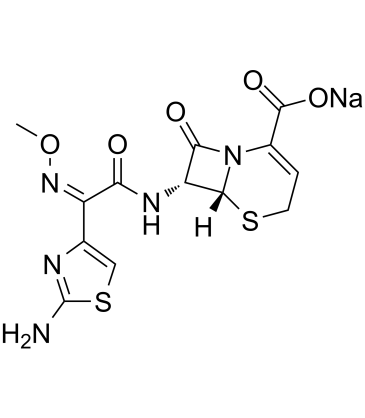
Ceftizoxime is the third generation cephalosporin effective against Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria. And it binds penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs) and inhibits the bacterial cell wall synthesis. Unlike other third-generation cephalosporins, the whole C-3 side chain in ceftizoxime has been removed to prevent deactivation by hydrolytic enzymes. Ceftizoxime rather resembles cefotaxime in its properties, but is not subject to metabolism.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C13H12N5NAO5S2 |
| Molecular Weight | 405.38 |
| Exact Mass | 405.017 |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 38.52; H, 2.98; N, 17.28; Na, 5.67; O, 19.73; S, 15.82 |
| CAS # | 68401-82-1 |
| Related CAS # | Ceftizoxime;68401-81-0 |
| PubChem CID | 23663938 |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid powder |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 10 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 5 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 26 |
| Complexity | 675 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 2 |
| SMILES | O=C(C(N12)=CCS[C@]2([H])[C@H](NC(/C(C3=CSC(N)=N3)=N\OC)=O)C1=O)[O-].[Na+] |
| InChi Key | ADLFUPFRVXCDMO-LIGXYSTNSA-M |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C13H13N5O5S2.Na/c1-23-17-7(5-4-25-13(14)15-5)9(19)16-8-10(20)18-6(12(21)22)2-3-24-11(8)18;/h2,4,8,11H,3H2,1H3,(H2,14,15)(H,16,19)(H,21,22);/q;+1/p-1/b17-7-;/t8-,11-;/m1./s1 |
| Chemical Name | sodium;(6R,7R)-7-[[(2Z)-2-(2-amino-1,3-thiazol-4-yl)-2-methoxyiminoacetyl]amino]-8-oxo-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylate |
| Synonyms | Ceftizoxime Sodium; Ceftizoxim-natrium; Cefizox; Epocelin; Eposerin; Ceftizoxime sodium salt; Monosodium Salt, Ceftizoxime; Salt, Ceftizoxime Monosodium; SK and F 88373 2; SK and F 88373-2; SK and F 883732; SKF 88373; SKF-88373; SKF88373; |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month Note: (1). This product is not stable in solution, please use freshly prepared working solution for optimal results.(2). Please store this product in a sealed and protected environment, avoid exposure to moisture. |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | β-lactam |
| ln Vitro | Ceftizoxime is a parenterally administered third-generation cephalosporin. Ceftizoxime, in contrast to other third-generation cephalosporins, has had its entire C-3 side chain removed to prevent hydrolytic enzyme deactivation. Its characteristics are rather similar to those of cefotaxime, but it is not metabolized. |
| Toxicity/Toxicokinetics |
Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation ◉ Summary of Use during Lactation Limited information indicates that ceftizoxime produces low levels in milk that are not expected to cause adverse effects in breastfed infants. Occasionally disruption of the infant's gastrointestinal flora, resulting in diarrhea or thrush have been reported with cephalosporins, but these effects have not been adequately evaluated. Ceftizoxime is acceptable in nursing mothers. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. |
| References | Türkeş C, Söyüt H, Beydemir Ş. Human serum paraoxonase-1 (hPON1): in vitro inhibition effects of moxifloxacin hydrochloride, levofloxacin hemihidrate, cefepime hydrochloride, cefotaxime sodium and ceftizoxime sodium. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2015;30(4):622-8. doi: 10.3109/14756366.2014.959511. Epub 2014 Dec 18. PubMed PMID: 25519764. |
| Additional Infomation |
Ceftizoxime sodium is the sodium salt of ceftizoxime. It contains a ceftizoxime(1-). Ceftizoxime Sodium is the sodium salt form of ceftizoxime and a semi-synthetic, broad-spectrum, beta-lactamase resistant, third-generation cephalosporin antibiotic with bactericidal activity. Ceftizoxime sodium inhibits bacterial cell wall synthesis by inactivating penicillin binding proteins (PBPs) thereby interfering with the final transpeptidation step required for cross-linking of peptidoglycan units which are a component of the cell wall. Lack of cross-linking results in a reduction of cell wall stability and leads to cell lysis. A semisynthetic cephalosporin antibiotic which can be administered intravenously or by suppository. The drug is highly resistant to a broad spectrum of beta-lactamases and is active against a wide range of both aerobic and anaerobic gram-positive and gram-negative organisms. It has few side effects and is reported to be safe and effective in aged patients and in patients with hematologic disorders. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
H2O : 81~100 mg/mL (199.81~246.68 mM ) DMSO : ~15 mg/mL (~37.00 mM) Water : ~81 mg/mL |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Note: Listed below are some common formulations that may be used to formulate products with low water solubility (e.g. < 1 mg/mL), you may test these formulations using a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples. Injection Formulations (e.g. IP/IV/IM/SC) Injection Formulation 1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO stock solution → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline) *Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH ₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) Example: Take the Injection Formulation 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) as an example, if 1 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can take 100 μL 25 mg/mL DMSO stock solution and add to 900 μL corn oil, mix well to obtain a clear or suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Injection Formulation 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in saline = 10 : 90 [i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in saline)] *Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 5: 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin : Saline = 50 : 50 (i.e. 500 μL 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin → 500 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 6: DMSO : PEG300 : castor oil : Saline = 5 : 10 : 20 : 65 (i.e. 50 μL DMSO → 100 μLPEG300 → 200 μL castor oil → 650 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 7: Ethanol : Cremophor : Saline = 10: 10 : 80 (i.e. 100 μL Ethanol → 100 μL Cremophor → 800 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 8: Dissolve in Cremophor/Ethanol (50 : 50), then diluted by Saline Injection Formulation 9: EtOH : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 900 μL Corn oil) Injection Formulation 10: EtOH : PEG300:Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Oral Formulations Oral Formulation 1: Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na (carboxymethylcellulose sodium) Oral Formulation 2: Suspend in 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Example: Take the Oral Formulation 1 (Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na) as an example, if 100 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can first prepare 0.5% CMC Na solution by measuring 0.5 g CMC Na and dissolve it in 100 mL ddH2O to obtain a clear solution; then add 250 mg of the product to 100 mL 0.5% CMC Na solution, to make the suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Oral Formulation 3: Dissolved in PEG400 Oral Formulation 4: Suspend in 0.2% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 5: Dissolve in 0.25% Tween 80 and 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 6: Mixing with food powders Note: Please be aware that the above formulations are for reference only. InvivoChem strongly recommends customers to read literature methods/protocols carefully before determining which formulation you should use for in vivo studies, as different compounds have different solubility properties and have to be formulated differently. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.4668 mL | 12.3341 mL | 24.6682 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4934 mL | 2.4668 mL | 4.9336 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2467 mL | 1.2334 mL | 2.4668 mL |