AVE-0991 is a novel, orally bioactive non-peptide mimic and high affinity agonist of angiotensin-(1-7) (IC50 = 21 nM) with important cardioprotective bioactivity. AVE-0991 significantly reduced the perfusion pressure in normal hearts while increasing the heart rate, systolic tension, and the rate at which tension rose and fell (+/-dT/dt).
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C29H32N4O5S2 |
| Molecular Weight | 580.71818 |
| Exact Mass | 580.181 |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 59.98; H, 5.55; N, 9.65; O, 13.78; S, 11.04 |
| CAS # | 304462-19-9 |
| Related CAS # | AVE 0991 sodium salt; 306288-04-0 |
| PubChem CID | 9851724 |
| Appearance | Off-white to yellow solid powder |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.639 |
| LogP | 4.6 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 7 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 11 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 40 |
| Complexity | 931 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
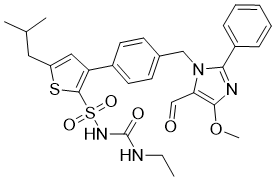
| SMILES | O=S(C1=C(C2=CC=C(CN3C(C=O)=C(OC)N=C3C4=CC=CC=C4)C=C2)C=C(CC(C)C)S1)(NC(NCC)=O)=O |
| InChi Key | QTOZBSNPDCWHPV-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C29H32N4O5S2/c1-5-30-29(35)32-40(36,37)28-24(16-23(39-28)15-19(2)3)21-13-11-20(12-14-21)17-33-25(18-34)27(38-4)31-26(33)22-9-7-6-8-10-22/h6-14,16,18-19H,5,15,17H2,1-4H3,(H2,30,32,35) |
| Chemical Name | 1-ethyl-3-[3-[4-[(5-formyl-4-methoxy-2-phenylimidazol-1-yl)methyl]phenyl]-5-(2-methylpropyl)thiophen-2-yl]sulfonylurea |
| Synonyms | AVE0991; AVE0991; AVE-0991 |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | Ang-(1-7) receptor ( IC50 = 21±35 nM ) |
| ln Vitro | AVE 0991 is a nonpeptide compound that acts on the endothelium in a manner akin to that of Ang-(1-3). The high-affinity binding of [125I]-Ang-(1-7) to bovine aortic endothelial cell membranes is competitive between AVE 0991 and unlabeled Ang-(1–7), with IC50s of 220±280 nM and 21±35 nM, respectively. The release of NO and O2-at peak concentrations by AVE 0991 sodium salt and Ang-(1–7) (both 10 μM) do not differ significantly (NO: 295±20 and 270±25 nM; O2-: 18±2 and 20±4 nM). In contrast to Ang-(1-7)[1], the amount of bioactive NO released by AVE 0991 is approximately five times greater. |
| ln Vivo | AVE 0991 (0.58 nmol/g) results in a significant reduction of water diuresis in WT mice as compared to animals treated with the vehicle (0.06±0.03 mL versus 0.27±0.05; n = 9 for each group; P<0.01). The antidiuretic action of AVE 0991 (AVE) is linked to a rise in urine osmolality (1669±231.0 mOsm/KgH2O) in comparison to 681.1±165.8 mOsm/KgH2O in mice treated with vehicle; P<0.01). When water is added, the antidiuretic effect of AVE 0991 is eliminated due to the genetic deletion of Mas (0.37±0.10 mL [n=9] versus 0.27±0.03 mL [n=11] in mice treated with AVE 0991). Administration of AVE 0991 (0.58 nmol/g) to water-loaded Swiss mice results in a significantly lower urinary volume than animals treated with a vehicle (0.13±0.05 mL [n=16] versus 0.51±0.04 mL [n=40]; P<0.01)[2]. This observation was also made with C57BL/6 mice on the same subject. AVE-0991 treatment for one week results in a significant decrease in perfusion pressure (56.55±0.86 vs. 68.73±0.69 mmHg in vehicle-treated rats) and an increase in systolic tension (11.40±0.05 vs. 9.84±0.15 g in vehicle-treated rats).It also causes a rise in the rate of tension (+dT/dt; 184.30±0.50 vs. 155.20±1.97 g/s in vehicle-treated rats), a fall in the rate of tension (dT/dt; 179.60±1.39 vs. 150.80±2.42 g/s in vehicle-treated rats). Notably, rats treated with vehicles showed a marginally higher heart rate (HR) of 220.40±0.71 beats/min as opposed to 214.20±0.74 beats/min[3]. |
| Cell Assay | Rat Mas cDNA is stably transfected into Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells and monkey kidney (COS) cells using a cytomegalovirus promoter. Neomycin is used to select the transfected cells. Either with or without AVE 0991 (AVE, 10-10 to -5 mol/L), 125I-Ang-(1-7) (0.5×10-9 mol/L) is cultured in 24-well plates for 60 minutes at 4°C in 0.3 mL of serum-free medium (DMEM) supplemented with 0.2% BSA, 0.005% bacitracin, 0.1 mol/L PMSF, and 0.5 mol/L orthophenanthroline with Mas-transfected COS cells. Following two cold, serum-free DMEM washes, 0.1% Triton X-100 is used to agitate the cells. A gamma counter is used to measure bound radioactivity. Using 2×10-9 mol/L rhodamine-labeled Ang-(1-7) in the presence or absence of AVE (10-6 mol/L), CV11974 (10-6 mol/L), or PD123319 (10-6 mol/L), binding of rhodamine-Ang-(1-7) in Mas-transfected CHO cells is carried out under equal circumstances. A concentration of 10-6 mol/L of Ang-(1-7) is required to calculate NSB [1]. |
| Animal Protocol |
Mice: The mice used are male Swiss mice, male Mas-KO (Mas-/-) mice on the pure genetic background C57BL/6, and male WT C57BL/6 control mice (Mas+/+). In conscious mice, an intraperitoneal water injection (0.05 mL/g of body weight [BW]) causes water diuresis. Predetermined volumes of water load (0.01 mL/g BW) are used to administer drugs in the same injection. In the first set of experiments, either vehicle for AVE 0991 (10 μM KOH, 0.01 mL/g; n = 9 control; n = 9 Mas-KO) or 0.58 nmol/g AVE 0991 (n = 9 control; n = 11 Mas-KO mice) is administered to WT (C57BL/6, control group) or Mas-KO mice. Swiss mice in the second set receive the following treatments: (1) vehicle (n = 36); (2) 0.58 nmol/g AVE 0991 (n = 16); (3) 46 pmol/g Ang-(1-7) antagonist A-779 (n = 4); (4) 2 nmol/g DuP-753 or CGP 48933 (n = 5); (5) 2 nmol/g AT2 receptor antagonists PD123319 or PD123177 (n = 9); (6) AVE 0991 combined with A-779; (7) AVE 0991 combined with DuP-753 or CGP 48933 (n = 4 for each); (8) or AVE 0991 combined with PD123319 (n = 5) or PD123177 (n = 4). The dosage of AVE 0991 is determined by means of pilot studies conducted on Swiss mice. Rats: We use male Wistar rats weighing between 250 and 300 grams. Rats are given AVE-0991 (1 mg/kg, n = 9) or vehicle (0.9% NaCl, n = 11) orally via gavage. |
| References |
[1]. AVE 0991, a nonpeptide mimic of the effects of angiotensin-(1-7) on the endothelium. Hypertension. 2002 Dec;40(6):847-52. [2]. Nonpeptide AVE 0991 is an angiotensin-(1-7) receptor Mas agonist in the mouse kidney. Hypertension. 2004 Oct;44(4):490-6. [3]. The nonpeptide angiotensin-(1-7) receptor Mas agonist AVE-0991 attenuates heart failure induced by myocardial infarction. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2007 Feb;292(2):H1113-9. [4]. AVE 0991 attenuates oxidative stress and neuronal apoptosis via Mas/PKA/CREB/UCP-2 pathway after subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats. Redox Biol. 2018 Sep 28;20:75-86. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | DMSO: ~41.7 mg/mL (~71.8 mM) |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (4.31 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: 2.5 mg/mL (4.31 mM) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), suspension solution; with ultrasonication. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (4.31 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.7220 mL | 8.6100 mL | 17.2200 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3444 mL | 1.7220 mL | 3.4440 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1722 mL | 0.8610 mL | 1.7220 mL |