Takinib is a novel, potent and selective TAK1 inhibitor with an IC50 of 9.5 nM. Takinib induces apoptosis following TNF-α stimulation in cell models of rheumatoid arthritis and metastatic breast cancer. Takinib is an inhibitor of autophosphorylated and non-phosphorylated TAK1 that binds within the ATP-binding pocket and inhibits by slowing down the rate-limiting step of TAK1 activation. Overall, Takinib is an attractive starting point for the development of inhibitors that sensitize cells to TNF-α-induced cell death, with general implications for cancer and autoimmune disease treatment. Tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) has both positive and negative roles in human disease. In certain cancers, TNF-α is infused locally to promote tumor regression, but dose-limiting inflammatory effects limit broader utility. In autoimmune disease, anti-TNF-α antibodies control inflammation in most patients, but these benefits are offset during chronic treatment. TAK1 acts as a key mediator between survival and cell death in TNF-α-mediated signaling.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C18H18N4O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 322.3611 |
| Exact Mass | 322.142 |
| CAS # | 1111556-37-6 |
| PubChem CID | 37750349 |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid powder |
| LogP | 2.3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 3 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 5 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 24 |
| Complexity | 470 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
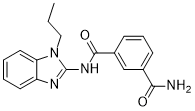
| SMILES | O=C(C1=CC=CC(C(N)=O)=C1)NC1=NC2=CC=CC=C2N1CCC |
| InChi Key | UOZVVPXKJGOFIG-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C18H18N4O2/c1-2-10-22-15-9-4-3-8-14(15)20-18(22)21-17(24)13-7-5-6-12(11-13)16(19)23/h3-9,11H,2,10H2,1H3,(H2,19,23)(H,20,21,24) |
| Chemical Name | 3-N-(1-Propylbenzimidazol-2-yl)benzene-1,3-dicarboxamide |
| Synonyms | EDHS-206; EDHS 206; EDHS206 |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| ln Vitro | After TNF-α activation, tikinib (10–10,000 nM; 24 hours) causes MDA-MB-231 cells to undergo apoptosis [1]. Takinib (10 μM; 0–1 hour) decreases p65 and IKK phosphorylation [1]. The chemical foundation for PfPK9 (KD(app) 0.46 μM) malaria inhibitor development is provided by tikinib [3]. TAK1Thr184/187, STAT3Tyr705, and STAT3Ser727 phosphorylation are induced in RASF treated with IL-1β (10 ng/mL; 30 minutes) by tikinib (2 hours; 0.1-20 μM; human RASF) [4]. |
| ln Vivo | In a mouse model of type II collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) of rheumatoid arthritis, tikinib (50 mg/kg; i.p.; once daily on days 18–36) lowers clinical scores [4]. ?In Hodgkin's lymphoma xenografted NSG mice, takinib (50 mg/kg; oral gavage; daily till day 17) inhibits the formation of tumors [5]. |
| Cell Assay |
Western Blot Analysis[1] Cell Types: Breast cancer cell line MDA-MB-231 Tested Concentrations: 10 μM Incubation Duration: 5, 15, 30, 60 minutes Experimental Results: IKK and p65 were maximally phosphorylated at 15 minutes, indicating activation of NF -κB pathway, whereas p38 phosphorylation peaked at 30 min. Western Blot Analysis[4] Cell Types: IL-1β treatment (10 ng/mL; 30 minutes) RASF Tested Concentrations: 0.1-20 µM Incubation Duration: 2 hrs (hours) Experimental Results: Induction of TAK1Thr184/187, STAT3Tyr705 and STAT3Ser727 phosphorylation. |
| Animal Protocol |
Animal/Disease Models: Male DBA/1 mouse (CIA arthritis model) [4] Doses: 50 mg/kg Route of Administration: intraperitoneal (ip) injection; one time/day starting on days 18-36 Experimental Results: compared to vehicle control , clinical arthritis scores diminished. Animal/Disease Models: Female NSG mice (8 weeks old) [5] Doses: 50 mg/kg Route of Administration: po (oral gavage); one time/day until 17 days Experimental Results: Tumor growth slowed down and tumor size/weight diminished. |
| References |
[1]. Takinib, a Selective TAK1 Inhibitor, Broadens the Therapeutic Efficacy of TNF-α Inhibition for Cancer and Autoimmune Disease. Cell Chem Biol. 2017 Aug 17;24(8):1029-1039. [2]. Scarneo SA, et.al. Pharmacological inhibition of TAK1, with the selective inhibitor takinib, alleviates clinical manifestation of arthritis in CIA mice. Arthritis Res Ther. 2019 Dec 17;21(1):292. [3]. Plasmodium PK9 Inhibitors Promote Growth of Liver-Stage Parasites. Cell Chem Biol. 2019 Mar 21;26(3):411-419.e7. [4]. Panipinto PM, et.al. Takinib Inhibits Inflammation in Human Rheumatoid Arthritis Synovial Fibroblasts by Targeting the Janus Kinase-Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 (JAK/STAT3) Pathway. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(22):12580. Published 2021 Nov 22. [5]. Song Z,et.al. Essential role of the linear ubiquitin chain assembly complex and TAK1 kinase in A20 mutant Hodgkin lymphoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Nov 17;117(46):28980-28991. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | DMSO : ~50 mg/mL (~155.11 mM) |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: 2.5 mg/mL (7.76 mM) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), suspension solution; with sonication. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: 2.5 mg/mL (7.76 mM) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), suspension solution; with ultrasonication. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.1021 mL | 15.5106 mL | 31.0212 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.6204 mL | 3.1021 mL | 6.2042 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3102 mL | 1.5511 mL | 3.1021 mL |