Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C72H95CLN14O14 |
| Molecular Weight | 1416.06 |
| Exact Mass | 1414.684 |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 61.07; H, 6.76; Cl, 2.50; N, 13.85; O, 15.82 |
| CAS # | 183552-38-7 |
| Related CAS # | 183552-38-7; 785804-17-3 (acetate) |
| PubChem CID | 16131215 |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid powder |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 1688.4±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Flash Point | 974.9±34.3 °C |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.3 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.601 |
| LogP | 5.18 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 13 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 16 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 38 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 101 |
| Complexity | 2770 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 10 |
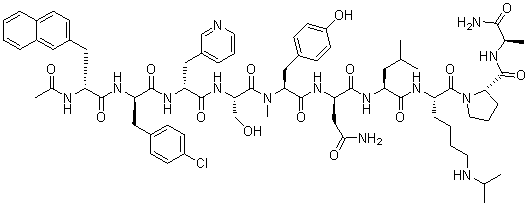
| SMILES | C[C@H](C(N)=O)NC([C@H]1N(C([C@H](CCCCNC(C)C)NC([C@H](CC(C)C)NC([C@@H](CC(N)=O)NC([C@H](CC2=CC=C(C=C2)O)N(C([C@H](CO)NC([C@@H](CC3=CC=CN=C3)NC([C@@H](CC4=CC=C(Cl)C=C4)NC([C@@H](CC5=CC=C6C=CC=CC6=C5)NC(C)=O)=O)=O)=O)=O)C)=O)=O)=O)=O)CCC1)=O |
| InChi Key | AIWRTTMUVOZGPW-HSPKUQOVSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C72H95ClN14O14/c1-41(2)32-54(64(93)80-53(17-10-11-30-77-42(3)4)72(101)87-31-13-18-60(87)69(98)78-43(5)63(75)92)81-68(97)58(38-62(74)91)84-70(99)61(37-46-22-27-52(90)28-23-46)86(7)71(100)59(40-88)85-67(96)57(36-48-14-12-29-76-39-48)83-66(95)56(34-45-20-25-51(73)26-21-45)82-65(94)55(79-44(6)89)35-47-19-24-49-15-8-9-16-50(49)33-47/h8-9,12,14-16,19-29,33,39,41-43,53-61,77,88,90H,10-11,13,17-18,30-32,34-38,40H2,1-7H3,(H2,74,91)(H2,75,92)(H,78,98)(H,79,89)(H,80,93)(H,81,97)(H,82,94)(H,83,95)(H,84,99)(H,85,96)/t43-,53+,54+,55-,56-,57-,58-,59+,60+,61+/m1/s1 |
| Chemical Name | (2R)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2R)-2-[[(2R)-2-[[(2R)-2-acetamido-3-naphthalen-2-ylpropanoyl]amino]-3-(4-chlorophenyl)propanoyl]amino]-3-pyridin-3-ylpropanoyl]amino]-3-hydroxypropanoyl]-methylamino]-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propanoyl]amino]-N-[(2S)-1-[[(2S)-1-[(2S)-2-[[(2R)-1-amino-1-oxopropan-2-yl]carbamoyl]pyrrolidin-1-yl]-1-oxo-6-(propan-2-ylamino)hexan-2-yl]amino]-4-methyl-1-oxopentan-2-yl]butanediamide |
| Synonyms | PPI-149; PPI 149; PPI149; R-3827; R3827; R 3827; Abarelix; Abarelix acetate. Brand name: Plenaxis |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month Note: Please store this product in a sealed and protected environment, avoid exposure to moisture. |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| ln Vitro | Abarelix causes a marked increase in histamine release at 30 and 300 µg/mL[1]. The first GnRH antagonist to be created,arelix has a very low short-term complication rate and can quickly and consistently lower testosterone levels to castrate levels without the need for co-administration of an antiandrogen[2]. Abarelix shows to quickly and significantly lower follicle-stimulating hormone levels to levels below those of an LHRH agonist. Abarelix causes medical castration more quickly and does not raise serum testosterone levels, which can worsen a patient's condition or trigger a flare phenomenon. This is especially dangerous for patients with symptomatic, metastatic diseases. |
| ADME/Pharmacokinetics |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion Following IM administration of 100 mg, abarelix is absorbed slowly with a mean peak concentration of 43.4 ng/mL observed approximately 3 days after the injection. Metabolism / Metabolites In vitro hepatocyte (rat, monkey, human) studies and in vivo studies in rats and monkeys showed that the major metabolites of abarelix were formed via hydrolysis of peptide bonds. No significant oxidative or conjugated metabolites of abarelix were found either in vitro or in vivo. There is no evidence of cytochrome P-450 involvement in the metabolism of abarelix. Biological Half-Life 13.2 ± 3.2 days |
| Toxicity/Toxicokinetics |
Protein Binding 96-99% |
| References |
[1]. A novel GnRH antagonist, causes minimal histamine release compared with abarelix in an ex vivo model of human skin samples. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2010 Oct;70(4):580-7. [2]. Abarelix and other gonadotrophin-releasing hormone antagonists in prostate cancer. BJU Int. 2009 Dec;104(11):1580-4. [3]. Abarelix for injectable suspension: first-in-class releasing hormone antagonist for prostate cancer. Future Oncol. 2006 Dec;2(6):677-96. |
| Additional Infomation |
Abarelix is a polypeptide compound composed of ten natural and non-natural amino acid resiudes in a linear sequence. It has a role as a hormone antagonist and an antineoplastic agent. Synthetic decapeptide antagonist to gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH). It is marketed by Praecis Pharmaceuticals as Plenaxis. Praecis announced in June 2006 that it was voluntarily withdrawing the drug from the market. Abarelix is a synthetic decapeptide and antagonist of naturally occurring gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH). Abarelix directly and competitively binds to and blocks the gonadotropin releasing hormone receptor in the anterior pituitary gland, thereby inhibiting the secretion and release of luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle stimulating hormone (FSH). In males, the inhibition of LH secretion prevents the release of testosterone. As a result, this may relieve symptoms associated with prostate hypertrophy or prostate cancer, since testosterone is required to sustain prostate growth. Drug Indication For palliative treatment of advanced prostate cancer. FDA Label Mechanism of Action Abarelix binds to the gonadotropin releasing hormone receptor and acts as a potent inhibitor of gonadotropin secretion. Pharmacodynamics Used in the palliative treatment of advanced prostate cancer. Abarelix is a luteinizing hormone agonist that results in suppression of testicular or follicular steroidogenesis. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | DMSO: ≥ 14.2 mg/mL (~10.0 mM) |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Note: Listed below are some common formulations that may be used to formulate products with low water solubility (e.g. < 1 mg/mL), you may test these formulations using a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples. Injection Formulations (e.g. IP/IV/IM/SC) Injection Formulation 1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO stock solution → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline) *Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH ₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) Example: Take the Injection Formulation 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) as an example, if 1 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can take 100 μL 25 mg/mL DMSO stock solution and add to 900 μL corn oil, mix well to obtain a clear or suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Injection Formulation 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in saline = 10 : 90 [i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in saline)] *Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 5: 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin : Saline = 50 : 50 (i.e. 500 μL 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin → 500 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 6: DMSO : PEG300 : castor oil : Saline = 5 : 10 : 20 : 65 (i.e. 50 μL DMSO → 100 μLPEG300 → 200 μL castor oil → 650 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 7: Ethanol : Cremophor : Saline = 10: 10 : 80 (i.e. 100 μL Ethanol → 100 μL Cremophor → 800 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 8: Dissolve in Cremophor/Ethanol (50 : 50), then diluted by Saline Injection Formulation 9: EtOH : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 900 μL Corn oil) Injection Formulation 10: EtOH : PEG300:Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Oral Formulations Oral Formulation 1: Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na (carboxymethylcellulose sodium) Oral Formulation 2: Suspend in 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Example: Take the Oral Formulation 1 (Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na) as an example, if 100 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can first prepare 0.5% CMC Na solution by measuring 0.5 g CMC Na and dissolve it in 100 mL ddH2O to obtain a clear solution; then add 250 mg of the product to 100 mL 0.5% CMC Na solution, to make the suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Oral Formulation 3: Dissolved in PEG400 Oral Formulation 4: Suspend in 0.2% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 5: Dissolve in 0.25% Tween 80 and 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 6: Mixing with food powders Note: Please be aware that the above formulations are for reference only. InvivoChem strongly recommends customers to read literature methods/protocols carefully before determining which formulation you should use for in vivo studies, as different compounds have different solubility properties and have to be formulated differently. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 0.7062 mL | 3.5309 mL | 7.0618 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.1412 mL | 0.7062 mL | 1.4124 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.0706 mL | 0.3531 mL | 0.7062 mL |