Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C₁₆H₁₈FNO₂S |
| Molecular Weight | 307.3834 |
| Exact Mass | 307.104 |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 62.52 H, 5.90 F, 6.18 N, 4.56 O, 10.41 S, 10.43 |
| CAS # | 346692-04-4 |
| PubChem CID | 2843133 |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid powder |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 423.6±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Flash Point | 210.0±31.5 °C |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.0 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.579 |
| LogP | 4.95 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 6 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 21 |
| Complexity | 391 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
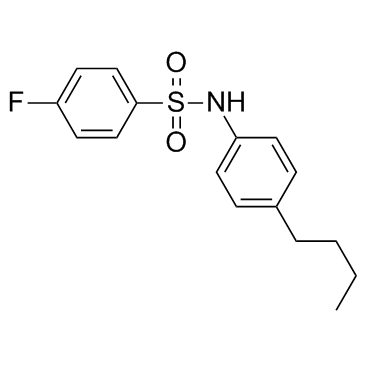
| SMILES | O=S(C1=CC=C(F)C=C1)(NC2=CC=C(CCCC)C=C2)=O |
| InChi Key | CNGHPXKWPGIDSK-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C16H18FNO2S/c1-2-3-4-13-5-9-15(10-6-13)18-21(19,20)16-11-7-14(17)8-12-16/h5-12,18H,2-4H2,1H3 |
| Chemical Name | N-(4-butylphenyl)-4-fluorobenzenesulfonamide |
| Synonyms | DC 260126; DC-260126; DC260126 |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| ln Vitro | DC260126 suppresses palmitic acid potentiated glucose-stimulated insulin secretion, decreases GTP-loading and ERK1/2 phosphorylation stimulated by linoleic acid in GPR40-CHO cells, and negatively regulates GPR40 mRNA expression induced by oleic acid in Min6 cells[1]. |
| Animal Protocol |
Mice: Male C57BL/KsJ-Lepdb (db/db) animals are kept in a 12-hour light-dark cycle at 23°C with free access to water and a regular diet of chow. Nine-week-old male db/db mice are split into four groups (n=6) to examine the dose-dependent effect of DC260126. Using a tail vein injection, mice are given either DC260126 (3, 10, 30 mg/kg) or vehicle (5% DMSO in PBS) once a day for five days. On day five, all mouse groups undergo a 6-hour fast, after which blood samples are taken from the orbital venous plexus and separated by centrifugation to extract serum. Next, an ELISA kit is used to measure the serum insulin concentration. In these long-term studies, eighteen six-week-old male, obese db/db mice are placed into two groups and given either DC260126 (10 mg/kg) or vehicle (5% DMSO in PBS) once a day by tail vein injection for 24 days. Rats: Zucker rats that are obese and female (fa/fa) are kept in a 12:12 light-dark cycle, given free access to water, and fed a high-fat diet consisting of 15% fat, 1% cholesterol, 0.5% sodium cholate, and 15% sucrose, with the exception of times when they are fasted prior to certain experiments. Based on body weight, two groups of six rats each are created at eight weeks of age. During eight weeks, rats receive intraperitoneal injections of DC260126 (6 mg/kg) or vehicle (propylene glycol) once a day. Periodically, food consumption and body weight are assessed. Following a 12-hour fast at the conclusion of the experiment, blood is drawn from the mice. Adipose, renal, and liver tissues are quickly removed and weighed. For western blotting analysis, liver samples are kept at -80°C after being snap frozen in liquid nitrogen. |
| References |
[1]. A novel class of antagonists for the FFAs receptor GPR40. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009;390(3):557-563. [2]. Inhibition of GPR40 protects MIN6 β cells from palmitate-induced ER stress and apoptosis [published correction appears in J Cell Biochem. 2013 May;114(5):1216]. J Cell Biochem. 2012;113(4):1152-1158. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
DMSO: ~61 mg/mL (~198.5 mM) Ethanol: ~61 mg/mL |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (8.13 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (8.13 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (8.13 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.2533 mL | 16.2665 mL | 32.5330 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.6507 mL | 3.2533 mL | 6.5066 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3253 mL | 1.6267 mL | 3.2533 mL |