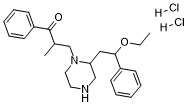
Eprazinone diHCl, the dihydrochloride salt of Eprazinone, is a novel and potent neurokinin 1 receptor (NK1R) ligand with mucolytic, secretolytic, and bronchialantispasmodic activities.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C₂₄H₃₄CL₂N₂O₂ |
| Molecular Weight | 453.44 |
| Exact Mass | 452.199 |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 63.57; H, 7.56; Cl, 15.64; N, 6.18; O, 7.06 |
| CAS # | 10402-53-6 |
| Related CAS # | 10402-53-6 (HCl); 10402-90-1 |
| PubChem CID | 73356 |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid powder |
| Density | 1.064 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 503.9ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Flash Point | 258.5ºC |
| Vapour Pressure | 2.8E-10mmHg at 25°C |
| LogP | 5.38 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 9 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 30 |
| Complexity | 450 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| SMILES | O=C(C1=CC=CC=C1)C(C)CN2CCN(CC(OCC)C3=CC=CC=C3)CC2.[H]Cl.[H]Cl |
| InChi Key | BPMQVOKMMQFZGV-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C24H32N2O2.2ClH/c1-3-28-23(21-10-6-4-7-11-21)19-26-16-14-25(15-17-26)18-20(2)24(27)22-12-8-5-9-13-22;;/h4-13,20,23H,3,14-19H2,1-2H3;2*1H |
| Chemical Name | 3-[4-(2-ethoxy-2-phenylethyl)piperazin-1-yl]-2-methyl-1-phenylpropan-1-one;dihydrochloride |
| Synonyms | Eprazinone diHCl |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month Note: Please store this product in a sealed and protected environment, avoid exposure to moisture. |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | NK1 |
| ln Vitro | Eprazinone binding to the NK1R is specifically displace. Etrimidine's mucolytic activity may be aided by NK1R blockade, despite the fact that it exhibits a relatively weak inhibition of [125I]BH-SP binding to NK1R at a concentration of 25 μM and an antagonistic effect of roughly 30%[2]. |
| ln Vivo | Eprazinone (50-200 mg/kg; oral gavage; daily; for 4 days; adult male rats) at 200 mg/kg, total and individual phospholipid levels (except for phosphatidylinositol) are significantly increased, while total neutral lipid levels are decreased. Eprazinone at lower doses dramatically reduces neutral lipid levels without changing phospholipid levels[1]. The addition of eprazinone to the mucosa in studies on airway epithelial cells results in a dose-dependent, partially reversible reduction in short-circuit current (Isc). When Eprazinone concentrations are higher, both sodium and chloride transport are impacted, but at lower concentrations, the decline in Isc is solely due to a decrease in net chloride secretion[1]. |
| Animal Protocol |
Adult male pathogen free Fischer 344 inbred rats (200-250 g) 50 mg/kg, 100 mg/kg, and 200 mg/kg Oral gavage; daily; for 4 days |
| References |
[1]. Eprazinone Alters Lung Lavage Lipid Levels and Transtracheal Ion Transport. Exp Lung Res. May-Jun 1992;18(3):409-20. [2]. Pharmacophore Modeling, Virtual Screening, and in Vitro Testing Reveal Haloperidol, Eprazinone, and Fenbutrazate as Neurokinin Receptors Ligands. J Chem Inf Model. 2014 Jun 23;54(6):1747-57. |
| Additional Infomation | Eprazinone hydrochloride is a hydrochloride obtained by combining eprazinone with two molar equivalents of hydrochloric acid. It has a role as a mucolytic. It contains an eprazinone(2+). |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
DMSO: 1~6.3 mg/mL (2.2~13.8 mM) Water: 18 mg/mL |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 6.25 mg/mL (13.78 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 62.5 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL corn oil and mix evenly. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 0.62 mg/mL (1.37 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 6.2 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 0.62 mg/mL (1.37 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 6.2 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.2054 mL | 11.0268 mL | 22.0536 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4411 mL | 2.2054 mL | 4.4107 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2205 mL | 1.1027 mL | 2.2054 mL |