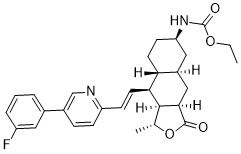
Vorapaxar (formerly SCH-530348; SCH530348; Zontivity), a new anti-platelet drug based on the natural product himbacine, is a thrombin receptor protease-activated receptor (PAR-1) antagonist that inhibits thrombin-induced platelet activation. In order to lower the risk of thrombotic cardiovascular events, vorapaxar, a platelet aggregation inhibitor, was approved in 2014. For those with poor blood flow or who have already experienced a heart attack, it can prevent heart attacks and strokes. Unlike other anti-platelet drugs like aspirin and P2Y12 inhibitors, vorapaxar works by preventing thrombin-related platelet aggregation.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C29H33FN2O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 492.5817 |
| Exact Mass | 492.242 |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 70.71; H, 6.75; F, 3.86; N, 5.69; O, 12.99 |
| CAS # | 618385-01-6 |
| Related CAS # | Vorapaxar sulfate; 705260-08-8 |
| PubChem CID | 10077130 |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid powder |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 676.0±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Flash Point | 362.6±31.5 °C |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.1 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.594 |
| LogP | 4.54 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 6 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 6 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 36 |
| Complexity | 821 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 7 |
| SMILES | FC1=C([H])C([H])=C([H])C(=C1[H])C1=C([H])N=C(C([H])=C1[H])/C(/[H])=C(\[H])/[C@]1([H])[C@]2([H])[C@@]([H])(C([H])([H])[H])OC([C@]2([H])C([H])([H])[C@]2([H])C([H])([H])[C@@]([H])(C([H])([H])C([H])([H])[C@]21[H])N([H])C(=O)OC([H])([H])C([H])([H])[H])=O |
| InChi Key | ZBGXUVOIWDMMJE-QHNZEKIYSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C29H33FN2O4/c1-3-35-29(34)32-23-10-11-24-20(14-23)15-26-27(17(2)36-28(26)33)25(24)12-9-22-8-7-19(16-31-22)18-5-4-6-21(30)13-18/h4-9,12-13,16-17,20,23-27H,3,10-11,14-15H2,1-2H3,(H,32,34)/b12-9+/t17-,20+,23-,24-,25+,26-,27+/m1/s1 |
| Chemical Name | ethyl N-[(1R,3aR,4aR,6R,8aR,9S,9aS)-9-[(E)-2-[5-(3-fluorophenyl)pyridin-2-yl]ethenyl]-1-methyl-3-oxo-3a,4,4a,5,6,7,8,8a,9,9a-decahydro-1H-benzo[f][2]benzofuran-6-yl]carbamate |
| Synonyms | Vorapaxar free base; Vorapaxar; SCH530348; SCH-530348; SCH 530348 |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | PAR-1 ( Ki = 8.1 nM ) |
| ln Vitro | SCH 530348 is an orally administered thrombin-receptor antagonist based on himbacine and a synthetic tricyclic 3-phenylpyridine. SCH 530348 exhibits no inhibition of platelet aggregation induced by other agonists such as ADP, collagen, and a PAR-4 agonist peptide, but it exhibits strong inhibition of thrombin-induced platelet aggregation (IC50 of 47 nM) and haTRAP-induced platelet aggregation (IC50 of 25 nM). Additionally, prothrombin time (PT), partial thromboplastin time (PTT), and activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT) are unaffected by SCH 530348. Furthermore, when SCH 530348 is used in place of an inactive control, there is no increase in bleeding time or surgical bleeding. When SCH530348 is tested against several ion channels and receptors, including the PAR-4 receptor, it is discovered to be selective for PAR-1.[1] |
| ln Vivo | SCH 530348 is well absorbed in rat (68%; 10 mg/kg) and in monkey (82%; 1 mg/kg) models. In rats, Tmax is measured at approximately 3 hours, while in monkeys, it is measured at 1 hour. In rats, the elimination half-life is 5.1 hours, while in monkeys, it is 13 hours. In rats, the oral bioavailability is 33%, while in monkeys, it is 86%. Oral SCH 530348 administration at a dose greater than 0.1 mg/kg resulted in 100% inhibition of thrombin-receptor agonist peptide (TRAP)-induced platelet aggregation for 24 hours, with partial recovery taking place at 48 hours, according to preclinical studies conducted on platelets from cynomolgus monkeys.[1] |
| Enzyme Assay | From 40 units of fresh human platelets, 700 mg of human platelet membranes are made. A thrombin receptor radioligand binding assay modification is used to screen for thrombin receptor antagonists. Human platelet membranes (40μg) are incubated in binding buffer (50 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.5, 10 mM MgCl2, 1 mM EGTA, 0.1% BSA) with 10nM of [3H]haTRAP (alanine-p-fluorophenylalaninearganine-cyclohexylalanine-homoarganine-[3H]phenylalanine amide) in the presence of compounds at concentrations of 1 nM, 3 nM, 30 nM, 100 nM, 300 nM, and 1μM (5% DMSO final concentration). The plates are placed on a plate shaker, covered, and gently vortexed for one hour at room temperature. Using a Packard FilterMate Universal Harvester, the incubated membranes are harvested onto Packard UniFilter GF/C filter plates. These plates are soaked in 0.1% polyethyleneimine for at least an hour and then quickly washed four times with 300 μL of ice cold binding buffer without BSA. Each well receives an addition of MicroScint 20 scintillation cocktail, and the plates are counted using a Packard TopCount Microplate Scintillation Counter. In the presence of excess (50 μM) unlabeled haTRAP, the specific binding is defined as the total binding minus the nonspecific binding. |
| Animal Protocol |
cynomolgus monkeys 0.5, 0.3, 0.1, and 0.05 mg/kg oral |
| ADME/Pharmacokinetics |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion After oral administration, vorapaxar is rapidly absorbed and peak concentrations occur at a median tmax of 1 hour under faster conditions. Vorapaxar may be taken with or without food as ingestion with a high-fat meal did not result in meaningful changes in AUC. The mean absolute bioavailability is 100%. Vorapaxar is primarily eliminated as its metabolite M19 through the feces (91.5%), and partially eliminated in the urine (8.5%). 424 L Metabolism / Metabolites Vorapaxar is metabolized to its major circulating metabolite, M20, and its predominant metabolite excreted into feces, M19, by CYP3A4 and CYP 2J2. Biological Half-Life Vorapaxar has an effective half life of 3-4 days and an apparent terminal half life of 8 days. |
| Toxicity/Toxicokinetics |
Hepatotoxicity Vorapaxar is associated with a low rate of serum enzyme elevations during therapy that was similar to the rate that occurred with placebo or comparator therapies. In a large controlled trial in over 10,000 patients monitored over a 2 year period, ALT elevations above 5 times the upper limit of normal occurred in 1% of vorapaxar vs 1.4% of placebo patients. In pooled analyses of laboratory studies from more than 39,000 patients receiving vorapaxar or placebo, GGT was the only liver test that was abnormal in a higher proportion of patients receiving vorapaxar (3.8%) than placebo (3.3%), and there were no reports of liver related serious adverse events or clinically apparent liver injury. Thus, liver injury from vorapaxar must be rare, if it occurs at all. Likelihood score: E (unlikely cause of clinically apparent liver injury). Protein Binding Vorapaxar is extensively bound (>99%) to human plasma proteins, such as human serum albumin. |
| References |
[1]. J Med Chem . 2008 Jun 12;51(11):3061-4. |
| Additional Infomation |
Vorapaxar is a carbamate ester that is the ethyl ester of [(1R,3aR,4aR,6R,8aR,9S,9aS)-9-{(E)-2-[5-(3-fluorophenyl)pyridin-2-yl]ethynyl}-1-methyl-3-oxododecahydronaphtho[2,3-c]furan-6-yl]carbamic acid. A protease-activated receptor-1 antagonist used (as its sulfate salt) for the reduction of thrombotic cardiovascular events in patients with a history of myocardial infarction (MI) or with peripheral arterial disease. It has been shown to reduce the rate of a combined endpoint of cardiovascular death, MI, stroke and urgent coronary revascularisation. It has a role as a protease-activated receptor-1 antagonist, a platelet aggregation inhibitor and a cardiovascular drug. It is a member of pyridines, a carbamate ester, an organofluorine compound, a naphthofuran and a lactone. It is a conjugate base of a vorapaxar(1+). Vorapaxar is a tricyclic himbacine-derived selective inhibitor of protease activated receptor (PAR-1) indicated for reducing the incidence of thrombotic cardiovascular events in patients with a history of myocardial infarction (MI) or with peripheral arterial disease (PAD). By inhibiting PAR-1, a thrombin receptor expressed on platelets, vorapaxar prevents thrombin-related platelet aggregation. Vorapaxar is a Protease-activated Receptor-1 Antagonist. The mechanism of action of vorapaxar is as a Protease-activated Receptor-1 Antagonist. Vorapaxar is an inhibitor of platelet aggregation that is used to decrease the risk of further cardiovascular thrombotic events in patients with a history of myocardial infarction or peripheral vascular disease. Vorapaxar therapy is associated with a low rate of serum aminotransferase elevations, but has not been linked to instances of clinically apparent acute liver injury. Vorapaxar is an orally bioavailable protease-activated receptor-1 (PAR-1) antagonist, with antiplatelet activity. Upon oral administration, vorapaxar binds to PAR-1 expressed on platelets, and inhibits PAR-1-mediated platelet aggregation. Vorapaxar inhibits thrombin-induced and thrombin receptor agonist peptide (TRAP)-induced platelet aggregation, and does not inhibit platelet aggregation induced by adenosine diphosphate (ADP), collagen or a thromboxane mimetic. See also: Vorapaxar Sulfate (active moiety of). Drug Indication Vorapaxar is indicated for the reduction of thrombotic cardiovascular events in patients with a history of myocardial infarction (MI) or peripheral arterial disease (PAD). It is usually co-administered with acetylsalicylic acid (ASA) and/or clopidogrel, and should therefore be administered as an addition to these medications as it has not been studied alone. FDA Label Zontivityis indicated for the reduction of atherothrombotic events in adult patients with- a history of myocardial infarction (MI), ,co-administered with acetylsalicylic acid (ASA) and, where appropriate, clopidogrel; or- symptomatic peripheral arterial disease(PAD), co-administered with acetylsalicylic acid (ASA) or, where appropriate, clopidogrel. Prevention of arterial thromboembolism Mechanism of Action Vorapaxar inhibits platelet aggregation through the reversible antagonism of protease-activated receptor 1 (PAR-1), also known as thrombin receptor. PARs are a family of G-protein coupled receptors highly expressed on platelets and activated by serine protease activity of thrombin to mediate thrombotic response. By blocking PAR-1 activating, vorapaxar inhibits thrombin-induced platelet aggregation and thrombin receptor agonist peptide (TRAP)-induced platelet aggregation. Vorapaxar does not inhibit platelet aggregation induced by other agonists such as adenosine diphosphate (ADP), collagen or a thromboxane mimetic. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
DMSO: 25~99 mg/mL (50.8~201 mM) Ethanol: ~99 mg/mL |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.08 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.08 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.08 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. Solubility in Formulation 4: 5%DMSO + 40%PEG300 + 5%Tween 80 + 50%ddH2O: 1.67mg/ml (3.39mM) (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.0301 mL | 10.1506 mL | 20.3013 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4060 mL | 2.0301 mL | 4.0603 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2030 mL | 1.0151 mL | 2.0301 mL |