ARS-1323 (ARS1323) is the racemic mixture of ARS-1620, which is a novel and potent inhibitor of mutant K-ras G12C with anticancer activity. ARS-1620 is a novel, potent, oral and covalent inhibitor that is oral and has a high potency and selectivity for KRASG12C. It was found using structure-based design, and it has the ability to cause tumor regression by achieving fast and long-lasting in vivo target occupancy. Recent research using allele-specific covalent targeting of Cys-12 in the vicinity of an inducible allosteric switch II pocket (S-IIP) revealed that KRASG12C may be druggable. Since the S-IIP can only be accessed in the GDP-bound state, the approach's success depends on KRASG12C actively cycling between its active-GTP and inactive-GDP conformations. It is unclear whether this tactic would work in vivo, despite the fact that it was successful in inhibiting mutant KRAS in vitro. In order to cause tumor regression, ARS-1620 can quickly and consistently occupy its target in vivo. The dissection of oncogenic KRAS dependency was carried out using ARS-1620, which revealed that KRAS dependency in vivo is greatly underestimated in monolayer culture formats. ARS-1620 is a novel class of KRASG12C-specific inhibitors with promising therapeutic potential, and this study shows that mutant KRAS can be selectively targeted in vivo.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C21H17CLF2N4O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 430.835090398788 |
| Exact Mass | 430.1 |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 58.54; H, 3.98; Cl, 8.23; F, 8.82; N, 13.00; O, 7.43 |
| CAS # | 1698024-73-5 |
| Related CAS # | ARS-1323-alkyne; 2436544-27-1; ARS-1630; 1698055-86-5; ARS-1620; 1698055-85-4 |
| PubChem CID | 137003167 |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid powder |
| LogP | 4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 7 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 3 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 30 |
| Complexity | 636 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
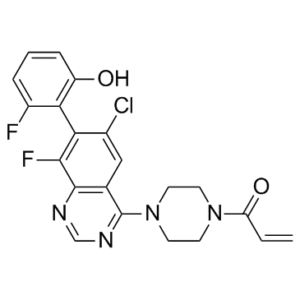
| SMILES | C(N1CCN(C2=C3C(=NC=N2)C(F)=C(C2=C(O)C=CC=C2F)C(Cl)=C3)CC1)(=O)C=C |
| InChi Key | ZRPZPNYZFSJUPA-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C21H17ClF2N4O2/c1-2-16(30)27-6-8-28(9-7-27)21-12-10-13(22)17(19(24)20(12)25-11-26-21)18-14(23)4-3-5-15(18)29/h2-5,10-11,29H,1,6-9H2 |
| Chemical Name | 1-[4-[6-chloro-8-fluoro-7-(2-fluoro-6-hydroxyphenyl)quinazolin-4-yl]piperazin-1-yl]prop-2-en-1-one |
| Synonyms | ARS1323; ARS-1323; ARS 1323 |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | KRas G12C |
| References |
[1]. Inhibitors of kras g12c. WO 2015054572 A1. |
| Additional Infomation |
ARS-1620 is a qinazoline derivative carrying chloro and fluoro substituents at positions 6 and 8 respectively, a 2-fluoro-6-hydroxyphenyl group at position 7, and a 4-(prop-2-enoyl)piperazin-1-yl group at position 4. A potent, selective, and orally bioavailable covalent KRAS-G12C inhibitor, it inhibits the protein coding gene KRAS (Kirsten rat sarcoma virus) with high potency in cells and animals. It has a role as an inhibitor, an antiviral agent and an antineoplastic agent. A series of novel thieno[2,3-d]pyrimidine analogs were designed and synthesized as KRAS G12D inhibitors via combinatorial virtual screening approach. Most compounds exhibited potent antiproliferative activity on KRAS G12D mutated Cancer cell lines (Panc1, SW1990 and CT26) with IC50 values in the low micromolar range. Among them, compound KD-8 showed the highest antiproliferative activity with an average IC50 of 2.1 μM against three KRAS G12D-mutated cells (Panc1, SW1990 and CT26). KD-8 decreased the active form of KRAS (KRAS-GTP) in KRAS G12D mutated Cancer cell lines (CT26 and SW1990) but not in KRAS G13D mutated Cancer cells (HCT116). Moreover, KD-8 down-regulated the phosphorylated Raf and ERK in CT26 and SW1990 Cancer cell lines but not in HeLa cells (KRAS WT). The binding affinity of KD-8 was further confirmed by the isothermal titration calorimetry (ITC) assay in which KD-8 exhibited a KD of 33 nM for binding to KRAS G12D protein. In addition, KD-8 (40 mg/kg or 60 mg/kg) exhibited significant antitumor efficacy in a CT26 tumor model with a tumor growth inhibition (TGI) of 42% or 53% without causing apparent toxicity. Taken together the above results suggest that KD-8 is a promising KRAS G12D inhibitor deserving further investigation. Eur J Med Chem. 2022 Apr 5;233:114243. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | DMSO: ~100 mg/mL (~232.1 mM) |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.80 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.80 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.80 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.3210 mL | 11.6052 mL | 23.2105 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4642 mL | 2.3210 mL | 4.6421 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2321 mL | 1.1605 mL | 2.3210 mL |