Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C16H21NO3 |
| Molecular Weight | 275.342844724655 |
| Exact Mass | 275.152 |
| CAS # | 87-00-3 |
| Related CAS # | Homatropine Bromide;51-56-9;Homatropine methylbromide;80-49-9;Homatropine hydrochloride;637-21-8 |
| PubChem CID | 5282593 |
| Appearance | Typically exists as solid at room temperature |
| Density | 1.21 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 403.3ºC |
| Melting Point | 100ºC |
| Flash Point | 197.7ºC |
| LogP | 1.826 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 20 |
| Complexity | 340 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 2 |
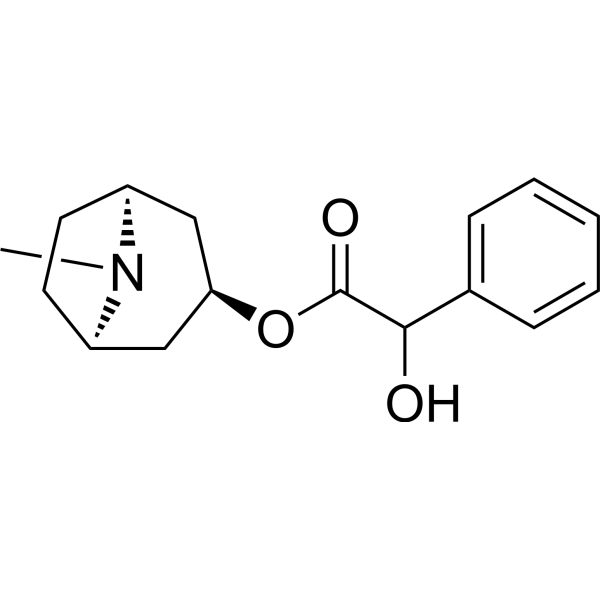
| SMILES | O([C@@H]1C[C@@H]2CC[C@@H](N2C)C1)C(=O)C(C1C=CC=CC=1)O |
| InChi Key | ZTVIKZXZYLEVOL-DGKWVBSXSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C16H21NO3/c1-17-12-7-8-13(17)10-14(9-12)20-16(19)15(18)11-5-3-2-4-6-11/h2-6,12-15,18H,7-10H2,1H3/t12-,13+,14?,15? |
| Chemical Name | [(1S,5R)-8-methyl-8-azabicyclo[3.2.1]octan-3-yl] 2-hydroxy-2-phenylacetate |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| ln Vitro | In the atrium of guinea pigs, homotropine (20 μM) alone results in a dosage ratio of 259, and when paired with hexamethonium bromide, it only yields a dose ratio of 95.0[1]. The muscarinic receptors in the stomach (pA2 = 7.13) and the atria (pA2 = 7.21) that mediate force (pA2 = 7.07) and rate (pA2 = 7.13) are affinities for homotropine[2]. |
| ln Vivo | Rats given a 9 mm x 5 mm conical suppository containing homotropine methylbromide experience rapid blocking of the effects of intravenous acetylcholine on blood pressure and of vagal stimulation on pulse rate[3]. |
| Animal Protocol |
Animal/Disease Models: Male albino rats[3] Doses: 9 mm x 5 mm conical suppository Route of Administration: By suppository Experimental Results: Blocked cardiovascular responses to vagal stimulation and acetylcholine; 10-20 min after insertion of the suppository the effects of vagal stimulation over a range of 2-16 Hz, 5 V, on pulse rate was virtually abolished and remained unchanged at 45-60 min. |
| ADME/Pharmacokinetics |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion No pharmacokinetic data available. No pharmacokinetic data available. No pharmacokinetic data available. No pharmacokinetic data available. Metabolism / Metabolites No pharmacokinetic data available. Biological Half-Life No pharmacokinetic data available. |
| Toxicity/Toxicokinetics |
Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation ◉ Summary of Use during Lactation No information is available on the use of homatropine hydrobromide during breastfeeding. Anticholinergic drugs might interfere with breastfeeding. A single dose of ophthalmic homatropine hydrobromide is not likely to interfere with breastfeeding; however, during long-term use, observe the infant for signs of decreased lactation (e.g., insatiety, poor weight gain). To substantially diminish the amount of drug that reaches the breastmilk after using eye drops, place pressure over the tear duct by the corner of the eye for 1 minute or more, then remove the excess solution with an absorbent tissue. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Anticholinergics can inhibit lactation in animals, apparently by inhibiting growth hormone and oxytocin secretion. Anticholinergic drugs can also reduce serum prolactin in nonnursing women. The prolactin level in a mother with established lactation may not affect her ability to breastfeed. Protein Binding No pharmacokinetic data available. |
| References |
[1]. Leung, E. and F. Mitchelson, Modification by hexamethonium of the muscarinic receptors blocking activity of pancuronium and homatropine in isolated tissues of the guinea-pig. Eur J Pharmacol, 1982. 80(1): p. 11-7. [2]. Gilani, S.A. and L.B. Cobbin, Interaction of himbacine with carbachol at muscarinic receptors of heart and smooth muscle. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther, 1987. 290(1): p. 46-53. [3]. Cramer, M.B., L.A. Cates, and D.E. Clarke, Rectal absorption of homatropine [14C]methylbromide in the rat. J Pharm Pharmacol, 1978. 30(5): p. 284-6. |
| Additional Infomation |
Homatropine is a monocarboxylic acid. Homatropine is an anticholinergic drug that acts as an antagonist at muscarinic acetylcholine receptors. It is present in antitussives, under the trade name Hycodan, in combination with hydrocodone (dihydrocodeinone) bitartrate indicated for the symptomatic relief of cough as oral tablets or solutions. Homatropine is included in subtherapeutic amounts as homatropine methylbromide to discourage deliberate overdosage. Homatropine hydrobromide has been administered as ophthalmic solutions as a cycloplegic to temporarily paralyze accomodation, and to induce mydriasis (the dilation of the pupil); however such therapeutic use has not been approved by the FDA to be safe and effective. Homatropine is a Cholinergic Muscarinic Antagonist. The mechanism of action of homatropine is as a Cholinergic Muscarinic Antagonist. Homatropine is a synthetic tertiary amine alkaloid with antimuscarinic properties. Homatropine, a competitive inhibitor of acetylcholine at the muscarinic receptor, blocks parasympathetic nerve stimulation. See also: Homatropine (annotation moved to). Drug Indication Indicated as an overdose-rescuing agent in combination with hydrocodone antitussive. Indicated for the induction of mydriasis in ophthalmic solutions. FDA Label Mechanism of Action Homatropine is a competitive muscarinic receptor antagonist with a bulky aromatic group in place of the acetyl group of acetylcholine. It is expected to act in similar manner as atropine, producing similar parasympatholytic effects. By blocking muscarinic receptors and cholinergic signalling pathways, homatropine blocks the response of the iris sphincter muscle and cause the pupil to become unresponsive to light upon dilation or mydriasis. It also blocks the accommodative muscle of the ciliary body to cholinergic stimulation. Pharmacodynamics Homatropine is an anticholinergic drug that produces typical anticholinergic effects inducing mydriasis and cycloplegia. Other effects of structurally-related atropine that could also apply to homatropine include inhibition of secretions, tachycardia, relaxation of smooth muscle and central nervous effects including excitation. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Note: Listed below are some common formulations that may be used to formulate products with low water solubility (e.g. < 1 mg/mL), you may test these formulations using a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples. Injection Formulations (e.g. IP/IV/IM/SC) Injection Formulation 1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO stock solution → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline) *Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH ₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) Example: Take the Injection Formulation 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) as an example, if 1 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can take 100 μL 25 mg/mL DMSO stock solution and add to 900 μL corn oil, mix well to obtain a clear or suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Injection Formulation 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in saline = 10 : 90 [i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in saline)] *Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 5: 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin : Saline = 50 : 50 (i.e. 500 μL 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin → 500 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 6: DMSO : PEG300 : castor oil : Saline = 5 : 10 : 20 : 65 (i.e. 50 μL DMSO → 100 μLPEG300 → 200 μL castor oil → 650 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 7: Ethanol : Cremophor : Saline = 10: 10 : 80 (i.e. 100 μL Ethanol → 100 μL Cremophor → 800 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 8: Dissolve in Cremophor/Ethanol (50 : 50), then diluted by Saline Injection Formulation 9: EtOH : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 900 μL Corn oil) Injection Formulation 10: EtOH : PEG300:Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Oral Formulations Oral Formulation 1: Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na (carboxymethylcellulose sodium) Oral Formulation 2: Suspend in 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Example: Take the Oral Formulation 1 (Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na) as an example, if 100 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can first prepare 0.5% CMC Na solution by measuring 0.5 g CMC Na and dissolve it in 100 mL ddH2O to obtain a clear solution; then add 250 mg of the product to 100 mL 0.5% CMC Na solution, to make the suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Oral Formulation 3: Dissolved in PEG400 Oral Formulation 4: Suspend in 0.2% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 5: Dissolve in 0.25% Tween 80 and 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 6: Mixing with food powders Note: Please be aware that the above formulations are for reference only. InvivoChem strongly recommends customers to read literature methods/protocols carefully before determining which formulation you should use for in vivo studies, as different compounds have different solubility properties and have to be formulated differently. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.6319 mL | 18.1594 mL | 36.3187 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.7264 mL | 3.6319 mL | 7.2637 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3632 mL | 1.8159 mL | 3.6319 mL |