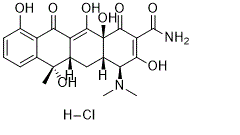
Tetracycline HCl (NSC-108579, Sumycin among others) is a potent and broad-spectrum antibiotic used to treat a number of infections such as gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. This includes acne, cholera, brucellosis, plague, malaria, and syphilis. It possesses some level of bacteriostatic activity against almost all medically relevant aerobic and anaerobic bacterial genera, both Gram-positive and Gram-negative.
Physicochemical Properties
| Exact Mass | 480.129 |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 54.95; H, 5.24; Cl, 7.37; N, 5.83; O, 26.62 |
| CAS # | 64-75-5 |
| Related CAS # | Tetracycline;60-54-8 |
| PubChem CID | 54704426 |
| Appearance | Light yellow to yellow solid powder |
| Boiling Point | 799.4ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 220-223 °C(lit.) |
| Flash Point | 437.3ºC |
| Vapour Pressure | 5.82E-27mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | -253 ° (C=0.5, 0.1mol/L HCl) |
| LogP | 1.287 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 7 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 9 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 2 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 33 |
| Complexity | 971 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 5 |
| SMILES | C[C@@]1([C@H]2C[C@H]3[C@@H](C(=O)C(=C([C@]3(C(=O)C2=C(C4=C1C=CC=C4O)O)O)O)C(=O)N)N(C)C)O.Cl |
| InChi Key | XMEVHPAGJVLHIG-FMZCEJRJSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C22H24N2O8.ClH/c1-21(31)8-5-4-6-11(25)12(8)16(26)13-9(21)7-10-15(24(2)3)17(27)14(20(23)30)19(29)22(10,32)18(13)28/h4-6,9-10,15,25,27-28,31-32H,7H2,1-3H3,(H2,23,30)1H/t9-,10-,15-,21+,22-/m0./s1 |
| Chemical Name | (4S,4aS,5aS,6S,12aS)-4-(dimethylamino)-3,6,10,12,12a-pentahydroxy-6-methyl-1,11-dioxo-1,4,4a,5,5a,6,11,12a-octahydrotetracene-2-carboxamide hydrochloride |
| Synonyms | Achromycin V; Hostacyclin; Sustamycin; Tetrabid; Tetracycline; Topicycline;Tetracycline HCl; Achromycin; |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month Note: Please store this product in a sealed and protected environment, avoid exposure to moisture. |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | Tetracycline |
| ln Vitro | Tetracyclines are broad-spectrum antibiotics that work against a variety of gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, as well as protozoan parasites and atypical organisms like chlamydiae, mycoplasmas, and rickettsiae. Tetracyclines stop aminoacyl-tRNA from attaching itself to the bacterial ribosome, which inhibits the synthesis of proteins by bacteria. Through the OmpF and OmpC porin channels, tetracyclines enter gram-negative enteric bacteria's outer membrane as positively charged cations (likely magnesium)-tetracycline coordination complexes [1]. |
| ln Vivo | Tetracyclines are useful for treating infections in pigs, sheep, cattle, and poultry. In certain situations, such as when treating a large number of commercially farmed chickens therapeutically, antibiotics can be given as aerosols or added straight to feed or water. Tetracyclines may be utilized to enhance or promote growth. In aquaculture, tetracyclines are used to manage infections in lobsters, salmon, and catfish[2]. |
| Toxicity/Toxicokinetics |
Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation ◉ Summary of Use during Lactation A number of reviews have stated that tetracycline is contraindicated during breastfeeding because of possible staining of infants' dental enamel or bone deposition of tetracyclines. However, a close examination of available literature indicates that there is not likely to be harm in short-term use of tetracycline during lactation because milk levels are low and absorption by the infant is inhibited by the calcium in breastmilk. Short-term use of tetracycline is acceptable in nursing mothers. As a theoretical precaution, avoid prolonged or repeat courses during nursing. Monitor the infant for rash and for possible effects on the gastrointestinal flora, such as diarrhea or candidiasis (thrush, diaper rash). ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants No adverse effects were noted in an unspecified number of breastfed infants whose mothers were taking oral tetracycline 1, 1.5 or 2 grams daily for 3 days. Ages of the infants and extent of breastfeeding were not stated. In one study, 5 infants breastfed during maternal therapy with tetracycline 500 mg 4 times daily with no adverse effects observed. In an observational study of 251 women, 23.8% of nursing mothers received tetracycline during breastfeeding. No gross adverse effect occurred in any of the breastfed infants. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. |
| References |
[1]. Tetracycline antibiotics: mode of action, applications, molecular biology, and epidemiology ofbacterial resistance.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2001 Jun;65(2):232-60 |
| Additional Infomation |
Tetracycline Hydrochloride (internal use) can cause developmental toxicity according to state or federal government labeling requirements. A naphthacene antibiotic that inhibits AMINO ACYL TRNA binding during protein synthesis. See also: Tetracycline Hydrochloride (annotation moved to). |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
DMSO : 62.5~96 mg/mL ( 129.96 ~199.62 mM) Water : 50~80 mg/mL (~103.97 mM) |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (4.33 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 20.8 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (4.33 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 20.8 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 3: 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween-80+45% Saline: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (4.33 mM) (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |