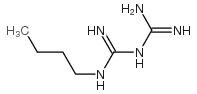
Buformin (NSC-528218; 1-butylbiguanide) is an orally bioavailable AMPK activator approved for use as an antidiabetic drug. It is structurally related to metformin and phenformin and is a member of the biguanide class. Buformin works in vivo by reducing blood glucose synthesis and hepatic gluconeogenesis. Silubin, a brand name for buformin, was sold by the German pharmaceutical company Grünenthal. Buformin increases insulin sensitivity and glucose uptake into cells, delays gastrointestinal absorption of glucose, and prevents the liver from synthesizing glucose. The biguanides, including buformin, are antihyperglycemic rather than hypoglycemic medications. They lessen basal and postprandial hyperglycemia in diabetics rather than causing hypoglycemia. Biguanides may counteract glucagon's effects, lowering fasting glucose levels.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C6H15N5 |
| Molecular Weight | 157.2168 |
| Exact Mass | 157.133 |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 45.84; H, 9.62; N, 44.55 |
| CAS # | 692-13-7 |
| Related CAS # | Buformin hydrochloride;1190-53-0;Buformin-d9 hydrochloride |
| PubChem CID | 2468 |
| Appearance | Solid powder |
| Density | 1.22g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 322.7ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Flash Point | 148.9ºC |
| Index of Refraction | 1.568 |
| LogP | 1.475 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 1 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 11 |
| Complexity | 156 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| SMILES | CCCCNC(=N)NC(=N)N |
| InChi Key | XSEUMFJMFFMCIU-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C6H15N5/c1-2-3-4-10-6(9)11-5(7)8/h2-4H2,1H3,(H6,7,8,9,10,11) |
| Chemical Name | 1-Butylbiguanide |
| Synonyms | Buformin; W-37; W37; W 37; H 224 |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| ln Vitro | Buformin (0–10 mM; 5 days) inhibits the growth of SKBR3 and BT474 cells in a concentration-dependent manner; the IC50 values for erbB-2–overexpressing SKBR3 and BT474 cells are 246.7 M and 98.6 M, respectively[1]. Buformin (0-3 mM; 48 hours) increases the percentage of cells in G0/G1 phase and reduced the percentage of cells in S phase, especially in the SKBR3 cells[1]. Buformin (0–3 mM; 24 hours) inhibits Akt activation/phosphorylation in both SKBR3 and BT474 cells and suppresses RTK activation, including erbB-2 and IGF1R signaling downstream[1]. |
| ln Vivo | Buformin (oral administation; 7.6 mmol/kg of chow; 7 days) has significantly decreased tumor weights and volumes, and MMTV-erbB-2 transgenic mice show decreased mammary morphogenesis and proliferation[1]. |
| References |
[1]. Amanda B Parris, et al. Buformin Inhibits the Stemness of erbB-2-overexpressing Breast Cancer Cells and Premalignant Mammary Tissues of MMTV-erbB-2 Transgenic Mice. J Exp Clin Cancer Res [2]. Buformin Suppresses Proliferation and Invasion via AMPK/S6 Pathway in Cervical Cancer and Synergizes With Paclitaxel. Cancer Biol Ther. 2018 Jun 3;19(6):507-517. |
| Additional Infomation |
Buformin is a member of the class of biguanides that is biguanide substituted by a butyl group at position 1. It is an antidiabetic drug with potential antitumor effect. It has a role as a hypoglycemic agent, a geroprotector, a radiosensitizing agent, an antineoplastic agent and an antiviral agent. It is functionally related to a biguanide. Buformin is an anti-diabetic drug of the biguanide class, chemically related to metformin and phenformin. It was withdrawn from the market in most countries due to a high risk of causing lactic acidosis. Buformin is an agent belonging to the biguanide class of antidiabetics with antihyperglycemic activity. Buformin is not metabolized and is excreted in the urine. This agent has been withdrawn from the market due to its elevated risk of lactic acidosis. An oral hypoglycemic agent that inhibits gluconeogenesis, increases glycolysis, and decreases glucose oxidation. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Note: Listed below are some common formulations that may be used to formulate products with low water solubility (e.g. < 1 mg/mL), you may test these formulations using a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples. Injection Formulations (e.g. IP/IV/IM/SC) Injection Formulation 1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO stock solution → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline) *Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH ₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) Example: Take the Injection Formulation 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) as an example, if 1 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can take 100 μL 25 mg/mL DMSO stock solution and add to 900 μL corn oil, mix well to obtain a clear or suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Injection Formulation 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in saline = 10 : 90 [i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in saline)] *Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 5: 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin : Saline = 50 : 50 (i.e. 500 μL 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin → 500 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 6: DMSO : PEG300 : castor oil : Saline = 5 : 10 : 20 : 65 (i.e. 50 μL DMSO → 100 μLPEG300 → 200 μL castor oil → 650 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 7: Ethanol : Cremophor : Saline = 10: 10 : 80 (i.e. 100 μL Ethanol → 100 μL Cremophor → 800 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 8: Dissolve in Cremophor/Ethanol (50 : 50), then diluted by Saline Injection Formulation 9: EtOH : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 900 μL Corn oil) Injection Formulation 10: EtOH : PEG300:Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Oral Formulations Oral Formulation 1: Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na (carboxymethylcellulose sodium) Oral Formulation 2: Suspend in 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Example: Take the Oral Formulation 1 (Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na) as an example, if 100 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can first prepare 0.5% CMC Na solution by measuring 0.5 g CMC Na and dissolve it in 100 mL ddH2O to obtain a clear solution; then add 250 mg of the product to 100 mL 0.5% CMC Na solution, to make the suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Oral Formulation 3: Dissolved in PEG400 Oral Formulation 4: Suspend in 0.2% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 5: Dissolve in 0.25% Tween 80 and 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 6: Mixing with food powders Note: Please be aware that the above formulations are for reference only. InvivoChem strongly recommends customers to read literature methods/protocols carefully before determining which formulation you should use for in vivo studies, as different compounds have different solubility properties and have to be formulated differently. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 6.3605 mL | 31.8026 mL | 63.6051 mL | |
| 5 mM | 1.2721 mL | 6.3605 mL | 12.7210 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.6361 mL | 3.1803 mL | 6.3605 mL |