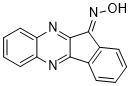
IQ-1S is a potent and selective c-Jun N-Terminal Kinase Inhibitor. IQ-1S inhibits delayed-type hypersensitivity in mice. The most prevalent species at physiologic pH is IQ-1S, which has a high level of specificity for JNK. With regard to rheumatoid arthritis, IQ-1S can be used as a small-molecule modulator for mechanistic studies of JNK function by reducing the inflammation and cartilage loss that are caused by CIA.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C15H9N3O |
| Molecular Weight | 247.2515 |
| Exact Mass | 247.074 |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 72.87; H, 3.67; N, 16.99; O, 6.47 |
| CAS # | 23146-22-7 |
| Related CAS # | 23146-22-7 |
| PubChem CID | 619002 |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid powder |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 511.8±43.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Flash Point | 263.3±28.2 °C |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.4 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.774 |
| LogP | 2.47 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 3 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 0 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 19 |
| Complexity | 361 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| SMILES | O=NC1C2=C([H])C([H])=C([H])C([H])=C2C2C=1N([H])C1=C([H])C([H])=C([H])C([H])=C1N=2 |
| InChi Key | YSYIWCNPSZNNKW-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C15H9N3O/c19-18-14-10-6-2-1-5-9(10)13-15(14)17-12-8-4-3-7-11(12)16-13/h1-8,17H |
| Chemical Name | 11-nitroso-10H-indeno[1,2-b]quinoxaline |
| Synonyms | IQ-1S |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | JNK3 (IC50 = 87 nM nM); JNK2 (IC50 = 360 nM); JNK1 (IC50 = 390 nM) |
| ln Vitro | Compound IQ-1S is a potent, noncytotoxic inhibitor of pro-inflammatory cytokine [interleukin (IL)-1α, IL-1β, IL-6, IL-10, tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, interferon-γ, and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor] and nitric oxide production by human and murine monocyte/macrophages. Evaluation of IQ-1S' impact on human PBMCs' LPS-induced cytokine production. LPS (200 ng/mL) consistently induces five of the 12 cytokines examined (IL-1α, IL-1β, IL-6, IL-10, and TNF-α) in PBMCs when compared to DMSO-treated control cells. 20 M IQ-1S significantly reduces the production of each of these cytokines. TNF-α production is completely prevented by IQ-1 (>99%), IL-1α, IL-1β, and IL-10 levels are all reduced by 85%, and IL-6 production is reduced by 33%[1]. |
| ln Vivo | The serum exposure of the drug is also good when given to mice via intraperitoneal injection at doses of 12.5 and 30 mg/kg of IQ-1S (the sodium salt of IQ-1S), with AUC0-12h values of 2.9 and 7.4 μM/h, respectively[1]. |
| Cell Assay | Human PBMCs are plated in 96-well plates at a density of 2×105 cells/well in culture medium supplemented with 3% (v/v) endotoxin-free FBS. Pretreatment of PBMCs with 20 μM IQ-1S or DMSO for 30 min is followed by the addition of 200 ng/ml LPS for 24 h. A human cytokine MultiAnalyte ELISArray Kit is used to analyze different cytokines (IL-1α, IL-1β, IL-2, IL-4, IL-6, IL-8, IL-10, IL-12, IL-17A, interferon (IFN)-γ, TNF-α, and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor) in PBMC supernatants[1]. |
| Animal Protocol | Mice: For in vivo analysis, BALB/c mice (15–20 animals per group) are given 12.5 or 30 mg/kg i.p. doses of IQ-1S (the sodium salt of IQ-1), and the mice are sacrificed at different intervals after compound administration. For quantification, mouse serum samples spiked with known concentrations of IQ-1S (0.1–20 μM) are used to create a calibration curve, and a linear dependence of the peak area with IQ-1S concentration is discovered (correlation coefficient r=0.997). The linear trapezoidal method is used to calculate the area under the serum concentration-time curve (AUC0-12h) up to the last concentration that was measured[1]. |
| References |
[1]. Identification and characterization of a novel class of c-Jun N-terminal kinase inhibitors. Mol Pharmacol. 2012 Jun;81(6):832-45. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
DMSO: ~16.7 mg/mL (~67.4 mM) Ethanol: ~1 mg/mL (~4.0 mM) |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 1.67 mg/mL (6.75 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 16.7 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: 1.67 mg/mL (6.75 mM) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), suspension solution; with ultrasonication. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 16.7 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 1.67 mg/mL (6.75 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 16.7 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.0445 mL | 20.2224 mL | 40.4449 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.8089 mL | 4.0445 mL | 8.0890 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.4044 mL | 2.0222 mL | 4.0445 mL |