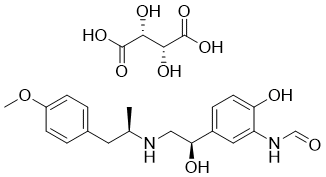
Formoterol (also named as Arformoterol) is a long-acting β2 agonist (LABA) used in the treatment of asthma and COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease). It is sold under several trade names, such as Atock, Atimos/Atimos Modulite, Foradil/Foradile, Oxeze/Oxis, and Perforomist, in three different forms: a dry powder inhaler, a metered-dose inhaler, and an inhalation solution. The combination formulations of mometasone/formoterol and budesonide/formoterol are also available for purchase. Compared to short-acting β2 agonists like salbutamol (albuterol), which have an efficacious duration of 4–6 hours, formoterol exhibits an extended duration of action (up to 12 hours). LABAs, like formoterol, are used in addition to prophylactic corticosteroid therapy as "symptom controllers." Since LABAs are not advised for the treatment of acute asthma, a "reliever" short-acting β2 agonist (such as salbutamol) is still needed.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C23H30N2O10 |
| Molecular Weight | 494.5 |
| Exact Mass | 494.19 |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 55.87; H, 6.12; N, 5.67; O, 32.35 |
| CAS # | 200815-49-2 |
| Related CAS # | Formoterol fumarate; 43229-80-7; Arformoterol; 67346-49-0; Arformoterol maleate; 1254575-18-2 |
| PubChem CID | 9827062 |
| Appearance | Solid powder |
| Boiling Point | 603.2ºC at 760mmHg |
| Vapour Pressure | 2.12E-15mmHg at 25°C |
| LogP | 1.2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 8 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 11 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 11 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 35 |
| Complexity | 521 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 4 |
| SMILES | C[C@@H](NC[C@H](O)C1=CC(NC=O)=C(O)C=C1)CC2=CC=C(OC)C=C2.O=C(O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)C(O)=O |
| InChi Key | FCSXYHUNDAXDRH-OKMNHOJOSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C19H24N2O4.C4H6O6/c1-13(9-14-3-6-16(25-2)7-4-14)20-11-19(24)15-5-8-18(23)17(10-15)21-12-22;5-1(3(7)8)2(6)4(9)10/h3-8,10,12-13,19-20,23-24H,9,11H2,1-2H3,(H,21,22);1-2,5-6H,(H,7,8)(H,9,10)/t13-,19+;1-,2-/m11/s |
| Chemical Name | (2R,3R)-2,3-dihydroxybutanedioic acid;N-[2-hydroxy-5-[(1R)-1-hydroxy-2-[[(2R)-1-(4-methoxyphenyl)propan-2-yl]amino]ethyl]phenyl]formamide |
| Synonyms | Formoterol; arformoterol; (R,R)-Formoterol; BD 40A; eformoterol; Foradil; formoterol fumarate; Trade names: Atock; Atimos/Atimos Modulite; Foradil/Foradile; Oxeze/Oxis; Perforomist |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | Beta-2 adrenergic receptor ( Kd = 2.9 nM ) | |
| ln Vitro |
|
|
| ln Vivo |
|
|
| Enzyme Assay | Formoterol(Arformoterol) is a brand-new, highly selective β2-adrenergic agonist that shows potential as a β2-agonist with selectively advantageous metabolic effects. | |
| Animal Protocol |
C57BL/6 male mice (8 wk old) 10 ng in 0.1 ml saline/20 g body weight instilled drop-wise in the external nares |
|
| References |
[1]. Tropical Journal of Pharmaceutical Research, Vol. 9, No. 6, November-December, 2010, pp. 595-603. [2]. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2011 Jul; 45(1): 88–94. |
|
| Additional Infomation |
Arformoterol Tartrate is the tartrate salt of arformoterol, the (R,R)-enantiomer of formoterol and a long-acting beta-2 adrenergic agonist with bronchodilator activity. Arformoterol selectively binds to and activates beta-2 adrenergic receptors in bronchiolar smooth muscle, thereby causing stimulation of adenyl cyclase, the enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) to cyclic-3',5'-adenosine monophosphate (cAMP). Increased intracellular cAMP levels cause relaxation of bronchial smooth muscle and lead to an inhibition of release of inflammatory mediators from mast cells. This may eventually lead to an improvement of airway function. See also: Arformoterol (has active moiety). |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
|
|||
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Note: Listed below are some common formulations that may be used to formulate products with low water solubility (e.g. < 1 mg/mL), you may test these formulations using a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples. Injection Formulations (e.g. IP/IV/IM/SC) Injection Formulation 1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO stock solution → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline) *Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH ₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) Example: Take the Injection Formulation 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) as an example, if 1 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can take 100 μL 25 mg/mL DMSO stock solution and add to 900 μL corn oil, mix well to obtain a clear or suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Injection Formulation 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in saline = 10 : 90 [i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in saline)] *Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 5: 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin : Saline = 50 : 50 (i.e. 500 μL 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin → 500 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 6: DMSO : PEG300 : castor oil : Saline = 5 : 10 : 20 : 65 (i.e. 50 μL DMSO → 100 μLPEG300 → 200 μL castor oil → 650 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 7: Ethanol : Cremophor : Saline = 10: 10 : 80 (i.e. 100 μL Ethanol → 100 μL Cremophor → 800 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 8: Dissolve in Cremophor/Ethanol (50 : 50), then diluted by Saline Injection Formulation 9: EtOH : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 900 μL Corn oil) Injection Formulation 10: EtOH : PEG300:Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Oral Formulations Oral Formulation 1: Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na (carboxymethylcellulose sodium) Oral Formulation 2: Suspend in 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Example: Take the Oral Formulation 1 (Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na) as an example, if 100 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can first prepare 0.5% CMC Na solution by measuring 0.5 g CMC Na and dissolve it in 100 mL ddH2O to obtain a clear solution; then add 250 mg of the product to 100 mL 0.5% CMC Na solution, to make the suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Oral Formulation 3: Dissolved in PEG400 Oral Formulation 4: Suspend in 0.2% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 5: Dissolve in 0.25% Tween 80 and 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 6: Mixing with food powders Note: Please be aware that the above formulations are for reference only. InvivoChem strongly recommends customers to read literature methods/protocols carefully before determining which formulation you should use for in vivo studies, as different compounds have different solubility properties and have to be formulated differently. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.0222 mL | 10.1112 mL | 20.2224 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4044 mL | 2.0222 mL | 4.0445 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2022 mL | 1.0111 mL | 2.0222 mL |