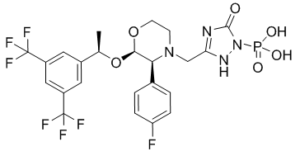
Fosaprepitant (also known as L-758298; MK0517) is a neurokinin-1 receptor antagonist for the prevention of chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting. Fosaprepitant is injected intravenously and used as an antiemetic medication. Merck & Co. developed fosaprepitant, which was authorized as an Aprepitant prodrug. It helps to avoid both acute and delayed nausea and vomiting brought on by chemotherapy. Prepitant, the active moiety, is a substrate, inducer, and inhibitor of CYP3A4, while fosaprepitant is a weak inhibitor of CYP3A4.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C23H22F7N4O6P |
| Molecular Weight | 614.41 |
| Exact Mass | 614.116 |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 44.96; H, 3.61; F, 21.64; N, 9.12; O, 15.62; P, 5.04 |
| CAS # | 172673-20-0 |
| Related CAS # | Fosaprepitant dimeglumine; 265121-04-8 |
| PubChem CID | 135413538 |
| Appearance | Solid powder |
| Density | 1.7±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 588.9ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Flash Point | 310ºC |
| Vapour Pressure | 1.03E-14mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.590 |
| LogP | 2.14 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 15 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 7 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 41 |
| Complexity | 997 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 3 |
| SMILES | O=C1N=C(CN2[C@@H](C3=CC=C(F)C=C3)[C@@H](O[C@H](C)C4=CC(C(F)(F)F)=CC(C(F)(F)F)=C4)OCC2)NN1P(O)(O)=O |
| InChi Key | BARDROPHSZEBKC-OITMNORJSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C23H22F7N4O6P/c1-12(14-8-15(22(25,26)27)10-16(9-14)23(28,29)30)40-20-19(13-2-4-17(24)5-3-13)33(6-7-39-20)11-18-31-21(35)34(32-18)41(36,37)38/h2-5,8-10,12,19-20H,6-7,11H2,1H3,(H,31,32,35)(H2,36,37,38)/t12-,19+,20-/m1/s1 |
| Chemical Name | [3-[[(2R,3S)-2-[(1R)-1-[3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]ethoxy]-3-(4-fluorophenyl)morpholin-4-yl]methyl]-5-oxo-4H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl]phosphonic acid |
| Synonyms | L-758298; L 758298; L758298; MK0517; MK 0517; Ivemend; fosaprepitantum; UNII-6L8OF9XRDC; 6L8OF9XRDC; L 758298; L-758298; MK-0517 |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | Neurokinin-1 receptor |
| ln Vitro | Fosaprepitant (1 mg/mL in 0.9 % sodium chloride injection solution) was combined in binary or tertiary fashion with therapeutic-dose preparations of a 5-HT3 antagonist (ondansetron, granisetron, palonosetron, or tropisetron) and/or a corticosteroid (dexamethasone sodium phosphate or methylprednisolone sodium succinate). For diluent compatibility assessment, fosaprepitant was also prepared 1 mg/mL in 0.9 % sodium chloride injection solution, water for injection, or 5 % dextrose injection solution. After 24-h storage under ambient conditions, samples were assayed for degradation[3]. |
| ln Vivo | Fosaprepitant (30 mg/kg; i.p.; daily; for 7 days) reduces morphine tolerance and heightens the antinociceptive impact in rats[1]. |
| Animal Protocol |
Sprague-Dawley rats 30 mg/kg Intraperitoneal injection, daily, for 7 days Sprague-Dawley rats were injected with morphine (10 mg/kg twice daily) and/or fosaprepitant (30 mg/kg once daily) for 7 days. Pain threshold was assessed by the hot plate test. Expression of SP and calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) in the spinal cords of these rats was evaluated by immunohistochemistry.[2] Fosaprepitant (also known as MK-0517 and L-758,298) is a water-soluble phosphoryl prodrug for aprepitant, which, when administered intravenously, is converted to aprepitant within 30 min of intravenous administration via the action of ubiquitous phosphatases. Owing to the rapid conversion of fosaprepitant to the active form (aprepitant), fosaprepitant 115 mg provided the same aprepitant exposure in terms of AUC as aprepitant 12 mg orally, and fosaprepitant is expected to provide a correspondingly similar antiemetic effect as aprepitant. Clinical studies have suggested that fosaprepitant could be appropriate as an intravenous alternative to the aprepitant oral capsule. In a study in healthy subjects, fosaprepitant 115 mg was generally well tolerated at a final drug concentration of 1 mg/ml, and fosaprepitant 115 mg was AUC bioequivalent to aprepitant 125 mg. Fosaprepitant in the dose of 115 mg has been approved by the US FDA, the EU and the Australian authorities on day 1 of a 3-day oral aprepitant regimen, with oral aprepitant administered on days 2 and 3. Fosaprepitant may be a useful parenteral alternative to oral aprepitant. Further study is needed to clarify the utility of fosaprepitant in the prevention of CINV and to clarify optimal dosing regimens that may be appropriate substitutes for oral aprepitant[2]. |
| ADME/Pharmacokinetics |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion Aprepitant is eliminated primarily by metabolism; aprepitant is not renally excreted. Aprepitant is excreted in the milk of rats. It is not known whether this drug is excreted in human milk. Metabolism / Metabolites Aprepitant is metabolized primarily by CYP3A4 with minor metabolism by CYP1A2 and CYP2C19. Seven metabolites of aprepitant, which are only weakly active, have been identified in human plasma. Biological Half-Life 9-13 hours |
| Toxicity/Toxicokinetics |
Protein Binding 95% + |
| References |
[1]. Role of fosaprepitant, a neurokinin Type 1 receptor antagonist, in morphine-induced antinociception in rats. Indian J Pharmacol. 2016 Jul-Aug; 48(4): 394-398. [2]. Fosaprepitant: a neurokinin-1 receptor antagonist for the prevention of chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther . 2008 Nov;8(11):1733-42.[3]. Compatibility of intravenous fosaprepitant with intravenous 5-HT3 antagonists and corticosteroids. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol . 2013 Sep;72(3):509-13. |
| Additional Infomation |
Fosaprepitant is a morpholine derivative that is the (1R)-1-[3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]ethyl ether of (3-{[(2R,3S)-3-(4-fluorophenyl)-2-hydroxymorpholin-4-yl]methyl}-5-oxo-4,5-dihydro-1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)phosphonic acid. It has a role as an antiemetic, a neurokinin-1 receptor antagonist and a prodrug. It is a member of morpholines, a member of triazoles, a cyclic acetal, a phosphoramide and a member of (trifluoromethyl)benzenes. It is a conjugate acid of a fosaprepitant(2-). Fosaprepitant is an intravenously administered antiemetic drug. It is a prodrug of Aprepitant. It aids in the prevention of acute and delayed nausea and vomiting associated with chemotherapy treatment. Fosaprepitant is a Substance P/Neurokinin-1 Receptor Antagonist. The mechanism of action of fosaprepitant is as a Neurokinin 1 Antagonist. Fosaprepitant Dimeglumine is the dimeglumine salt form of fosaprepitant, the water-soluble, N-phosphorylated prodrug of aprepitant, with antiemetic activity. Upon intravenous administration and rapid conversion to aprepitant, this agent binds selectively to the human substance P/neurokinin 1 (NK1) receptors in the central nervous system (CNS). This inhibits receptor binding of the endogenous substance P and prevents substance P-induced emesis. Fosaprepitant is a water-soluble, N-phosphorylated prodrug of the substance P (SP; neurokinin 1 (NK1)) antagonist aprepitant, with antiemetic activity. Upon intravenous administration and rapid conversion to aprepitant, this agent selectively binds to and blocks the human substance P receptors in the central nervous system (CNS). This inhibits receptor binding of the endogenous substance P and prevents substance P-induced emesis. See also: Aprepitant (has active moiety); Fosaprepitant Dimeglumine (is active moiety of). Drug Indication Fosaprepitant is indicated in adult and pediatric patients ≥6 months of age, in combination with other antiemetic agents, for the prevention of acute and delayed nausea and vomiting associated with initial and repeat courses of highly emetogenic cancer chemotherapy, including high-dose [cisplatin]. It is also indicated for the treatment of delayed nausea and vomiting with initial and repeat courses of moderately emetogenic cancer chemotherapy. Prevention of nausea and vomiting associated with highly and moderately emetogenic cancer chemotherapy in adults and paediatric patients aged 6 months and older. Ivemend 150 mg is given as part of a combination therapy. Prevention of nausea and vomiting Mechanism of Action Aprepitant has been shown in animal models to inhibit emesis induced by cytotoxic chemotherapeutic agents, such as cisplatin, via central actions. Animal and human Positron Emission Tomography (PET) studies with Aprepitant have shown that it crosses the blood brain barrier and occupies brain NK1 receptors. Animal and human studies show that Aprepitant augments the antiemetic activity of the 5-HT3-receptor antagonist ondansetron and the corticosteroid ethasone and inhibits both the acute and delayed phases of cisplatin induced emesis. In summary, the active form of fosaprepitant is as an NK1 antagonist which is because it blocks signals given off by NK1 receptors. This therefore decreases the likelihood of vomiting in patients experiencing. Pharmacodynamics Fosaprepitant is a prodrug of Aprepitant. Once biologically activated, the drug acts as a substance P/neurokinin 1 (NK1) receptor antagonist which, in combination with other antiemetic agents, is indicated for the prevention of acute and delayed nausea and vomiting associated with initial and repeat courses of highly emetogenic cancer chemotherapy. Aprepitant is a selective high-affinity antagonist of human substance P/neurokinin 1 (NK1) receptors. Aprepitant has little or no affinity for serotonin (5-HT3), dopamine, and corticosteroid receptors, the targets of existing therapies for chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting (CI NV). |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Note: Listed below are some common formulations that may be used to formulate products with low water solubility (e.g. < 1 mg/mL), you may test these formulations using a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples. Injection Formulations (e.g. IP/IV/IM/SC) Injection Formulation 1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO stock solution → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline) *Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH ₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) Example: Take the Injection Formulation 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) as an example, if 1 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can take 100 μL 25 mg/mL DMSO stock solution and add to 900 μL corn oil, mix well to obtain a clear or suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Injection Formulation 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in saline = 10 : 90 [i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in saline)] *Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 5: 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin : Saline = 50 : 50 (i.e. 500 μL 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin → 500 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 6: DMSO : PEG300 : castor oil : Saline = 5 : 10 : 20 : 65 (i.e. 50 μL DMSO → 100 μLPEG300 → 200 μL castor oil → 650 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 7: Ethanol : Cremophor : Saline = 10: 10 : 80 (i.e. 100 μL Ethanol → 100 μL Cremophor → 800 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 8: Dissolve in Cremophor/Ethanol (50 : 50), then diluted by Saline Injection Formulation 9: EtOH : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 900 μL Corn oil) Injection Formulation 10: EtOH : PEG300:Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Oral Formulations Oral Formulation 1: Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na (carboxymethylcellulose sodium) Oral Formulation 2: Suspend in 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Example: Take the Oral Formulation 1 (Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na) as an example, if 100 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can first prepare 0.5% CMC Na solution by measuring 0.5 g CMC Na and dissolve it in 100 mL ddH2O to obtain a clear solution; then add 250 mg of the product to 100 mL 0.5% CMC Na solution, to make the suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Oral Formulation 3: Dissolved in PEG400 Oral Formulation 4: Suspend in 0.2% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 5: Dissolve in 0.25% Tween 80 and 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 6: Mixing with food powders Note: Please be aware that the above formulations are for reference only. InvivoChem strongly recommends customers to read literature methods/protocols carefully before determining which formulation you should use for in vivo studies, as different compounds have different solubility properties and have to be formulated differently. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.6276 mL | 8.1379 mL | 16.2758 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3255 mL | 1.6276 mL | 3.2552 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1628 mL | 0.8138 mL | 1.6276 mL |