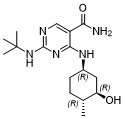
CC-90001 (CC90001; CC 90001) is a novel, potent and selective inhibitor of c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) with potential anti-fibrotic activity. With IC50 values of 11 and 31 nM, it inhibits JNK1/2. CC-90001 has a low nanomolar JNK inhibitory potency, broad kinome selectivity, and the capacity to prevent cellular phosphorylation of the direct JNK substrate c-Jun. Regarding the physicochemical characteristics, CC-90001 also showed excellent systemic exposure after oral dosing, enabling in vivo efficacy studies and the choice of CC-90001 for clinical development. Patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis are currently participating in Phase II clinical trials for CC-90001 (NCT03142191).
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C16H27N5O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 321.41788315773 |
| Exact Mass | 321.22 |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 59.79; H, 8.47; N, 21.79; O, 9.96 |
| CAS # | 1403859-14-2 |
| Related CAS # | 1946833-77-7 (HCl);1403859-14-2;1946833-89-1;1946833-91-5 (mesylate); 1946833-97-1 (tartarte); 1946833-81-3 (lactate); 1946833-85-7 (citrate); 1946833-97-1 (fumarate); |
| PubChem CID | 71237511 |
| Appearance | White to yellow solid powder |
| LogP | 2.3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 6 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 5 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 23 |
| Complexity | 412 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 3 |
| SMILES | C[C@@H]1CC[C@H](C[C@H]1O)NC2=NC(=NC=C2C(=O)N)NC(C)(C)C |
| InChi Key | QBBRJRLJWXRSHQ-CKYFFXLPSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C16H27N5O2/c1-9-5-6-10(7-12(9)22)19-14-11(13(17)23)8-18-15(20-14)21-16(2,3)4/h8-10,12,22H,5-7H2,1-4H3,(H2,17,23)(H2,18,19,20,21)/t9-,10-,12-/m1/s1 |
| Chemical Name | 2-(tert-butylamino)-4-[[(1R,3R,4R)-3-hydroxy-4-methylcyclohexyl]amino]pyrimidine-5-carboxamide |
| Synonyms | CC 90001; CC-90001; CC90001 |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | JNK1; JNK2 |
| ln Vitro | In cell tests, CC-90001 suppresses LPS-induced c-jun phosphorylation with an EC50 of 480 nM [1]. JNK1 is 12.9 times more efficiently inhibited by CC-90001 than JNK2 is by the use of JNK1 and JNK2 knockout fibroblasts [1]. |
| ln Vivo | A 48% reduction in collagen and a 53% reduction in alpha-smooth actin (α-SMA) in an adipose collagen model demonstrate that CC-90001 (3 mg/kg bid) inhibits the development of fibrosis [1]. CC-90001 lowers lung collagen extraction markers and disease-causing elevations in α-SMA to levels close to baseline in a home dust mite pulmonary fibrosis model [1]. |
| References |
[1]. CC-90001, a Second Generation Jun N-Terminal Kinase (JNK) Inhibitor for the Treatment of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 2017; 195:A5409. [2]. Therapeutic targets in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Respir Med. 2017 Oct;131:49-57. |
| Additional Infomation | JNK1 Inhibitor BMS-986360 is an orally bioavailable, second-generation inhibitor of c-Jun N-terminal kinase 1 (JNK-1; JNK1; mitogen-activated protein kinase 8; MAPK8), with potential antineoplastic, anti-inflammatory and anti-fibrotic activities. Upon oral administration, JNK1 inhibitor BMS-986360 selectively targets, binds to and inhibits the activity of JNK1. Inhibition of JNK1-mediated mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK)-signaling pathways induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis, decreases migration and invasion, and inhibits proliferation in JNK1-overexpressing cancer cells. Inhibition of JNK1-mediated pathways may also decrease fibrosis. JNK1, a member of the MAPK family and stress-activated protein, plays a role in the MAPK-mediated signaling pathway. It is often dysregulated in cancer cells and fibrosis. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | DMSO: ~125 mg/mL (~388.9 mM) |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (6.47 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 20.8 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (6.47 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 20.8 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (6.47 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 20.8 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.1112 mL | 15.5560 mL | 31.1119 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.6222 mL | 3.1112 mL | 6.2224 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3111 mL | 1.5556 mL | 3.1112 mL |