Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C22H34O5 |
| Molecular Weight | 378.50 |
| Exact Mass | 378.24 |
| CAS # | 61263-49-8 |
| PubChem CID | 21636178 |
| Appearance | Typically exists as solid at room temperature |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 501.5±40.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Flash Point | 166.6±20.8 °C |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.9 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.529 |
| LogP | 3.69 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 5 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 5 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 27 |
| Complexity | 651 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 5 |
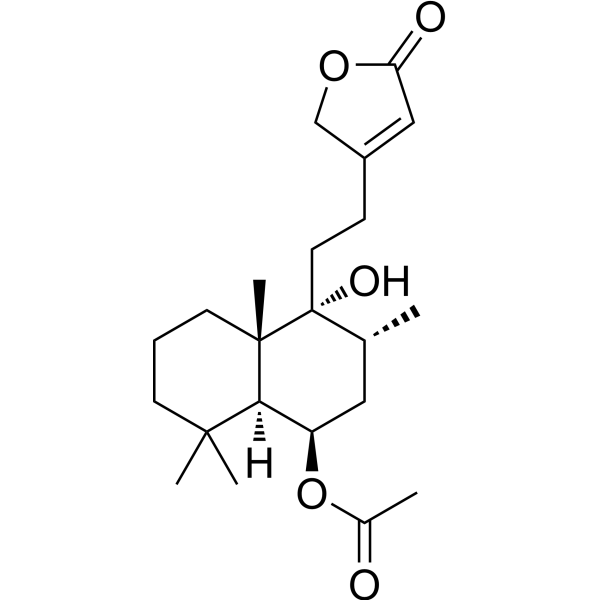
| SMILES | C[C@H]1[C@]([C@@]2([C@H]([C@@](CCC2)(C)C)[C@@H](C1)OC(=O)C)C)(O)CCC3=CC(=O)OC3 |
| InChi Key | FBWWXAGANVJTLU-HEXLTJKYSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C22H34O5/c1-14-11-17(27-15(2)23)19-20(3,4)8-6-9-21(19,5)22(14,25)10-7-16-12-18(24)26-13-16/h12,14,17,19,25H,6-11,13H2,1-5H3/t14-,17-,19+,21+,22-/m1/s1 |
| Chemical Name | [(1R,3R,4R,4aS,8aS)-4-hydroxy-3,4a,8,8-tetramethyl-4-[2-(5-oxo-2H-furan-3-yl)ethyl]-2,3,5,6,7,8a-hexahydro-1H-naphthalen-1-yl] acetate |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| ln Vitro | Vitexilactone significantly inhibits the growth of E. coli bacteria. coli, possessing a minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) greater than 90 μg/mL [1]. Mammalian cancer cell growth is inhibited by vitexilactone (0-100 μg/mL; 17-24 h) [2]. In tsFT210 and K562 cells, vitexilactone (25–100 μg/mL; 17 h) suppresses the G0/G1 phase of the cell cycle at low concentrations and causes apoptosis at high concentrations [2]. |
| Cell Assay |
Cell Proliferation Assay[2] Cell Types: tsFT210 and K562 cells lines Tested Concentrations: 0-100 μg/mL Incubation Duration: 17-24 hrs (hours) Experimental Results: Inhibited cell proliferation of mammalian cancer cells with IC50 values of 86.9 and 57.9 μg/mL for tsFT210 and K562 cells, respectively. Apoptosis Analysis[2] Cell Types: tsFT210 and K562 cell lines Tested Concentrations: 25-100 μg/mL Incubation Duration: 17 hrs (hours) Experimental Results: Induced cell apoptosis of tsFT210 with a MIC value of 25 μg/mL. Cell Cycle Analysis[2] Cell Types: tsFT210 and K562 cell lines Tested Concentrations: 25-100 μg/mL Incubation Duration: 17 hrs (hours) Experimental Results: Inhibited G0/G1 phase of cell cycle with the dose ranges of 50-6.25 μg/mL in tsFT210 cells. |
| References |
[1]. A new labdane-type diterpenoid from the leaves of Vitex negundo L. Nat Prod Res. 2021 Jul;35(14):2329-2334. [2]. Labdane-type diterpenes as new cell cycle inhibitors and apoptosis inducers from Vitex trifolia L. J Asian Nat Prod Res. 2005 Apr;7(2):95-105. |
| Additional Infomation |
Vitexilactone is a labdane diterpenoid that is isolated from the fruits of Vitex trifolia L. and Vitex agnus-castus It has a role as a plant metabolite, an apoptosis inducer and an antineoplastic agent. It is an acetate ester, a carbobicyclic compound, a labdane diterpenoid, a tertiary alcohol and a butenolide. Vitexilactone has been reported in Tinospora crispa, Vitex negundo var. cannabifolia, and other organisms with data available. See also: Chaste tree fruit (part of). |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Note: Listed below are some common formulations that may be used to formulate products with low water solubility (e.g. < 1 mg/mL), you may test these formulations using a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples. Injection Formulations (e.g. IP/IV/IM/SC) Injection Formulation 1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO stock solution → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline) *Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH ₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) Example: Take the Injection Formulation 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) as an example, if 1 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can take 100 μL 25 mg/mL DMSO stock solution and add to 900 μL corn oil, mix well to obtain a clear or suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Injection Formulation 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in saline = 10 : 90 [i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in saline)] *Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 5: 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin : Saline = 50 : 50 (i.e. 500 μL 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin → 500 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 6: DMSO : PEG300 : castor oil : Saline = 5 : 10 : 20 : 65 (i.e. 50 μL DMSO → 100 μLPEG300 → 200 μL castor oil → 650 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 7: Ethanol : Cremophor : Saline = 10: 10 : 80 (i.e. 100 μL Ethanol → 100 μL Cremophor → 800 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 8: Dissolve in Cremophor/Ethanol (50 : 50), then diluted by Saline Injection Formulation 9: EtOH : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 900 μL Corn oil) Injection Formulation 10: EtOH : PEG300:Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Oral Formulations Oral Formulation 1: Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na (carboxymethylcellulose sodium) Oral Formulation 2: Suspend in 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Example: Take the Oral Formulation 1 (Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na) as an example, if 100 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can first prepare 0.5% CMC Na solution by measuring 0.5 g CMC Na and dissolve it in 100 mL ddH2O to obtain a clear solution; then add 250 mg of the product to 100 mL 0.5% CMC Na solution, to make the suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Oral Formulation 3: Dissolved in PEG400 Oral Formulation 4: Suspend in 0.2% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 5: Dissolve in 0.25% Tween 80 and 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 6: Mixing with food powders Note: Please be aware that the above formulations are for reference only. InvivoChem strongly recommends customers to read literature methods/protocols carefully before determining which formulation you should use for in vivo studies, as different compounds have different solubility properties and have to be formulated differently. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.6420 mL | 13.2100 mL | 26.4201 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5284 mL | 2.6420 mL | 5.2840 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2642 mL | 1.3210 mL | 2.6420 mL |