Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C18H16O5 |
| Molecular Weight | 312.32 |
| Exact Mass | 312.099 |
| CAS # | 97465-71-9 |
| PubChem CID | 126072 |
| Appearance | Brown to red solid powder |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 561.5±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Flash Point | 293.4±30.1 °C |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.6 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.661 |
| LogP | 2.25 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 5 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 0 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 23 |
| Complexity | 546 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 2 |
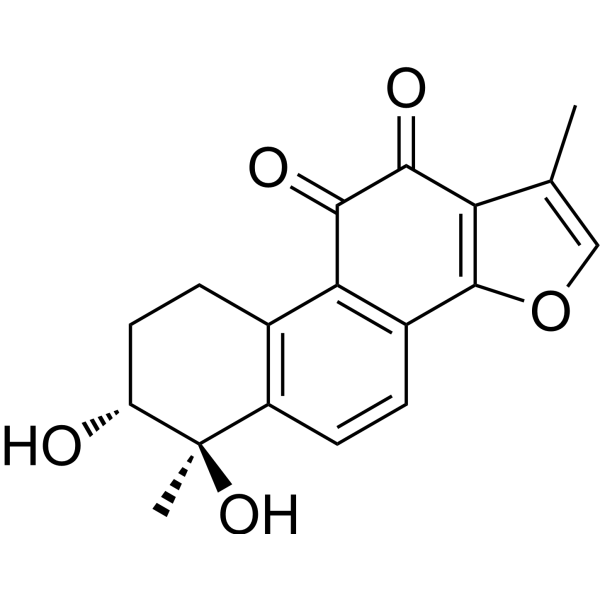
| SMILES | CC1=COC2=C1C(=O)C(=O)C3=C2C=CC4=C3CC[C@H]([C@]4(C)O)O |
| InChi Key | RTKDBIDPGKCZJS-KZULUSFZSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C18H16O5/c1-8-7-23-17-10-3-5-11-9(4-6-12(19)18(11,2)22)14(10)16(21)15(20)13(8)17/h3,5,7,12,19,22H,4,6H2,1-2H3/t12-,18-/m1/s1 |
| Chemical Name | (6R,7R)-6,7-dihydroxy-1,6-dimethyl-8,9-dihydro-7H-naphtho[1,2-g][1]benzofuran-10,11-dione |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month Note: This product requires protection from light (avoid light exposure) during transportation and storage. |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | EZH2 0.55 μM (IC50) SIRT1 |
| ln Vitro | Tanshindiol C (1–10 μM; for 24 hours) stimulates Prdx1 expression and mRNA levels in macrophages while activating Nrf2. Tanshindiol C inhibits the development of foam cells in macrophages caused by oxLDL by triggering the Prdx1/ABCA1 signaling pathway [1]. Tanshindiol C has a similar potency to that of EZH2 wild type (Ki value 176 nM) in inhibiting its activity [2]. With GI50 values of 1.5 μM and 9.5 μM, respectively, tanshindiol C suppresses the growth of Pfeiffer, U-2932 and Daudi (lymphoma), PC3 (prostate cancer), T98G and U87MG (glioma), and A549 (lung cancer) cell lines. 10.6, 4, 6, 5.7, 4.2, and 4 μM[2]. Pfeiffer cells accumulate in the sub-G1 phase when exposed to tanshindiol C (1–5 μM) for 72 hours, a sign that the cells had progressed to necrosis and apoptosis [2]. Important apoptosis-related protein indicators, such as cleaved caspase-3, caspase-7, and poly ADP-ribose polymerase (PRAP), have higher protein levels in cells when exposed to tanshindiol C (1-3 μM) over 72 hours. In cells, tanshindiol C dramatically lowers H3K27me3[2]. |
| Cell Assay |
RT-PCR[1] Cell Types: RAW264.7 cells Tested Concentrations: 1 μM, 3 μM, 10 μM Incubation Duration: 24 h Experimental Results: Upregulated the Nrf2 and Prdx1 mRNA levels. Western Blot Analysis[1] Cell Types: Mouse peritoneal macrophages Tested Concentrations: 1 μM, 3 μM, 10 μM Incubation Duration: 24 h Experimental Results: Activated Nrf2 and upregulated Prdx1 expression in macrophages. Cell Cycle Analysis[2] Cell Types: Pfeiffer cells Tested Concentrations: 1 μM, 2.5 μM and 5 μM Incubation Duration: 72 hrs (hours) Experimental Results: Induced accumulation of Pfeiffer cells in sub-G1 phase. Western Blot Analysis[2] Cell Types: Pfeiffer cells Tested Concentrations: 1 μM, 3 μM Incubation Duration: 72 hrs (hours) Experimental Results: The levels of H3K27me3 was Dramatically diminished in the cells. |
| References |
[1]. Tanshindiol C inhibits oxidized low-density lipoprotein induced macrophage foam cell formation via a peroxiredoxin 1 dependent pathway. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2018 Mar;1864(3):882-890. [2]. Biological evaluation of tanshindiols as EZH2 histone methyltransferase inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2014 Jun 1;24(11):2486-92. |
| Additional Infomation | Tanshindiol C has been reported in Salvia miltiorrhiza and Salvia miltiorrhiza var. miltiorrhiza with data available. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Note: Listed below are some common formulations that may be used to formulate products with low water solubility (e.g. < 1 mg/mL), you may test these formulations using a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples. Injection Formulations (e.g. IP/IV/IM/SC) Injection Formulation 1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO stock solution → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline) *Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH ₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) Example: Take the Injection Formulation 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) as an example, if 1 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can take 100 μL 25 mg/mL DMSO stock solution and add to 900 μL corn oil, mix well to obtain a clear or suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Injection Formulation 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in saline = 10 : 90 [i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in saline)] *Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 5: 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin : Saline = 50 : 50 (i.e. 500 μL 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin → 500 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 6: DMSO : PEG300 : castor oil : Saline = 5 : 10 : 20 : 65 (i.e. 50 μL DMSO → 100 μLPEG300 → 200 μL castor oil → 650 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 7: Ethanol : Cremophor : Saline = 10: 10 : 80 (i.e. 100 μL Ethanol → 100 μL Cremophor → 800 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 8: Dissolve in Cremophor/Ethanol (50 : 50), then diluted by Saline Injection Formulation 9: EtOH : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 900 μL Corn oil) Injection Formulation 10: EtOH : PEG300:Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Oral Formulations Oral Formulation 1: Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na (carboxymethylcellulose sodium) Oral Formulation 2: Suspend in 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Example: Take the Oral Formulation 1 (Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na) as an example, if 100 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can first prepare 0.5% CMC Na solution by measuring 0.5 g CMC Na and dissolve it in 100 mL ddH2O to obtain a clear solution; then add 250 mg of the product to 100 mL 0.5% CMC Na solution, to make the suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Oral Formulation 3: Dissolved in PEG400 Oral Formulation 4: Suspend in 0.2% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 5: Dissolve in 0.25% Tween 80 and 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 6: Mixing with food powders Note: Please be aware that the above formulations are for reference only. InvivoChem strongly recommends customers to read literature methods/protocols carefully before determining which formulation you should use for in vivo studies, as different compounds have different solubility properties and have to be formulated differently. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.2018 mL | 16.0092 mL | 32.0184 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.6404 mL | 3.2018 mL | 6.4037 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3202 mL | 1.6009 mL | 3.2018 mL |