AM251 (AM-251; AM 251) is a novel, potent and selective cannabinoid (CB) receptor antagonist with potential anti-obesity effect. It functions by inhibiting the brain's presynaptic cannabinoid 1 receptors, which binds to both endocannabinoids and synthetic cannabinoid agonists to suppress transmitter release. Rats' recognition memory is enhanced by AM251, and the ERK signaling pathway is activated, leading to nocifensive behavior. Furthermore, through the proteolytic degradation of ERRα, AM251 modifies mitochondrial physiology and reduces mechanical allodynia and thermal hyperalgesia following burn injuries.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C22H21CL2IN4O | |
| Molecular Weight | 555.24 | |
| Exact Mass | 554.013 | |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 47.59; H, 3.81; Cl, 12.77; I, 22.86; N, 10.09; O, 2.88 | |
| CAS # | 183232-66-8 | |
| Related CAS # |
|
|
| PubChem CID | 2125 | |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid powder | |
| Density | 1.7±0.1 g/cm3 | |
| Melting Point | 195-196℃ | |
| Index of Refraction | 1.703 | |
| LogP | 6.45 | |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 | |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 3 | |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 | |
| Heavy Atom Count | 30 | |
| Complexity | 586 | |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 | |
| SMILES | IC1C([H])=C([H])C(=C([H])C=1[H])C1=C(C([H])([H])[H])C(C(N([H])N2C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C2([H])[H])=O)=NN1C1C([H])=C([H])C(=C([H])C=1Cl)Cl |
|
| InChi Key | BUZAJRPLUGXRAB-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C22H21Cl2IN4O/c1-14-20(22(30)27-28-11-3-2-4-12-28)26-29(19-10-7-16(23)13-18(19)24)21(14)15-5-8-17(25)9-6-15/h5-10,13H,2-4,11-12H2,1H3,(H,27,30) | |
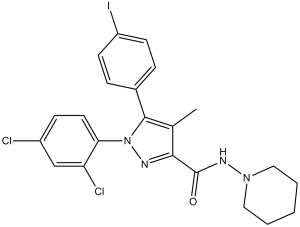
| Chemical Name | 1-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-5-(4-iodophenyl)-4-methyl-N-piperidin-1-ylpyrazole-3-carboxamide | |
| Synonyms |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 | |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | CB1 receptor ( IC50 = 8 nM ) | |
| ln Vitro |
|
|
| ln Vivo |
|
|
| Enzyme Assay |
In 12-well culture plates, macrophages are seeded at a density of 2×108/well. Seven-ketocholesterol (7KC) from a 2 mg/mL ethanol stock solution is added one hour before AM251 or SR144528 are added from 4 mM stock solutions made in DMSO. To give controls the same amounts of ethanol and DMSO, adjustments are made. The activity of caspase-3 is measured after 16 hours. The data is displayed as the mean RFLU/mg protein±SD for each treatment, which is carried out in triplicate[3]. FACS measurement of T1117 binding to CB1[1] HEK293 were transiently transfected with cDNA encoding for rat CB1-GFP. 48 hours after the transfection cell were harvested by gentle resuspension in warm culture medium. While in suspension cells were treated with 1 μM T1117 for 30 minutes. When indicated, cells were treated for 15 minutes with 5 μM AM251 . After being treated cells were sorted in a Bekton-Dickinson FACS-Sorted FACScan equipped with an Argon lamp in a linear data mode. Absorbance measurement of T1117 binding to CB1 and T117 partition into membranes[1] Rat brain membranes (60 μg) were incubated with the indicated amount T117 in a final volume of 100 μl for 15 minutes. When indicated 5 μM AM251 was added. Membranes were sedimented at 14.000 r.p.m. in a tabletop centrifuge at 4°C. Pellets were resuspended in PBS and absorbance measured at 530 nm and plotted versus T1117 concentration. |
|
| Cell Assay |
Caspase-3 Assay[3] Macrophages were seeded (2 × 106/well) in 12-well culture plates. AM-251 or SR144528 were added from 4 mM stock solutions prepared in DMSO, 1h prior to the addition of 7KC from a 2 mg/ml ethanol stock solution. Controls were adjusted to receive equivalent volumes of DMSO and ethanol. After 16 h, caspase-3 activity was determined as previously described [10]. All treatments were done in triplicate and the data presented as the mean RFLU/mg protein ± SD.[3] APOPercentage Assay[3] Macrophages, seeded (50,000/well) in 96-well plates and supplemented with AM-251, SR144528 or vehicle alone 1h prior to the addition of 7KC as described above for caspase-3 assays. After 16 h, apoptosis was quantified using the APOPercentage (Biocolor) colorimetric protocol according to the manufacturer’s directions.[3] In A375 human melanoma cells, treatment with AM251 (5 μmol/l) caused apoptosis, G2/M cell cycle arrest, and an increase in cAMP. Furthermore, AM-251 prevented Raw 264.7 macrophages from undergoing apoptosis caused by 7-ketocholesterol. |
|
| Animal Protocol |
|
|
| References |
[1]. Beyond radio-displacement techniques for identification of CB1 ligands: the first application of afluorescence-quenching assay. Sci Rep. 2014 Jan 20;4:3757. [2]. Pharmacological characterization of GPR55, a putative cannabinoid receptor. Pharmacol Ther. 2010 Jun;126(3):301-13 [3]. AM-251 and SR144528 are acyl CoA:cholesterol acyltransferase inhibitors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009 Apr 3;381(2):181-6. [4]. A pro-nociceptive phenotype unmasked in mice lacking fatty-acid amide hydrolase. Mol Pain. 2016 May 13;12. pii: 1744806916649192. [5]. Study the Effect of Endocannabinoid System on Rat Behavior in Elevated Plus-Maze. Basic Clin Neurosci. 2015 Jul;6(3):147-53. [6]. Role of cannabinoid receptor type 1 in tibial and pudendal neuromodulation of bladder overactivity in cats. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2017 Mar 1;312(3):F482-F488. [7]. Endocannabinoid activation of CB1 receptors contributes to long-lasting reversal of neuropathic pain by repetitive spinal cord stimulation. Eur J Pain. 2017 May;21(5):804-814. |
|
| Additional Infomation |
AM-251 is a carbohydrazide obtained by formal condensation of the carboxy group of 1-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-5-(4-iodophenyl)-4-methyl-1H-pyrazole-3-carboxylic acid with the amino group of 1-aminopiperidine. An antagonist at the CB1 cannabinoid receptor. It has a role as a CB1 receptor antagonist, an apoptosis inducer, an antidepressant and an antineoplastic agent. It is a member of pyrazoles, a dichlorobenzene, an organoiodine compound, an amidopiperidine and a carbohydrazide. Cannabinoid type 1 Receptor (CB1) belongs to the GPCR family and it has been targeted, so far, for the discovery of drugs aimed at the treatment of neuropathic pain, nausea, vomit, and food intake disorders. Here, we present the development of the first fluorescent assay enabling the measurement of kinetic binding constants for CB1 orthosteric ligands. The assay is based on the use of T1117, a fluorescent analogue of AM251. We prove that T1117 binds endogenous and recombinant CB1 receptors with nanomolar affinity. Moreover, T1117 binding to CB1 is sensitive to the allosteric ligand ORG27569 and thus it is applicable to the discovery of new allosteric drugs. The herein presented assay constitutes a sustainable valid alternative to the expensive and environmental impacting radiodisplacement techniques and paves the way for an easy, fast and cheap high-throughput drug screening toward CB1 for identification of new orthosteric and allosteric modulators. [1] Oxysterol-induced macrophage apoptosis may have a role in atherosclerosis. Macrophages lacking the type 2 cannabinoid receptor (CB2) are partially resistant to apoptosis induced by 7-ketocholesterol (7KC). AM-251 and SR144528 are selective antagonists of CB1 and CB2 receptors, respectively. We observed that both compounds reduce 7KC-induced apoptosis in Raw 264.7 macrophages. As oxysterol-induced macrophage apoptosis requires acyl-coenzymeA:cholesterol acyltransferase (ACAT) activity, we tested their affects on ACAT activity. AM-251 and SR144528 both reduced cholesteryl ester synthesis in unstimulated and acetylated LDL-stimulated Raw 264.7 macrophages, CB2(+/+) and CB2(-/-) peritoneal macrophages, as well as in vitro, in mouse liver microsomes. Consistent with inhibition of ACAT, the development of foam cell characteristics in macrophages by treatment with acetylated LDL was reduced by both compounds. This work is the first evidence that AM-251 and SR144528 are inhibitors of ACAT and as a result, might have anti-atherosclerotic activities independent of their affect on cannabinoid signaling. [3] |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
|
|||
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (4.50 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (4.50 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. Solubility in Formulation 3: 1% DMSO +30% polyethylene glycol+1% Tween 80 : 8 mg/mL (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.8010 mL | 9.0051 mL | 18.0102 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3602 mL | 1.8010 mL | 3.6020 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1801 mL | 0.9005 mL | 1.8010 mL |