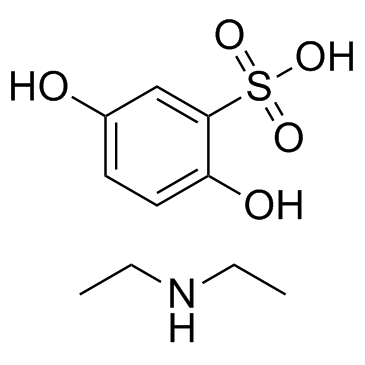
Ethamsylate (E-141; MD-141; Aglumin; Altodor; Eselin), a benzenesulfonate analogue, is an antihemorrhagic drug (haemostatic drug) which works by increasing resistance in the endothelium of capillaries and promoting platelet adhesion. Moreover, it suppresses the production and function of prostaglandins that lead to vasodilation, enhanced capillary permeability, and platelet disaggregation.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C10H17NO5S |
| Molecular Weight | 263.308 |
| Exact Mass | 263.082 |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 45.62; H, 6.51; N, 5.32; O, 30.38; S, 12.18 |
| CAS # | 2624-44-4 |
| PubChem CID | 17506 |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid powder |
| Boiling Point | 496.4ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 127-131ºC |
| Flash Point | 254ºC |
| Vapour Pressure | 1.13E-10mmHg at 25°C |
| LogP | 2.432 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 6 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 3 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 17 |
| Complexity | 252 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| SMILES | S(C1C([H])=C(C([H])=C([H])C=1O[H])O[H])(=O)(=O)O[H].N([H])(C([H])([H])C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])[H] |
| InChi Key | HBGOLJKPSFNJSD-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C6H6O5S.C4H11N/c7-4-1-2-5(8)6(3-4)12(9,10)11;1-3-5-4-2/h1-3,7-8H,(H,9,10,11);5H,3-4H2,1-2H3 |
| Chemical Name | 2,5-dihydroxybenzenesulfonic acid;N-ethylethanamine |
| Synonyms | MD 141; E 141; E141; MD141; Ethamsylate; E 141; MD 141; E-141; MD-141; Aglumin; Altodor; Eselin |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.03.00 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month Note: (1). This product requires protection from light (avoid light exposure) during transportation and storage.(2). Please store this product in a sealed and protected environment (e.g. under nitrogen), avoid exposure to moisture. |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | prostaglandins |
| ln Vitro | Ethamsylate has an IC50 of 0.5 mM and inhibits prostaglandin biosynthesis in microsomes of human pregnant myometrium.[1] Ethamsylate is particularly active against hydroxyl radicals (OH.), which are scavenged at therapeutic Ethamsylate concentrations (0.1–10 μM). To scavenge superoxide radicals, higher concentrations of ethhamsylate are needed. The effects of arachidonic acid, thromboxane A2, collagen, and calcium ionophore A23187 on human platelet aggregation and ATP release are enhanced by ethamsylate.[2] |
| ln Vivo | Ethamsylate lowers the mean bleeding time when given systemically or orally to rabbits. Ethamsylate, when administered intravenously, reduces bleeding time in half at doses greater than 5 mg/kg. The effect begins to take effect five minutes after the injection, peaks between thirty minutes and four hours later, and then fades away six hours later. A comparable maximal effect is seen when taking the medication orally, with a dosage of 10 mg/kg. Ethamsylate's ability to lessen intraventricular hemorrhage is linked to a decrease in the production of prostacyclin and thromboxane A2. Ethamsylate (>25 mg/kg) administered orally also prevents rat paw edema caused by carrageenan. [2] |
| Cell Assay |
Cell Line: HMEC-1 and HUVECs cells Concentration: 0-100 μM Incubation Time: 3-8 h Result: Didn’t affect the migration of HMEC-1 cells. Inhibited the migration of HUVECs cells. Thinned the morphology of the closed network and enlarged the closed cells. |
| Animal Protocol |
C57BL/6J female mice of spinal cord injury 100 mg/kg Oral gavage (p.o.), twice a day, three days |
| References |
[1]. Experientia . 1981 Nov 15;37(11):1182-3. [2]. Am J Ther . 2006 May-Jun;13(3):236-47. |
| Additional Infomation |
Etamsylate is a sulfonic acid derivative and an organosulfur compound. Benzenesulfonate derivative used as a systemic hemostatic. See also: Dobesilic acid (has active moiety). |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
DMSO: 53~120 mg/mL (201.3~455.7 mM) Water: ~53 mg/mL |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 3 mg/mL (11.39 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 30.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 3 mg/mL (11.39 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 30.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 3 mg/mL (11.39 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 30.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. Solubility in Formulation 4: 100 mg/mL (379.78 mM) in PBS (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution; with ultrasonication. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.7978 mL | 18.9890 mL | 37.9780 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.7596 mL | 3.7978 mL | 7.5956 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3798 mL | 1.8989 mL | 3.7978 mL |