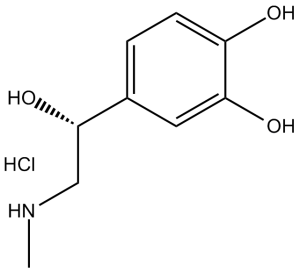
Epinephrine HCl (Adrenaline; Adrenaline; EINECS 200-230-3; l-Adrenaline chloride), the hydrochloride salt of epinephrine, is a hormone and a neurotransmitter that has many biological functions, including regulating heart rate, blood vessel and air passage diameters, and metabolic shifts. Epinephrine release is an essential part of the sympathetic nervous system's fight-or-flight reaction.Chemically speaking, catecholamines are a class of monoamines that includes adrenaline. It is created from the amino acids phenylalanine and tyrosine in certain central nervous system neurons as well as in the chromaffin cells of the adrenal medulla.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C9H13NO3.HCL | |
| Molecular Weight | 219.67 | |
| Exact Mass | 219.066 | |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 49.21; H, 6.42; Cl, 16.14; N, 6.38; O, 21.85 | |
| CAS # | 55-31-2 | |
| Related CAS # |
|
|
| PubChem CID | 441411 | |
| Appearance | Solid powder | |
| Boiling Point | 413.1ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Melting Point | 157°C | |
| Flash Point | 207.9ºC | |
| LogP | 1.543 | |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 5 | |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 | |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 3 | |
| Heavy Atom Count | 14 | |
| Complexity | 154 | |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 | |
| SMILES | CNC[C@@H](C1=CC(=C(C=C1)O)O)O.Cl |
|
| InChi Key | ATADHKWKHYVBTJ-FVGYRXGTSA-N | |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C9H13NO3.ClH/c1-10-5-9(13)6-2-3-7(11)8(12)4-6;/h2-4,9-13H,5H2,1H3;1H/t9-;/m0./s1 | |
| Chemical Name | 4-[(1R)-1-hydroxy-2-(methylamino)ethyl]benzene-1,2-diol;hydrochloride | |
| Synonyms |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 | |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | Adrenergic Receptor | ||
| ln Vitro |
|
||
| ln Vivo |
|
||
| Animal Protocol |
|
||
| Toxicity/Toxicokinetics |
Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation ◉ Summary of Use during Lactation No information is available on the use of epinephrine during breastfeeding. Because of its poor oral bioavailability and short half-life, any epinephrine in milk is unlikely to affect the infant. High intravenous doses of epinephrine might reduce milk production or milk letdown. Low-dose intramuscular (such as Epi-Pen), epidural, topical, inhaled or ophthalmic epinephrine are unlikely to interfere with breastfeeding. To substantially diminish the effect of the drug after using eye drops, place pressure over the tear duct by the corner of the eye for 1 minute or more, then remove the excess solution with an absorbent tissue. Epinephrine is the first line-medication of choice for treatment of anaphylaxis; it should be used in the same manner in breastfeeding and non-breastfeeding patients. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information in nursing mothers was not found as of the revision date. Intravenous epinephrine infusion in nonnursing subjects and in women with hyperprolactinemia decreases serum prolactin concentrations. Animal data indicate that intraarterial epinephrine can decrease serum oxytocin and inhibit milk ejection. However, low-dose infusion of epinephrine as part of epidural analgesia does not impair breastfeeding in nursing mothers. The prolactin level in a mother with established lactation may not affect her ability to breastfeed. An Egyptian study compared lidocaine 2% (n = 75) to lidocaine 2% plus epinephrine 1:200,000 (n = 70) as a wound infiltration following cesarean section. Patients who received epinephrine in combination with lidocaine began breastfeeding at 89 minutes following surgery compared to 132 minutes for those receiving lidocaine alone. The difference was statistically significant. |
||
| References |
[1]. Am J Physiol . 1982 Apr;242(4):H593-601. [2]. Annu Rev Neurosci . 1979:2:113-68. |
||
| Additional Infomation |
Crystals. Used medically as a cardiostimulant. Epinephrine Hydrochloride is the hydrochloride salt of the naturally occurring sympathomimetic amine with vasoconstricting, intraocular pressure-reducing, and bronchodilating activities. By stimulating vascular alpha-adrenergic receptors, epinephrine causes vasoconstriction, thereby increasing vascular resistance and blood pressure. When administered in the conjunctiva, this agent binds to alpha-adrenergic receptors in the iris sphincter muscle, resulting in vasoconstriction, a decrease in the production of aqueous humor, and a lowering of intraocular pressure. Through its beta1 receptor-stimulating actions, epinephrine increases the force and rate of myocardial contraction and relaxes bronchial smooth muscle, resulting in bronchodilation. The active sympathomimetic hormone from the ADRENAL MEDULLA. It stimulates both the alpha- and beta- adrenergic systems, causes systemic VASOCONSTRICTION and gastrointestinal relaxation, stimulates the HEART, and dilates BRONCHI and cerebral vessels. It is used in ASTHMA and CARDIAC FAILURE and to delay absorption of local ANESTHETICS. See also: Epinephrine (has active moiety); Epinephrine hydrochloride; lidocaine (component of); Epinephrine Hydrochloride; Lidocaine Hydrochloride (component of) ... View More ... |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
|
|||
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Note: Listed below are some common formulations that may be used to formulate products with low water solubility (e.g. < 1 mg/mL), you may test these formulations using a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples. Injection Formulations (e.g. IP/IV/IM/SC) Injection Formulation 1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO stock solution → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline) *Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH ₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) Example: Take the Injection Formulation 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) as an example, if 1 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can take 100 μL 25 mg/mL DMSO stock solution and add to 900 μL corn oil, mix well to obtain a clear or suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Injection Formulation 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in saline = 10 : 90 [i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in saline)] *Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 5: 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin : Saline = 50 : 50 (i.e. 500 μL 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin → 500 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 6: DMSO : PEG300 : castor oil : Saline = 5 : 10 : 20 : 65 (i.e. 50 μL DMSO → 100 μLPEG300 → 200 μL castor oil → 650 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 7: Ethanol : Cremophor : Saline = 10: 10 : 80 (i.e. 100 μL Ethanol → 100 μL Cremophor → 800 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 8: Dissolve in Cremophor/Ethanol (50 : 50), then diluted by Saline Injection Formulation 9: EtOH : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 900 μL Corn oil) Injection Formulation 10: EtOH : PEG300:Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Oral Formulations Oral Formulation 1: Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na (carboxymethylcellulose sodium) Oral Formulation 2: Suspend in 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Example: Take the Oral Formulation 1 (Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na) as an example, if 100 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can first prepare 0.5% CMC Na solution by measuring 0.5 g CMC Na and dissolve it in 100 mL ddH2O to obtain a clear solution; then add 250 mg of the product to 100 mL 0.5% CMC Na solution, to make the suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Oral Formulation 3: Dissolved in PEG400 Oral Formulation 4: Suspend in 0.2% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 5: Dissolve in 0.25% Tween 80 and 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 6: Mixing with food powders Note: Please be aware that the above formulations are for reference only. InvivoChem strongly recommends customers to read literature methods/protocols carefully before determining which formulation you should use for in vivo studies, as different compounds have different solubility properties and have to be formulated differently. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.5523 mL | 22.7614 mL | 45.5228 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.9105 mL | 4.5523 mL | 9.1046 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.4552 mL | 2.2761 mL | 4.5523 mL |