 mg/kg for PO, 0.3-1 mg/kg for IV; single dosage) areduces the foot-tapping response induced by GR-73632 in Mongolian Gerbils[1]. Rolapitant (0.03–1 mg/kg; PO; single dosage; monitored for 72 hours) prevents acute emesis brought on by cisplatin and apomorphine in ferrets[1]. |
| Animal Protocol |
Female Mongolian Gerbils (30-60 g; anesthetized by inhalation of an oxygen:isofluorane mixture after 4 h PO or immediately after IV, then injected with 5 μl of 3 pmol solution of GR-73632 via ICV) 0.03, 0.1, 0.3 and 1 mg/kg for PO, 0.3 and 1 mg/kg for IV PO or IV, single dosage |
| ADME/Pharmacokinetics |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion Following administration of rolapitant, plasma concentrations reached peak levels in about 4 hours. Rolapitant was found to be 14.2% renally excreted and 73% fecally excreted. Of the fecally excreted compounds 460 L 0.96 L/hour Metabolism / Metabolites Rolapitant is metabolized primarily by Cytochrome P450 enzyme 3A4 (CYP3A4) to its major active and circulating metabolite M19 (C4-pyrrolidine-hydroxylated rolapitant). Biological Half-Life Mean terminal half life ranged from 169 to 183 hours (~7 days). |
| Toxicity/Toxicokinetics |
Hepatotoxicity Serum aminotransferase elevations following initial cycles of chemotherapy occurred in less than 2% of rolapitant treated patients and a similar proportion of controls (1.3% vs 1.4% for AST). The aminotransferase elevations were transient, mild-to-moderate in severity, and not associated with symptoms or jaundice. There was no increase in frequency of serum enzyme elevations with subsequent chemotherapy cycles. No cases of clinically apparent liver injury attributable to rolapitant were described in the preregistration clinical trials of this agent, and there have been no cases published in the literature since its approval and more widescale use. Thus, significant liver injury from rolapitant must be rare if it occurs at all. Likelihood score: E (unlikely cause of clinically apparent liver injury). Protein Binding Rolapitant is 99.8% bound to human plasma protein. |
| References |
[1]. Rolapitant (SCH 619734): a potent, selective and orally active neurokininNK1 receptor antagonist with centrally-mediated antiemetic effects inferrets. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2012 Jul;102(1):95-100. [2]. Study of rolapitant, a novel, long-acting, NK-1 receptor antagonist, for the prevention of chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting (CINV) due to highly emetogenic chemotherapy (HEC). Support Care Cancer. 2015 Nov;23(11):3281-8. |
| Additional Infomation |
Rolapitant is an azaspiro compound that is 1,7-diazaspiro[4.5]decan-2-one carrying additional phenyl and 1-{[3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]ethoxy}methyl substituents at position 8. Used (in the form of the hydrochloride hydrate) for the prevention of delayed nausea and vomiting associated with initial and repeat courses of emetogenic cancer chemotherapy. It has a role as an antiemetic and a neurokinin-1 receptor antagonist. It is an ether, an azaspiro compound, a member of pyrrolidin-2-ones, a member of piperidines and an organofluorine compound. It is a conjugate base of a rolapitant(1+). Rolapitant is a potent, highly selective, long-acting Neurokinin-1 (NK-1) receptor antagonist approved for the prevention of delayed chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting (CINV) in adults. Delayed-phase CINV typically occurs >24 hours after chemotherapy treatment and is principally mediated by Neurokinin-1 and its ligand Substance P, which is released in the gut following chemotherapy administration. Neurokinin-1 is also known as Tachykinin Receptor 1 (TACR1), Neurokinin 1 Receptor (NK1R), and Substance P Receptor (SPR). By blocking Substance P from interacting with NK-1 receptors in the gut and the central nervous system, rolapitant prevents late-phase CINV. Unlike other available NK-1 receptor antagonists, rolapitant is not an inhibitor of Cytochrome P450 enzyme CYP3A4 and has a long elimination half-life, allowing a single dose to prevent both acute and late-phase CINV during the first 120 hours post-chemotherapy. Rolapitant is a Substance P/Neurokinin-1 Receptor Antagonist. The mechanism of action of rolapitant is as a Neurokinin 1 Antagonist, and Cytochrome P450 2D6 Inhibitor, and Breast Cancer Resistance Protein Inhibitor, and P-Glycoprotein Inhibitor. Rolapitant is an orally available antiemetic agent that is used to prevent cancer chemotherapy related nausea and vomiting. Rolapitant therapy has not been associated with serum enzyme elevations or with instances of clinically apparent liver injury with jaundice. Rolapitant is an orally bioavailable, centrally-acting, selective, neurokinin 1 receptor (NK1-receptor) antagonist, with potential antiemetic activity. Upon oral administration, rolapitant competitively binds to and blocks the activity of the NK1-receptor in the central nervous system, thereby inhibiting the binding of the endogenous ligand, substance P (SP). This may prevent both SP-induced emesis and chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting (CINV). The interaction of SP with the NK1-receptor plays a key role in the induction of nausea and vomiting caused by emetogenic cancer chemotherapy. Compared to other NK1-receptor antagonists, rolapitant has both a more rapid onset of action and a much longer half-life. See also: Rolapitant Hydrochloride (has salt form). Drug Indication This drug is indicated in adults in combination with other antiemetics for the prevention of delayed nausea and vomiting associated with emetogenic chemotherapy. FDA Label Prevention of delayed nausea and vomiting associated with highly and moderately emetogenic cancer chemotherapy in adults. Varuby is given as part of combination therapy. Prevention of nausea and vomiting Mechanism of Action Rolapitant is an orally active, highly selective Neurokinin-1 Receptor (NK1R) antagonist. NK1 receptors are located primarily in the gut and central nervous system and are activated by Substance P following chemotherapy administration. By binding to the NK1 receptor, rolapitant prevents binding of its ligand Substance P, which is released in the gut following chemotherapy administration. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
|
|||
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.00 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.00 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.9980 mL | 9.9902 mL | 19.9804 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3996 mL | 1.9980 mL | 3.9961 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1998 mL | 0.9990 mL | 1.9980 mL |