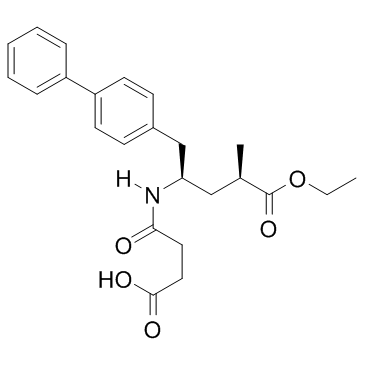
2R,4R-Sacubitril is an impurity of Sacubitril (AHU377), which is an FDA approved medication acting as a NEP (neutral endopeptidase 24.11) inhibitor and used as a component of the heart failure medicine LCZ696.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C24H29NO5 |
| Molecular Weight | 411.490767240524 |
| Exact Mass | 411.204 |
| CAS # | 766480-48-2 |
| Related CAS # | Sacubitril;149709-62-6 |
| PubChem CID | 9829628 |
| Appearance | Colorless to light yellow ointment |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 656.9±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Flash Point | 351.1±31.5 °C |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.1 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.549 |
| LogP | 3.96 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 5 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 12 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 30 |
| Complexity | 550 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 2 |
| SMILES | O(CC)C(C(C)CC(CC1C=CC(C2C=CC=CC=2)=CC=1)NC(CCC(=O)O)=O)=O |
| InChi Key | PYNXFZCZUAOOQC-DYESRHJHSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C24H29NO5/c1-3-30-24(29)17(2)15-21(25-22(26)13-14-23(27)28)16-18-9-11-20(12-10-18)19-7-5-4-6-8-19/h4-12,17,21H,3,13-16H2,1-2H3,(H,25,26)(H,27,28)/t17-,21-/m1/s1 |
| Chemical Name | 4-[[(2R,4R)-5-ethoxy-4-methyl-5-oxo-1-(4-phenylphenyl)pentan-2-yl]amino]-4-oxobutanoic acid |
| Synonyms | 2R,4R-Sacubitril; 766480-48-2; LCZ 696 Impurity B; (2R,4R)-Sacubitril; 4-((Rel-1-([1,1'-biphenyl]-4-yl)-5-ethoxy-4-methyl-5-oxopentan-2-yl)amino)-4-oxobutanoic acid; 4-[[(2R,4R)-5-ethoxy-4-methyl-5-oxo-1-(4-phenylphenyl)pentan-2-yl]amino]-4-oxobutanoic acid; (R*,R*)-?-[(3-Carboxy-1-oxopropyl)amino]-a-methyl-[1,1'-biphenyl]-4-pentanoic Acid a-Ethyl Ester; (aR,?R)-rel-?-[(3-Carboxy-1-oxopropyl)amino]-a-methyl-[1,1'-biphenyl]-4-pentanoic Acid 4-Ethyl Ester; Sacubitril-(2R,4R) Isomer;Impurity B; SCHEMBL18574632; |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | Impurity of Sacubitril |
| ln Vitro | Sacubitril was recently approved by the Food and Drug Administration for use in combination with valsartan for the treatment of patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction. As a prodrug, sacubitril must be metabolized (hydrolyzed) to its active metabolite sacubitrilat (LBQ657) to exert its intended therapeutic effects. Thus, understanding the determinants of sacubitril activation will lead to the improvement of sacubitril pharmacotherapy. The objective of this study was to identify the enzyme(s) responsible for the activation of sacubitril, and determine the impact of genetic variation on sacubitril activation. First, an incubation study of sacubitril with human plasma and the S9 fractions of human liver, intestine, and kidney was conducted. Sacubitril was found to be activated by human liver S9 fractions only. Moreover, sacubitril activation was significantly inhibited by the carboxylesterase 1 (CES1) inhibitor bis-(p-nitrophenyl) phosphate in human liver S9. Further incubation studies with recombinant human CES1 and carboxylesterase 2 confirmed that sacubitril is a selective CES1 substrate. The in vitro study of cell lines transfected with wild-type CES1 and the CES1 variant G143E (rs71647871) demonstrated that G143E is a loss-of-function variant for sacubitril activation. Importantly, sacubitril activation was significantly impaired in human livers carrying the G143E variant. In conclusion, sacubitril is selectively activated by CES1 in human liver. The CES1 genetic variant G143E can significantly impair sacubitril activation. Therefore, CES1 genetic variants appear to be an important contributing factor to interindividual variability in sacubitril activation, and have the potential to serve as biomarkers to optimize sacubitril pharmacotherapy[1]. |
| References |
[1]. Sacubitril Is Selectively Activated by Carboxylesterase 1 (CES1) in the Liver and the Activation Is Affected by CES1 Genetic Variation. Drug Metab Dispos. 2016 Apr;44(4):554-9. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | DMSO : ~100 mg/mL (~243.02 mM) |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (6.08 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (6.08 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (6.08 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.4302 mL | 12.1510 mL | 24.3019 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4860 mL | 2.4302 mL | 4.8604 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2430 mL | 1.2151 mL | 2.4302 mL |