Ac-DEVD-CHO is a potent and specific aldehyde inhibitor of Group II caspases with Ki values of 0.2 nM and 0.3 nM for for caspase-3 and caspase-7, respectively. Weak caspase-2 inhibition. This aldehyde only moderately inhibits caspase-2 (Ki = 1.7 μM), which only cleaves the tetrapeptide substrate. Ac-DEVD-CHO has a broad inhibitory effect on group III caspases, with Ki values ranging from 1 to 300 nM. Even when given after the onset of ischemia, Ac-DEVD-CHO'scaspase-3inhibition significantly improves the stunned myocardium's post-ischemic contractile recovery in the isolated working-heart rat model. Ac-DEVD-CHO appears to have protection mechanisms that are separate from apoptosis. Ac-DEVD-CHO did not prevent troponin I cleavage.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C20H30N4O11 | |
| Molecular Weight | 502.47 | |
| Exact Mass | 502.191 | |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 47.81; H, 6.02; N, 11.15; O, 35.02 | |
| CAS # | 169332-60-9 | |
| Related CAS # |
|
|
| PubChem CID | 644345 | |
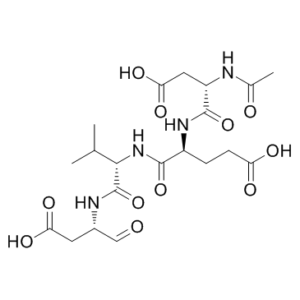
| Sequence | N-Acetyl-Asp-Glu-Val-Asp-al | |
| SequenceShortening | Ac-DEVD-al | |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid powder | |
| Density | 1.374g/cm3 | |
| Boiling Point | 1021.1ºC at 760mmHg | |
| Flash Point | 571.3ºC | |
| Vapour Pressure | 0mmHg at 25°C | |
| Index of Refraction | 1.535 | |
| LogP | -2.6 | |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 7 | |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 11 | |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 16 | |
| Heavy Atom Count | 35 | |
| Complexity | 843 | |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 4 | |
| SMILES | O=C([C@]([H])(C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C(=O)O[H])N([H])C([C@]([H])(C([H])([H])C(=O)O[H])N([H])C(C([H])([H])[H])=O)=O)N([H])[C@]([H])(C(N([H])[C@]([H])(C([H])=O)C([H])([H])C(=O)O[H])=O)C([H])(C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])[H] |
|
| InChi Key | UMBVAPCONCILTL-MRHIQRDNSA-N | |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C20H30N4O11/c1-9(2)17(20(35)22-11(8-25)6-15(29)30)24-18(33)12(4-5-14(27)28)23-19(34)13(7-16(31)32)21-10(3)26/h8-9,11-13,17H,4-7H2,1-3H3,(H,21,26)(H,22,35)(H,23,34)(H,24,33)(H,27,28)(H,29,30)(H,31,32)/t11-,12-,13-,17-/m0/s1 | |
| Chemical Name | (4S)-4-[[(2S)-2-acetamido-3-carboxypropanoyl]amino]-5-[[(2S)-1-[[(2S)-1-carboxy-3-oxopropan-2-yl]amino]-3-methyl-1-oxobutan-2-yl]amino]-5-oxopentanoic acid | |
| Synonyms |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 | |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month Note: Please store this product in a sealed and protected environment (e.g. under nitrogen), avoid exposure to moisture and light. |
|
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | Caspase 3 (Ki = 0.23 nM); Caspase-8 (Ki = 0.92 nM); Caspase-7 (Ki = 1.6 nM); Caspase-10 (Ki = 12 nM); Caspase-1 (Ki = 18 nM); Caspase-6 (Ki = 31 nM); Caspase-9 (Ki = 60 nM); Caspase-4 (Ki = 132 nM); Caspase-5 (Ki = 205 nM); Caspase-2 (Ki = 1710 nM) | ||
| ln Vitro | Ac-DEVD-CHO is a potent inhibitor of caspase-3 (Ki = 230 pM). In contrast, this aldehyde only slightly inhibits caspase-2 (Ki = 1.7 μM) and exhibits poor cleavage of the tetrapeptide substrate. With Ki values ranging from 1 to 300 nM, Ac-DEVD-CHO significantly inhibits Group III caspases[1]. Even when administered after the onset of ischemia, Ac-DEVD-CHO'scaspase-3inhibition significantly improves post-ischemic contractile recovery of stunned myocardium in the isolated working-heart rat model. Ac-DEVD-CHO'sprotectivemechanism(s) seem to operate independently of apoptosis. Ac-DEVD-CHO[2] did not inhibit troponin I cleavage. | ||
| ln Vivo | Receiving Ac-DEVD-CHO at the time of MI causes a 61% decrease in the expression of activated caspase-3 in cardiomyocytes (p<0.05) and an 84% decrease in cardiomyocyte apoptosis in young animals. Caspase inhibition, however, had no impact on cardiomyocyte apoptosis or activated caspase-3 expression in the aging mice[4]. Ac-DEVD-CHO inhibited and/or postponed the development of photoreceptor cell damage in rats, as well as slows the disease's progression in rd gene-carrying mice, which typically experience retinal degeneration in their early years of life[2]. | ||
| Enzyme Assay | Studies with peptide-based and macromolecular inhibitors of the caspase family of cysteine proteases have helped to define a central role for these enzymes in inflammation and mammalian apoptosis. A clear interpretation of these studies has been compromised by an incomplete understanding of the selectivity of these molecules. Here we describe the selectivity of several peptide-based inhibitors and the coxpox serpin CrmA against 10 human caspases. The peptide aldehydes that were examined (Ac-WEHD-CHO, Ac-DEVD-CHO, Ac-YVAD-CHO, t-butoxycarbonyl-IETD-CHO, and t-butoxycarbonyl-AEVD-CHO) included several that contain the optimal tetrapeptide recognition motif for various caspases. These aldehydes display a wide range of selectivities and potencies against these enzymes, with dissociation constants ranging from 75 pM to >10 microM. The halomethyl ketone benzyloxycarbonyl-VAD fluoromethyl ketone is a broad specificity irreversible caspase inhibitor, with second-order inactivation rates that range from 2.9 x 10(2) M-1 s-1 for caspase-2 to 2.8 x 10(5) M-1 s-1 for caspase-1. The results obtained with peptide-based inhibitors are in accord with those predicted from the substrate specificity studies described earlier. The cowpox serpin CrmA is a potent (Ki < 20 nM) and selective inhibitor of Group I caspases (caspase-1, -4, and -5) and most Group III caspases (caspase-8, -9, and -10), suggesting that this virus facilitates infection through inhibition of both apoptosis and the host inflammatory response[1]. | ||
| Cell Assay | OCLs are incubated with RANKL and treated with 0.5 mM SIN for 24 hours, either with or without the particular caspase-3 inhibitor Ac-DEVD-CHO (10 μM). After the treatment, the cells are rinsed with PBS and stained for 15 min with 10 μM Hoechst 33258 dye. A fluorescent microscope is used to take pictures of the staining cells. By counting the number of cells with apoptotic nuclear condensation in each well, the differences are measured[4]. | ||
| Animal Protocol |
|
||
| References |
[1]. J Biol Chem . 1998 Dec 4;273(49):32608-13. [2]. J Am Coll Cardiol . 2001 Dec;38(7):2063-70. [3]. Mol Cell Biol . 2006 Nov;26(21):7880-91. [4]. Cardiovasc Ther . 2013 Dec;31(6):e102-10. [5] Acta Histochem. 2003, 36(4):263-270. |
||
| Additional Infomation | Ac-Asp-Glu-Val-Asp-H is a tetrapeptide consisting of two L-aspartic acid residues, an L-glutamyl residue and an L-valine residue with an acetyl group at the N-terminal and with the C-terminal carboxy group reduced to an aldehyde. It is an inhibitor of caspase-3/7. It has a role as a protease inhibitor. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
|
|||
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: 100 mg/mL (199.02 mM) in PBS (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution; with sonication. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.9902 mL | 9.9508 mL | 19.9017 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3980 mL | 1.9902 mL | 3.9803 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1990 mL | 0.9951 mL | 1.9902 mL |