Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C20H32N2O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 332.48 |
| CAS # | 64192-56-9 |
| Appearance | Typically exists as solids at room temperature |
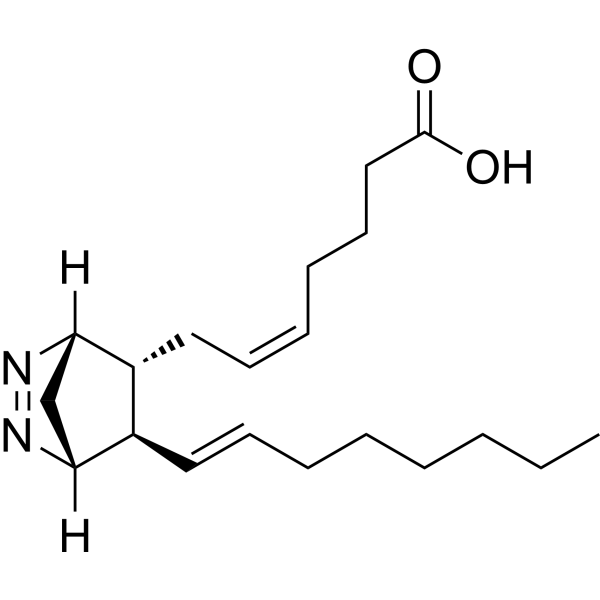
| SMILES | C(O)(=O)CCC/C=C\C[C@@H]1[C@@H](/C=C/CCCCCC)[C@@]2([H])C[C@]1([H])N=N2 |
| Synonyms | 9,11-Azoprosta-5,13-dienoic acid; U 51605; 64192-56-9; (Z)-7-[(1R,4S,5R)-1-[(E)-Oct-6-enyl]-2,3-diazabicyclo[2.2.1]hept-2-en-5-yl]hept-5-enoic acid |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | Prostaglandin I2 synthase inhibitor 9α[2] |
| ln Vitro | U-51605 (3 μM) inhibits acetylcholine-induced endothelium-dependent contraction[1]. U-51605 (0.5, 1, 3, 10 μM) increases acetylcholine-induced PGE2 and PGF2α release[1]. U-51605 simultaneously inhibited thromboxane synthesis and platelet suspension aggregation.[1] |
| ln Vivo | The prostanoid IP receptor antagonist 4,5-dihydro-N-[4-[[4-(1-methylethoxy)phenyl]methyl]phenyl]-1H-imadazol-2-amine (CAY10441), and the prostaglandin I2 synthase inhibitor 9α,11α-azoprosta-5Z,13E-dien-1-oic acid (U-51605), both showed similar preventive effects against the NOR3-induced retinal vasodilator response. Neither CAY10441 nor U-51605 showed any significant effects on the depressor response to NOR3. NOR3 enhanced the release of prostaglandin I2 from cultured human retinal microvascular endothelial cells and the NOR3-induced prostaglandin I2 release was almost completely abolished by the cyclooxygenase-1 inhibitor SC-560, but not by the cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor NS-398. However, NOR3 did not increase the release of prostaglandin I2 from human intestinal microvascular endothelial cells. These results suggest that NO exerts its dilatory effect via cyclooxygenase-1/prostaglandin I2/prostanoid IP receptor signaling mechanisms in the retinal vasculature [2]. |
| Animal Protocol |
Stock solutions of U-51605 in methyl acetate (5 mg/ml) and CAY10441 in dimethyl sulfoxide (20 mg/ml) were diluted in saline, separately. The final concentrations of methyl acetate and dimethyl sulfoxide in these solutions were 12% and 45%, respectively. [2] Indomethacin (5 mg/kg), U-51605 (0.6 mg/kg) or CAY10441 (6 mg/kg) was administered i.v., and the methoxamine infusion was started 45 min later (15 min for indomethacin). The timing of administration and dose of each compound were selected based on previous reports (Ogawa et al., 2007, Ogawa et al., 2009, Gohin et al., 2011). After hemodynamic parameters had reached a stable level (~15 min later), NOR3 (0.5–10 μg/kg/min) or prostaglandin I2 (0.005–0.3 μg/kg/min) was injected into the femoral vein, using a syringe pump. [2] |
| References |
[1]. Thromboxane synthetase inhibitors as pharmacological tools: differential biochemical and biological effects on platelet suspensionsJ. Prostaglandins, 1977, 14(5): 897-907. [2]. Involvement of prostaglandin I2 in nitric oxide-induced vasodilation of retinal arterioles in ratsJ. European Journal of Pharmacology, 2015, 764: 249-255. |
| Additional Infomation |
The comparative effects of three so called “thromboxane-synthetase- inhibitors” (imisazole, N-0.164, and U-51065) on arachidonate metabolism and on platelet aggregation were studied. All three compounds blocked platelet microsomal thromboxane synthesis from prostaglandin endoperoxides without affecting platelet adenyl cyclase. Imidazole, blocked thromboxane synthesis in intact platelets either from arachidonic acid or PGH2, without affecting aggregation. U-51605 simultaneously inhibited thromboxane synthesis and platelet suspension aggregation. N-0164 inhibited aggregation probably at extracellular sites, at concentrations that did not alter arachidonate or PGH2 metabolism. High concentrations of N-0164 simultaneously inhibited PG cyclo-oxygenase and thromboxane synthetase. The lack of specificity of these compounds requires that other actions of these compound must be considered when they are used as pharmacological tools to inhibit thromboxane synthetase. [2] The soluble guanylyl cyclase/cGMP system plays an important role in the vasodilator response to nitric oxide (NO) in various vascular beds. However, in rat retinal arterioles, the cyclooxygenase-1/cAMP-mediated pathway contributes to the vasodilator effects of NO, although the specific prostanoid involved remains to be elucidated. In the present study, we investigated the role of prostaglandin I2 and its receptor (prostanoid IP receptor) system in NO-induced vasodilation of rat retinal arterioles in vivo. Fundus images were captured using a digital camera that was equipped with a special objective lens. Changes in diameter of retinal arterioles were assessed. The NO donor (±)-(E)-4-ethyl-2-[(E)-hydroxyimino]-5-nitro-3-hexenamide (NOR3) increased the diameter of retinal arterioles but decreased systemic blood pressure in a dose-dependent manner. Treatment of rats with indomethacin, a non-selective cyclooxygenase inhibitor, markedly attenuated the retinal vasodilator, but not depressor responses to NOR3. The prostanoid IP receptor antagonist 4,5-dihydro-N-[4-[[4-(1-methylethoxy)phenyl]methyl]phenyl]-1H-imadazol-2-amine (CAY10441), and the prostaglandin I2 synthase inhibitor 9α,11α-azoprosta-5Z,13E-dien-1-oic acid (U-51605), both showed similar preventive effects against the NOR3-induced retinal vasodilator response. Neither CAY10441 nor U-51605 showed any significant effects on the depressor response to NOR3. NOR3 enhanced the release of prostaglandin I2 from cultured human retinal microvascular endothelial cells and the NOR3-induced prostaglandin I2 release was almost completely abolished by the cyclooxygenase-1 inhibitor SC-560, but not by the cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor NS-398. However, NOR3 did not increase the release of prostaglandin I2 from human intestinal microvascular endothelial cells. These results suggest that NO exerts its dilatory effect via cyclooxygenase-1/prostaglandin I2/prostanoid IP receptor signaling mechanisms in the retinal vasculature. [2] In the present study, we used U-51605 as an inhibitor of prostaglandin I2 synthase. However, the compound can inhibit thromboxane synthase (Gorman et al., 1977) and act on prostanoid TP receptors as a partial agonist (Gluais et al., 2005). The results clearly indicated that U-51605 reduced the NOR3-induced vasodilation of retinal arterioles to a similar degree as the prostanoid IP receptor antagonist CAY10441. However, we cannot exclude the possibility that effects of U-51605 on the thromboxane A2/prostanoid TP receptor system could also contribute to its inhibitory effect on NOR3-induced responses. Unfortunately, selective inhibitors for prostaglandin I2 synthase are not currently available. In the future, when highly selective inhibitors for this enzyme are developed, these issues should be addressed. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Note: Listed below are some common formulations that may be used to formulate products with low water solubility (e.g. < 1 mg/mL), you may test these formulations using a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples. Injection Formulations (e.g. IP/IV/IM/SC) Injection Formulation 1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO stock solution → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline) *Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH ₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) Example: Take the Injection Formulation 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) as an example, if 1 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can take 100 μL 25 mg/mL DMSO stock solution and add to 900 μL corn oil, mix well to obtain a clear or suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Injection Formulation 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in saline = 10 : 90 [i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in saline)] *Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 5: 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin : Saline = 50 : 50 (i.e. 500 μL 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin → 500 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 6: DMSO : PEG300 : castor oil : Saline = 5 : 10 : 20 : 65 (i.e. 50 μL DMSO → 100 μLPEG300 → 200 μL castor oil → 650 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 7: Ethanol : Cremophor : Saline = 10: 10 : 80 (i.e. 100 μL Ethanol → 100 μL Cremophor → 800 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 8: Dissolve in Cremophor/Ethanol (50 : 50), then diluted by Saline Injection Formulation 9: EtOH : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 900 μL Corn oil) Injection Formulation 10: EtOH : PEG300:Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Oral Formulations Oral Formulation 1: Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na (carboxymethylcellulose sodium) Oral Formulation 2: Suspend in 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Example: Take the Oral Formulation 1 (Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na) as an example, if 100 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can first prepare 0.5% CMC Na solution by measuring 0.5 g CMC Na and dissolve it in 100 mL ddH2O to obtain a clear solution; then add 250 mg of the product to 100 mL 0.5% CMC Na solution, to make the suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Oral Formulation 3: Dissolved in PEG400 Oral Formulation 4: Suspend in 0.2% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 5: Dissolve in 0.25% Tween 80 and 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 6: Mixing with food powders Note: Please be aware that the above formulations are for reference only. InvivoChem strongly recommends customers to read literature methods/protocols carefully before determining which formulation you should use for in vivo studies, as different compounds have different solubility properties and have to be formulated differently. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.0077 mL | 15.0385 mL | 30.0770 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.6015 mL | 3.0077 mL | 6.0154 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3008 mL | 1.5038 mL | 3.0077 mL |