Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C18H19NO2 |
| Molecular Weight | 281.3490 |
| Exact Mass | 281.141 |
| CAS # | 4846-19-9 |
| PubChem CID | 12313579 |
| Appearance | Off-white to light yellow solid powder |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 446.4±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 128-129 ºC |
| Flash Point | 182.8±18.2 °C |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.1 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.598 |
| LogP | 3.23 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 3 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 2 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 21 |
| Complexity | 374 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
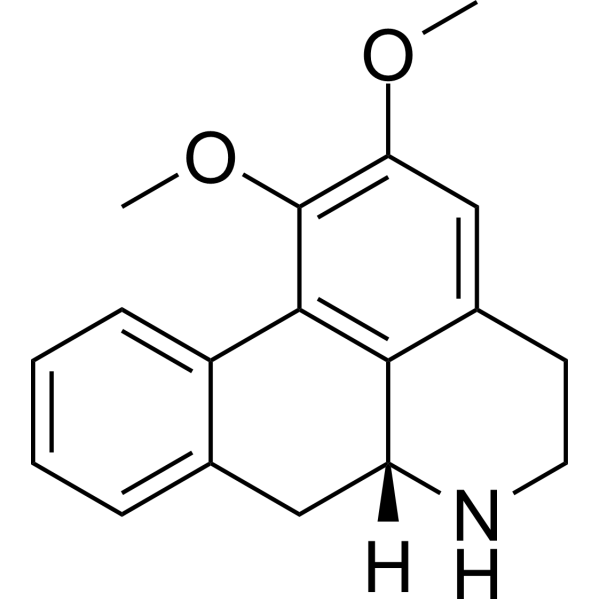
| SMILES | COC1=C(C2=C3[C@@H](CC4=CC=CC=C42)NCCC3=C1)OC |
| InChi Key | QQKAHDMMPBQDAC-CQSZACIVSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C18H19NO2/c1-20-15-10-12-7-8-19-14-9-11-5-3-4-6-13(11)17(16(12)14)18(15)21-2/h3-6,10,14,19H,7-9H2,1-2H3/t14-/m1/s1 |
| Chemical Name | (6aR)-1,2-dimethoxy-5,6,6a,7-tetrahydro-4H-dibenzo[de,g]quinoline |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| ln Vitro | Lotus leaf is a widely used traditional Chinese medicine that has a variety of physiological and pharmacological effects, particularly lowering cholesterol and blood triglyceride levels. The four P450 isoenzymes (CYP2C19, CYP3A4, CYP2E1, and CYP2C9) are all weakly or not inhibited by N-nornuciferine, whereas CYP2D6 activity is severely inhibited. With an apparent Ki value of 2.34 μM, n-nitroferine competitively inhibits the ortho-position demethylation of dextromethorphan catalyzed by CYP2D6[1]. |
| References |
[1]. Identification and characterization of potent CYP2D6 inhibitors in lotus leaves. J Ethnopharmacol. 2014 Apr 11;153(1):190-6. |
| Additional Infomation | N-Nornuciferine has been reported in Magnolia officinalis, Neolitsea konishii, and other organisms with data available. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | DMSO : ~100 mg/mL (~355.43 mM) |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (8.89 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (8.89 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (8.89 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.5543 mL | 17.7715 mL | 35.5429 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.7109 mL | 3.5543 mL | 7.1086 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3554 mL | 1.7771 mL | 3.5543 mL |