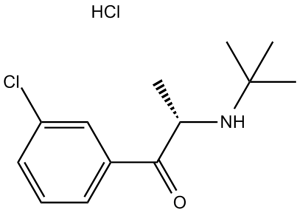
Amfebutamone HCl (Bupropion, Wellbutrin, Zyban; BW-323; NSC315851; NSC-315851), the hydrochloride salt of Amfebutamone, is a potent and selective norepinephrine-dopamine reuptake inhibitor used as an antidepressant and for smoking cessation. It suppresses dopamine and norepinephrine reuptake with IC50s of 6.5 and 3.4 μM, respectively. One of the antidepressants that doctors prescribe the most in the US is amfebutamone.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C13H19CL2NO | |
| Molecular Weight | 276.2 | |
| Exact Mass | 275.084 | |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 56.53; H, 6.93; Cl, 25.67; N, 5.07; O, 5.79 | |
| CAS # | 31677-93-7 | |
| Related CAS # | Bupropion morpholinol; 357399-43-0; Bupropion morpholinol-d6; 1216893-18-3; Bupropion; 34911-55-2; Bupropion hydrobromide; 905818-69-1 | |
| PubChem CID | 62884 | |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid powder | |
| Melting Point | 233-234 °C | |
| LogP | 4.492 | |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 | |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 2 | |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 | |
| Heavy Atom Count | 17 | |
| Complexity | 247 | |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 | |
| SMILES | CC(C(=O)C1=CC(=CC=C1)Cl)NC(C)(C)C.Cl |
|
| InChi Key | HEYVINCGKDONRU-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C13H18ClNO.ClH/c1-9(15-13(2,3)4)12(16)10-6-5-7-11(14)8-10;/h5-9,15H,1-4H3;1H | |
| Chemical Name | 2-(tert-butylamino)-1-(3-chlorophenyl)propan-1-one;hydrochloride | |
| Synonyms |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 | |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month Note: Please store this product in a sealed and protected environment, avoid exposure to moisture. |
|
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | Dopamine receptor; AChR |
| ln Vitro |
Bupropion (Amfebutamone) hydrochloride inhibits CYP2D6 with an IC50 of 58 μM[1]. Bupropion hydrochloride, an atypical antidepressant, causes caspase-dependent cytotoxicity and endoplasmic reticulum stress in SH-SY5Y cells[3]. Bupropion hydrochloride causes apoptotic cell death in SH-SY5Y cells by inducing endoplasmic reticulum stress responses and activating JNK, which in turn activates caspase 3[3]. Bupropion (1-100 µg/mL) hydrochloride decreases the viability of cells. The decrease in cell viability caused by bupropion could have resulted from apoptotic processes[3]. Bupropion (100 μg/mL) hydrochloride increases GRP78 expression in less than a hour, as well as the phosphorylated forms of EIF-2α, JNK, and p38 MAPK[3]. |
| ln Vivo |
Bupropion (Amfebutamone) hydrochloride exhibits both anticonvulsant and convulsant properties in mice. In mice, bupropion induces clonic convulsions in a dose-dependent manner; the convulsive dose50 (or dose that produces convulsions in 50% of mice) is 119.7 mg/kg[4]. Bupropion hydrochloride dose-dependently reduces the immobility period (in seconds) in male albino mice weighing between 22 and 30 g (10, 15, 20, and 40 mg/kg, i.p.). This effect is observed in comparison to the vehicle control group. In the forced swim test and tail suspension test, bupropion's ED50 values for shortening the immobility period were determined to be 18.5 and 18 mg/kg i.p., respectively. In the mouse brain, bupropion hydrochloride (10, 20, and 40 mg/kg, i.p.) increases the concentration of free dopamine and its metabolite homovanillic acid in a dose-dependent manner[5]. |
| Cell Assay |
Cell Line: SH-SY5Y human catecholaminergic cells Concentration: 0, 1, 10, 50, and 100 µg/mL Incubation Time: 24 hours Result: Cell viability decreased significantly in a concentration-dependent manner. |
| Animal Protocol |
Male Swiss mice weighing 20-25 g 100-160 mg/kg IP |
| References |
[1]. Antidepressant-drug interactions are potentially but rarely clinically significant. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2006 Aug;31(8):1594-604; discussion 1614-5. [2]. Bupropion, methylphenidate, and 3,4-methylenedioxypyrovalerone antagonize methamphetamine-induced efflux of dopamine according to their potencies as dopamine uptake inhibitors: implications for the treatment of methamphetamine dependence. BMC Res Notes. 2013 Jun 5;6:220. [3]. Bupropion, an atypical antidepressant, induces endoplasmic reticulum stress and caspase-dependent cytotoxicity in SH-SY5Y cells. Toxicology. 2011 Jul 11;285(1-2):1-7. [4]. Convulsant and anticonvulsant effects of bupropion in mice. Eur J Pharmacol. 2004 Sep 19;499(1-2):117-20. [5]. The efficacy and tolerability of bupropion in the treatment of major depressive disorder. Clin Drug Investig, 2011. 31 Suppl 1: p. 5-17. |
| Additional Infomation |
Bupropion hydrochloride is an aromatic ketone. Bupropion Hydrochloride is the hydrochloride salt of the aminoketone bupropion, with antidepressant activity and for potential use in promoting smoking cessation and improving sexual desire. Bupropion is a weak blocker of the neuronal uptake of serotonin, dopamine and norepinephrine and is a central nicotinic acetylcholine receptor antagonist. A propiophenone-derived antidepressant and antismoking agent that inhibits the uptake of DOPAMINE. See also: Bupropion (has active moiety); Bupropion Hydrochloride; Naltrexone Hydrochloride (component of); Naltrexone hydrochloride; bupropion hydrochloride (component of) ... View More ... |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
|
|||
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (9.05 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (9.05 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (9.05 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.6206 mL | 18.1028 mL | 36.2056 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.7241 mL | 3.6206 mL | 7.2411 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3621 mL | 1.8103 mL | 3.6206 mL |