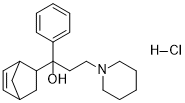
Biperiden HCl (trade name Akineton; Akinophyl), the hydrochloride salt of Biperiden, is a potent muscarinic antagonist and a medication used to treat Parkinson disease and certain drug-induced movement disorders. For tardive dyskinesias, it is not advised. It is injected into a vein, muscle, or taken orally.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C21H30CLNO |
| Molecular Weight | 347.92 |
| Exact Mass | 347.201 |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 72.49; H, 8.69; Cl, 10.19; N, 4.03; O, 4.60 |
| CAS # | 1235-82-1 |
| Related CAS # | Biperiden; 514-65-8; Biperiden lactate; 7085-45-2; Biperiden-d5 hydrochloride; rel-Biperiden-d5; rel-Biperiden EP impurity A-d5; rel-Biperiden EP impurity B-d5 |
| PubChem CID | 92151 |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid powder |
| Boiling Point | 462.1ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 101ºC |
| Flash Point | 224.5ºC |
| Vapour Pressure | 2.45E-09mmHg at 25°C |
| LogP | 4.702 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 2 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 5 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 24 |
| Complexity | 422 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| SMILES | OC(C1CC2C=CC1C2)(CCN3CCCCC3)C4=CC=CC=C4.[H]Cl |
| InChi Key | RDNLAULGBSQZMP-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C21H29NO.ClH/c23-21(19-7-3-1-4-8-19,11-14-22-12-5-2-6-13-22)20-16-17-9-10-18(20)15-17;/h1,3-4,7-10,17-18,20,23H,2,5-6,11-16H2;1H |
| Chemical Name | 1-(2-bicyclo[2.2.1]hept-5-enyl)-1-phenyl-3-piperidin-1-ylpropan-1-ol;hydrochloride |
| Synonyms | Akineton hydrochloride; Akineton; Akinophyl; Biperiden Hydrochloride; Biperiden; Biperiden |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month Note: Please store this product in a sealed and protected environment, avoid exposure to moisture. |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| ln Vitro | Biperiden hydrochloride (29.6 μg/ml, 72 hours) can dramatically suppress proliferation and cause apoptosis in human pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cells when applied at high concentrations[1]. |
| ln Vivo |
Biperiden hydrochloride (intraperitoneal injection, 10 mg/kg, everyday, 3 weeks) reduces tumor size by 83% in subcutaneous xenograft mice using Panc-1 human pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cells[1]. Biperiden hydrochloride (intraperitoneal injection, 8 mg/kg, every 8 hours, 10 days) can lower extracellular hippocampal glutamate levels and the frequency of spontaneous seizures while permanently lowering hippocampal excitability[2]. |
| Cell Assay |
Cell Line: Panc-1, Panc-2 and BxPC3 human pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cells Concentration: 29.6 μg/mL Incubation Time: 72 hours Result: Inhibited cell proliferation at 72 hours significantly by reducing nuclear c-Rel translocation. |
| Animal Protocol |
Subcutaneous xenograft mouse using Panc-1 human pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cells[1] 10 mg/kg Intraperitoneal injection; everyday; 3 weeks |
| References |
[1]. Biperiden and mepazine effectively inhibit MALT1 activity and tumor growth in pancreatic cancer. Int J Cancer. 2020 Mar 15;146(6):1618-1630. [2]. Modification of the natural progression of epileptogenesis by means of biperiden in the pilocarpine model of epilepsy. Epilepsy Res. 2017 Dec;138:88-97. doi: 10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2017.10.019. Epub 2017 Oct 29. [3]. Effects of two anticholinergic drugs, trospium chloride and biperiden, on motility and evoked potentials of the oesophagus. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 1998 Oct;12(10):979-84. [4]. Identification of novel functional inhibitors of acid sphingomyelinase. PLoS One. 2011;6(8):e23852. [5]. Antiparkinson drugs used as prophylactics for nerve agents: studies of cognitive side effects in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2008 Jun;89(4):633-8. |
| Additional Infomation | A muscarinic antagonist that has effects in both the central and peripheral nervous systems. It has been used in the treatment of arteriosclerotic, idiopathic, and postencephalitic parkinsonism. It has also been used to alleviate extrapyramidal symptoms induced by phenothiazine derivatives and reserpine. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
DMSO: ~20 mg/mL (~57.5 mM) H2O: ~5 mg/mL (~14.4 mM) |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Note: Listed below are some common formulations that may be used to formulate products with low water solubility (e.g. < 1 mg/mL), you may test these formulations using a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples. Injection Formulations (e.g. IP/IV/IM/SC) Injection Formulation 1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO stock solution → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline) *Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH ₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) Example: Take the Injection Formulation 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) as an example, if 1 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can take 100 μL 25 mg/mL DMSO stock solution and add to 900 μL corn oil, mix well to obtain a clear or suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Injection Formulation 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in saline = 10 : 90 [i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in saline)] *Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 5: 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin : Saline = 50 : 50 (i.e. 500 μL 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin → 500 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 6: DMSO : PEG300 : castor oil : Saline = 5 : 10 : 20 : 65 (i.e. 50 μL DMSO → 100 μLPEG300 → 200 μL castor oil → 650 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 7: Ethanol : Cremophor : Saline = 10: 10 : 80 (i.e. 100 μL Ethanol → 100 μL Cremophor → 800 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 8: Dissolve in Cremophor/Ethanol (50 : 50), then diluted by Saline Injection Formulation 9: EtOH : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 900 μL Corn oil) Injection Formulation 10: EtOH : PEG300:Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Oral Formulations Oral Formulation 1: Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na (carboxymethylcellulose sodium) Oral Formulation 2: Suspend in 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Example: Take the Oral Formulation 1 (Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na) as an example, if 100 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can first prepare 0.5% CMC Na solution by measuring 0.5 g CMC Na and dissolve it in 100 mL ddH2O to obtain a clear solution; then add 250 mg of the product to 100 mL 0.5% CMC Na solution, to make the suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Oral Formulation 3: Dissolved in PEG400 Oral Formulation 4: Suspend in 0.2% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 5: Dissolve in 0.25% Tween 80 and 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 6: Mixing with food powders Note: Please be aware that the above formulations are for reference only. InvivoChem strongly recommends customers to read literature methods/protocols carefully before determining which formulation you should use for in vivo studies, as different compounds have different solubility properties and have to be formulated differently. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.8742 mL | 14.3711 mL | 28.7422 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5748 mL | 2.8742 mL | 5.7484 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2874 mL | 1.4371 mL | 2.8742 mL |