AMG-3969 is a potent, novel and metabolically stable disruptor of glucokinase-glucokinase regulatory protein interaction (GK-GKRP) with IC50 of 4 nM. AMG-3969 exhibits potent cellular activity with an EC50 of 0.202 μM and IC50 of 4 nM. It potently reverses the inhibitory effect of GKRP on GK activity and promotes GK translocation in vitro (isolated hepatocytes). When administered to db/db mice, AMG-3969 demonstrated a robust pharmacodynamic response (GK translocation) as well as statistically significant dose-dependent reductions in fed blood glucose levels. Furthermore, with AMG-1694 and AMG-3969 (but not GK activators), blood glucose lowering was restricted to diabetic and not normoglycaemic animals. These findings exploit a new cellular mechanism for lowering blood glucose levels with reduced potential for hypoglycaemic risk in patients with type II diabetes mellitus.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C21H20F6N4O3S | |
| Molecular Weight | 522.46 | |
| Exact Mass | 522.116 | |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 48.28; H, 3.86; F, 21.82; N, 10.72; O, 9.19; S, 6.14 | |
| CAS # | 1361224-53-4 | |
| Related CAS # |
|
|
| PubChem CID | 73053709 | |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid powder | |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 | |
| Boiling Point | 648.8±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Flash Point | 346.2±34.3 °C | |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.0 mmHg at 25°C | |
| Index of Refraction | 1.598 | |
| LogP | 4.51 | |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 | |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 13 | |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 | |
| Heavy Atom Count | 35 | |
| Complexity | 901 | |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 | |
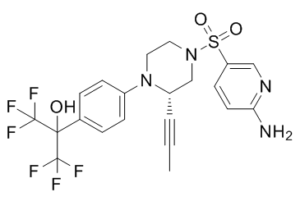
| SMILES | CC#C[C@@H]1N(C2=CC=C(C(C(F)(F)F)(O)C(F)(F)F)C=C2)CCN(S(=O)(C3=CN=C(N)C=C3)=O)C1 |
|
| InChi Key | SIFKNECWLVONIH-INIZCTEOSA-N | |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C21H20F6N4O3S/c1-2-3-16-13-30(35(33,34)17-8-9-18(28)29-12-17)10-11-31(16)15-6-4-14(5-7-15)19(32,20(22,23)24)21(25,26)27/h4-9,12,16,32H,10-11,13H2,1H3,(H2,28,29)/t16-/m0/s1 | |
| Chemical Name | 2-[4-[(2S)-4-(6-aminopyridin-3-yl)sulfonyl-2-prop-1-ynylpiperazin-1-yl]phenyl]-1,1,1,3,3,3-hexafluoropropan-2-ol | |
| Synonyms |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 | |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| ln Vitro | Strong cellular activity is demonstrated by AMG-3969, which has an EC50 of 0.202 μM and an IC50 of 4 nM[1], [2]. In vitro (isolated hepatocytes), it effectively counteracts the inhibitory effect of GKRP on GK activity and stimulates GK translocation[3]. | ||
| ln Vivo | According to research, AMG-3969 significantly lowers blood glucose levels in db/db mice in a dose-dependent manner and exhibits good in vivo pharmacokinetic (PK) properties in rats (75%). Blood glucose levels are significantly lowered by AMG-3969 (100 mg/kg), with a strong efficacy (56% reduction) seen at the 8-hour mark[2]. In three diabetes models—diet-induced obese (DIO), ob/ob, and db/db mice—AMG-3969 shows dose-dependent efficacy. In normoglycaemic C57BL/6 (B6) mice, however, AMG-3969 is ineffective in lowering blood glucose. When it comes to promoting carbohydrate substrate, AMG-3969 is very effective. After a single dosage, AMG-3969 shows prolonged changes to carbohydrate oxidation, as evidenced by an increased respiratory exchange ratio into the following day and night[3]. | ||
| Animal Protocol |
|
||
| References |
[1]. Antidiabetic effects of glucokinase regulatory protein small-molecule disruptors. Nature. 2013 Dec 19;504(7480):437-40. [2]. Small molecule disruptors of the glucokinase-glucokinase regulatory protein interaction: 3. Structure-activity relationships within the aryl carbinol region of the N-arylsulfonamido-N'-arylpiperazine series. J Med Chem. 2014 Apr 10;5. [3]. Small molecule disruptors of the glucokinase-glucokinase regulatory protein interaction: 2. Leveraging structure-based drug design to identify analogues with improved pharmacokinetic profiles. J Med Chem. 2014 Jan 23;57(2):325-38. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
|
|||
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (4.79 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (4.79 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (4.79 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.9140 mL | 9.5701 mL | 19.1402 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3828 mL | 1.9140 mL | 3.8280 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1914 mL | 0.9570 mL | 1.9140 mL |