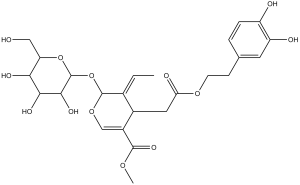
Oleuropein is a naturally occuring antioxidant polyphenol isolated from olive leaf. In both J774A.1 cells and primary mouse macrophages, Oleuropein increases LPS-induced NO production. Oleuropein prevents oxidative myocardial injury induced by ischemia and reperfusion. In TF-1a; 786-O, T-47D, RPMI-7951, LoVo, and NL-Fib cells, Oleuropein inhibits cell proliferation and migration. In swiss albino mice that spontaneously develop soft tissue sarcomas, Oleuropein (i.p. or p.o.) completely regresses tumors. In rats, Oleuropein (40 mg/kg, p.o.) protects from cardiac remodeling process after isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarction through inhibiting angiotensin-converting enzyme activity.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C25H32O13 | |
| Molecular Weight | 540.51 | |
| Exact Mass | 540.184 | |
| CAS # | 32619-42-4 | |
| Related CAS # |
|
|
| PubChem CID | 5281544 | |
| Appearance | White to light yellow solid powder | |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 | |
| Boiling Point | 772.9±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Melting Point | 89-90ºC | |
| Flash Point | 257.0±26.4 °C | |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.8 mmHg at 25°C | |
| Index of Refraction | 1.630 | |
| LogP | -0.91 | |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 6 | |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 13 | |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 11 | |
| Heavy Atom Count | 38 | |
| Complexity | 873 | |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 7 | |
| SMILES | C/C=C/1\[C@@H](C(=CO[C@H]1O[C@H]2[C@@H]([C@H]([C@@H]([C@H](O2)CO)O)O)O)C(=O)OC)CC(=O)OCCC3=CC(=C(C=C3)O)O |
|
| InChi Key | RFWGABANNQMHMZ-ZCHJGGQASA-N | |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C25H32O13/c1-3-13-14(9-19(29)35-7-6-12-4-5-16(27)17(28)8-12)15(23(33)34-2)11-36-24(13)38-25-22(32)21(31)20(30)18(10-26)37-25/h3-5,8,11,14,18,20-22,24-28,30-32H,6-7,9-10H2,1-2H3/b13-3+/t14-,18+,20+,21-,22+,24-,25-/m0/s1 | |
| Chemical Name | methyl (4S,5E,6S)-4-[2-[2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)ethoxy]-2-oxoethyl]-5-ethylidene-6-[(2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxy-4H-pyran-3-carboxylate | |
| Synonyms |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 | |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| ln Vitro | In the context of treating breast cancer, the cytochrome P450 enzyme aromatase represents a significant pharmacological target[2]. | ||
| ln Vivo |
|
||
| Animal Protocol |
|
||
| References |
[1]. Oleuropein as an inhibitor of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma. Genes Nutr. 2014 Jan;9(1):376. [2]. Potential Health Benefits of Olive Oil and Plant Polyphenols. Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Feb 28;19(3). pii: E686. |
||
| Additional Infomation |
Oleuropein is a secoiridoid glycoside that is the methyl ester of 3,4-dihydro-2H-pyran-5-carboxylic acid which is substituted at positions 2, 3, and 4 by hydroxy, ethylidene, and carboxymethyl groups, respectively and in which the anomeric hydroxy group at position 2 has been converted into its beta-D-glucoside and the carboxylic acid moiety of the carboxymethyl substituent has been converted to the corresponding 3,4-dihydroxyphenethyl ester (the 2S,3E,4S stereoisomer). The most important phenolic compound present in olive cultivars. It has a role as a plant metabolite, a radical scavenger, an anti-inflammatory agent, an antineoplastic agent, an antihypertensive agent, a NF-kappaB inhibitor, an apoptosis inducer, an antioxidant and a nutraceutical. It is a secoiridoid glycoside, a beta-D-glucoside, a methyl ester, a member of catechols, a diester and a member of pyrans. Oleuropein has been reported in Ligustrum obtusifolium, Fraxinus insularis, and other organisms with data available. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
|
|||
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (3.85 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 20.8 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (3.85 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 20.8 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (3.85 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 20.8 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. Solubility in Formulation 4: PBS: 30mg/mL (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.8501 mL | 9.2505 mL | 18.5010 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3700 mL | 1.8501 mL | 3.7002 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1850 mL | 0.9251 mL | 1.8501 mL |