Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C14H19N4O2CL |
| Molecular Weight | 310.779 |
| Exact Mass | 310.119 |
| CAS # | 913723-61-2 |
| Related CAS # | Cl-amidine hydrochloride;1373232-26-8;D-Cl-amidine hydrochloride;Cl-amidine TFA;1043444-18-3;D-Cl-amidine;1404060-15-6 |
| PubChem CID | 24970878 |
| Appearance | Typically exists as solid at room temperature |
| LogP | 0.518 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 3 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 8 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 21 |
| Complexity | 381 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
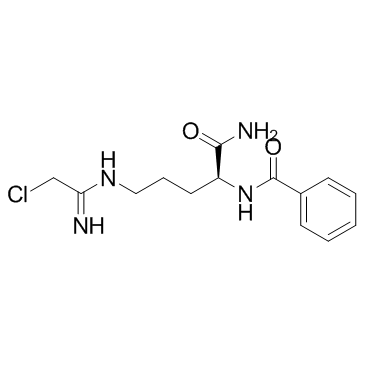
| SMILES | O=C(N[C@H](C(N)=O)CCCNC(CCl)=N)C1=CC=CC=C1 |
| InChi Key | BPWATVWOHQZVRP-NSHDSACASA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C14H19ClN4O2/c15-9-12(16)18-8-4-7-11(13(17)20)19-14(21)10-5-2-1-3-6-10/h1-3,5-6,11H,4,7-9H2,(H2,16,18)(H2,17,20)(H,19,21)/t11-/m0/s1 |
| Chemical Name | N-[(2S)-1-amino-5-[(1-amino-2-chloroethylidene)amino]-1-oxopentan-2-yl]benzamide |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| ln Vitro | Cl-amidine is a bioavailable haloacetamidine-based drug that inhibits all active PAD isozymes with nearly identical efficacy (kinact/KI=13,000 M-1·min-1 for PAD4) [1]. TK6 lymphoblastoid cells and HT29 colon cancer cells underwent dose-dependent apoptosis in response to Cl-amidine (0, 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 50 μg/mL, 24 h). It's interesting to note that Cl-amidine-induced apoptosis does not fully kill the colon cancer cell line HT29 [2]. The enzymatic activity of PADs is dependent on the active site cysteine, which is covalently modified by clonidine, rendering PADs permanently inactive [4]. |
| ln Vivo | Cl-amidine (75 mg/kg, intraperitoneal injection once daily) can prevent and cure colitis in mice produced by DSS [2]. Histological scores can be significantly lowered in a dose-dependent manner with clonidine (5, 25, 75 mg/kg, oral gavage, once daily) [2]. |
| Cell Assay |
Apoptosis analysis[2]. Cell Types: TK6 lymphoblastoid cells and HT29 colon cancer cells. Tested Concentrations: 0, 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 50 μg/mL. Incubation Duration: 24 hrs (hours). Experimental Results: The induction of apoptosis was dose-dependent. |
| Animal Protocol |
Animal/Disease Models: C57BL/6 mice (8-12 weeks old, DSS colitis mouse model) [2]. Doses: 75 mg/kg. Management: IP one time/day. Experimental Results: Inhibition of PAD activity in vivo, protein citrullination, and PAD levels in the colon. Animal/Disease Models: C57BL/6 mice (8-12 weeks old, DSS colitis mouse model) [2]. Doses: 5, 25, 75 mg/kg. Route of Administration: po (oral gavage), one time/day. Experimental Results: Resultant in Dramatically lower histological scores. |
| References |
[1]. Inhibitors and Inactivators of Protein Arginine Deiminase 4: Functional and Structural Characterization. Biochemistry. 2006 Oct 3; 45(39): 11727–11736. [2]. Suppression of colitis in mice by Cl-amidine: a novel peptidylarginine deiminase inhibitor. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2011 Jun;300(6):G929-38. [3]. Molecular targeting of protein arginine deiminases to suppress colitis and prevent colon cancer. Oncotarget. 2015 Nov 3;6(34):36053-62. [4]. Cl-Amidine Prevents Histone 3 Citrullination and Neutrophil Extracellular Trap Formation, and Improves Survival in a Murine Sepsis Model. J Innate Immun. 2017;9(1):22-32. [5]. Substrate Specificity and Kinetic Studies of PADs 1, 3, and 4 Identify Potent and Selective Inhibitors of Protein Arginine Deiminase 3. Biochemistry. 2010 Jun 15;49(23):4852-63. |
| Additional Infomation | Cl-Amidine is a member of benzenes. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Note: Listed below are some common formulations that may be used to formulate products with low water solubility (e.g. < 1 mg/mL), you may test these formulations using a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples. Injection Formulations (e.g. IP/IV/IM/SC) Injection Formulation 1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO stock solution → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline) *Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH ₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) Example: Take the Injection Formulation 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) as an example, if 1 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can take 100 μL 25 mg/mL DMSO stock solution and add to 900 μL corn oil, mix well to obtain a clear or suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Injection Formulation 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in saline = 10 : 90 [i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in saline)] *Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 5: 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin : Saline = 50 : 50 (i.e. 500 μL 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin → 500 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 6: DMSO : PEG300 : castor oil : Saline = 5 : 10 : 20 : 65 (i.e. 50 μL DMSO → 100 μLPEG300 → 200 μL castor oil → 650 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 7: Ethanol : Cremophor : Saline = 10: 10 : 80 (i.e. 100 μL Ethanol → 100 μL Cremophor → 800 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 8: Dissolve in Cremophor/Ethanol (50 : 50), then diluted by Saline Injection Formulation 9: EtOH : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 900 μL Corn oil) Injection Formulation 10: EtOH : PEG300:Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Oral Formulations Oral Formulation 1: Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na (carboxymethylcellulose sodium) Oral Formulation 2: Suspend in 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Example: Take the Oral Formulation 1 (Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na) as an example, if 100 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can first prepare 0.5% CMC Na solution by measuring 0.5 g CMC Na and dissolve it in 100 mL ddH2O to obtain a clear solution; then add 250 mg of the product to 100 mL 0.5% CMC Na solution, to make the suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Oral Formulation 3: Dissolved in PEG400 Oral Formulation 4: Suspend in 0.2% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 5: Dissolve in 0.25% Tween 80 and 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 6: Mixing with food powders Note: Please be aware that the above formulations are for reference only. InvivoChem strongly recommends customers to read literature methods/protocols carefully before determining which formulation you should use for in vivo studies, as different compounds have different solubility properties and have to be formulated differently. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.2177 mL | 16.0886 mL | 32.1771 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.6435 mL | 3.2177 mL | 6.4354 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3218 mL | 1.6089 mL | 3.2177 mL |