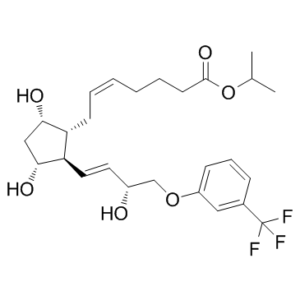
Travoprost (also known as Fluprostenol isopropyl ester; AL6221; Flu-Ipr; brand name Travatan) is medication used to treat high pressure inside the eye including glaucoma. It is specifically used in cases where other agents are insufficient for open angle glaucoma. It's applied as an ocular drop. In most cases, effects happen in two hours.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C26H35F3O6 |
| Molecular Weight | 500.5477 |
| Exact Mass | 500.24 |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 62.39; H, 7.05; F, 11.39; O, 19.18 |
| CAS # | 157283-68-6 |
| Related CAS # | 5,6-trans-Travoprost; 1563176-59-9 |
| PubChem CID | 5282226 |
| Appearance | Colorless to light yellow liquid (Oil like) |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 237.5±9.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Flash Point | 90.6±0.0 °C |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.1±0.5 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.545 |
| LogP | 3.17 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 9 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 13 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 35 |
| Complexity | 693 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 5 |
| SMILES | FC(C1C([H])=C([H])C([H])=C(C=1[H])OC([H])([H])[C@@]([H])(/C(/[H])=C(\[H])/[C@@]1([H])[C@@]([H])(C([H])([H])[C@@]([H])([C@]1([H])C([H])([H])C([H])=C([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C(=O)OC([H])(C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])[H])O[H])O[H])O[H])(F)F |
| InChi Key | MKPLKVHSHYCHOC-AHTXBMBWSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C26H35F3O6/c1-17(2)35-25(33)11-6-4-3-5-10-21-22(24(32)15-23(21)31)13-12-19(30)16-34-20-9-7-8-18(14-20)26(27,28)29/h3,5,7-9,12-14,17,19,21-24,30-32H,4,6,10-11,15-16H2,1-2H3/b5-3-,13-12+/t19-,21-,22-,23+,24-/m1/s1 |
| Chemical Name | propan-2-yl (Z)-7-[(1R,2R,3R,5S)-3,5-dihydroxy-2-[(E,3R)-3-hydroxy-4-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenoxy]but-1-enyl]cyclopentyl]hept-5-enoate |
| Synonyms | Fluprostenol isopropyl ester; AL6221; Flu-Ipr; Travatan; Travatan Z; Travoprost; Izba; AL-6221; Travaprost; Otx-tp; |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | FP receptor |
| ln Vitro | Travoprost has affinity for the IP, TP, DP, EP1, EP3, and EP4 receptors that is sub-micromolar[1]. |
| ln Vivo | At a dose of 1 μg, travoprost causes less ocular irritation in the New Zealand albino (NZA) rabbit than PGF20 isopropyl ester. Travoprost applied topically to the eyes causes a noticeable miotic effect in cats after doses of 0.01, 0.03, and 0.1 μg. Applying 0.1 and 0.3 μg of travoprost orally every day resulted in a peak reduction of 22.7% and 28.6% in intraocular pressure (IOP) in the ocular hypertensive monkey. Travoprost applied topically to rabbits, cats, and monkeys did not result in ocular irritation or discomfort at doses up to 1 μg[1]. |
| Enzyme Assay | Travoprost is the isopropyl ester prodrug of a high affinity, selective FP prostaglandin full receptor agonist. In contrast to travoprost acid's high affinity and efficacy at the FP receptor, there is only sub-micromolar affinity for the DP, EP1, EP3, EP4, IP, and TP receptors[1]. |
| Cell Assay | The ability of a number of prostaglandin F 2 alpha (PGF 2 alpha) analogs to mobilize intracellular Ca2+[Ca2+]iand to compete for [3H]PGF 2 alpha binding to prostaglandin F 2 alpha receptors (FP) was evaluated. Radioligand binding studies measuring displacement of [3H]PGF 2 alpha by a variety of FP prostaglandin analogs yielded the following rank order of affinities: travoprost acid [(+)-16-m-trifluorophenoxy tetranor PGF 2 alpha; (+)-fluprostenol] > bimatoprost acid (17-phenyl-trinor PGF 2 alpha) >> unoprostone (13,14-dihydro-15-keto-20-ethyl PGF 2 alpha) = bimatoprost (17-phenyl-trinor PGF 2 alpha ethyl amide) > or = Lumigan (bimatoprost ophthalmic solution). In FP functional studies, travoprost acid (EC50= 17.5-37 nM, n = 13), bimatoprost acid (EC50= 23.3-49.0 nM, n = 6-12), unoprostone (EC50= 306-1270 nM, n = 4-8), bimatoprost (EC50= 3070- 3940 nM, n = 4-9), and Lumigan (EC50= 1470-3190 nM, n = 5-9) concentration dependently stimulated [Ca2+]imobilization via the rat (A7r5 cells), mouse (3T3 cells), and cloned human ocular FP prostanoid receptors. The rank order of potency of these compounds at the FP receptor of the three species was similar and in good agreement with the determined binding affinities. The agonist effects of these compounds were concentration dependently blocked by the FP receptor-selective antagonist, AL-8810 (11beta-fluoro-15-epi-15-indanyl-tetranor PGF 2 alpha) (Ki= 0.6-1.3 microM). These studies have demonstrated that bimatoprost, unoprostone, and bimatoprost acid possess direct agonist activities at the rat, mouse, and human FP prostanoid receptor and that travoprost acid is the most potent of the synthetic FP prostaglandin analogs tested[2]. |
| Animal Protocol | Travoprost produced a lower incidence of ocular irritation than PGF20 isopropyl ester at a dose of 1 microg in the New Zealand albino (NZA) rabbit. Topical ocular application of travoprost produced a marked miotic effect in cats following doses of 0.01, 0.03 and 0.1 microg. In the ocular hypertensive monkey, b.i.d. application of 0.1 and 0.3 microg of travoprost afforded peak reduction in intraocular pressure (IOP) of 22.7% and 28.6%, respectively. Topical application of travoprost was well tolerated in rabbits, cats and monkeys, causing no ocular irritation or discomfort at doses up to 1 microg. Travoprost is a promising ocular hypotensive prostaglandin FP derivative that has the ocular hypotensive efficacy of PGF2alpha isopropyl ester but with less severe ocular side effects.[1] |
| ADME/Pharmacokinetics |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion Following ophthalmic administration, travoprost is absorbed through the cornea. In many patients in multiple-dose pharmacokinetic studies, the plasma concentrations of the free acid were below 0.01 ng/mL, which was the quantitation limit of the assay. In these studies, the mean plasma Cmax of travoprost free acid was 0.018 ± 0.007 ng/mL (ranging from 0.01 to 0.052 ng/mL), and the Tmax was about 30 minutes. The elimination of travoprost free acid from plasma is rapid. The levels of travoprost free acid were generally below the limit of quantification within one hour after dosing. Less than 2% of the topical ocular dose of travoprost was excreted in the urine within 4 hours as the travoprost free acid. No information is available. No information is available. Metabolism / Metabolites Travoprost, an isopropyl ester prodrug, is hydrolyzed by esterases in the cornea to its biologically active free acid. Systemically, travoprost free acid is metabolized to inactive metabolites via beta-oxidation of the α (carboxylic acid) chain to give the 1,2-dinor and 1,2,3,4-tetranor analogs, via oxidation of the 15-hydroxyl moiety, as well as via reduction of the 13, 14 double bond. Biological Half-Life The terminal elimination half-life of travoprost free acid was estimated from fourteen subjects and ranged from 17 minutes to 86 minutes with the mean half-life of 45 minutes. |
| Toxicity/Toxicokinetics |
Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation ◉ Summary of Use during Lactation No information is available on the use of travoprost during breastfeeding. Because of its short half-life it is not likely to reach the bloodstream of the infant or cause any adverse effects in breastfed infants. Professional guidelines consider prostaglandin eye drops acceptable during breastfeeding. To substantially diminish the amount of drug that reaches the breastmilk after using eye drops, place pressure over the tear duct by the corner of the eye for 1 minute or more, then remove the excess solution with an absorbent tissue. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. Protein Binding No information is available. |
| References |
[1]. Preclinical efficacy of travoprost, a potent and selective FP prostaglandin receptor agonist. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2001 Oct;17(5):421-32. [2]. Real-time intracellular Ca2+ mobilization by travoprost acid, bimatoprost, unoprostone, and other analogs via endogenous mouse, rat, and cloned human FP prostaglandin receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther . 2003 Jan;304(1):238-45. |
| Additional Infomation |
Travoprost is the isopropyl ester of prostaglandin F2alpha in which the pentyl group is replaced by a 3-(trifluoromethyl)phenoxymethyl group. A synthetic analogue of prostaglandin F2alpha, ophthalmic solutions of travoprost are used as a topical medication for controlling the progression of open-angle glaucoma and ocular hypertension, by reducing intraocular pressure. It is a pro-drug; the isopropyl ester group is hydrolysed by esterases in the cornea to the biologically active free acid, fluprostenol. It has a role as an antiglaucoma drug, an antihypertensive agent, a prodrug, an ophthalmology drug and a prostaglandin receptor agonist. It is a prostaglandins Falpha, a member of (trifluoromethyl)benzenes and an isopropyl ester. It is functionally related to a fluprostenol. Travoprost is a synthetic isopropyl ester prodrug of a prostaglandin F2alpha (F2α) analogue and selective FP prostanoid receptor agonist. It is used to decrease intraocular pressure in open-angle glaucoma and ocular hypertension. Unlike other prostaglandin analogues, travoprost demonstrates full agonism and high selectivity at the prostanoid receptor, reporting a higher efficacy in reducing intraocular pressure and a reduced risk for developing off-target side effects. Travoprost is a Prostaglandin Analog. Travoprost is a synthetic lipophilic isopropyl ester prodrug of the active compound travoprost free acid, a prostaglandin F2alpha analog with anti-glaucoma property. Upon administration, travoprost is hydrolysed to a free acid by corneal esterases, and then selectively stimulating the prostaglandin F (FP prostanoid) receptor, thereby increasing the uveoscleral outflow which leads to a reduction in intra-ocular pressure. A cloprostenol derivative that is used as an ANTIHYPERTENSIVE AGENT in the treatment of OPEN-ANGLE GLAUCOMA and OCULAR HYPERTENSION. Drug Indication Travoprost is indicated for the reduction of elevated intraocular pressure in patients with open-angle glaucoma or ocular hypertension. It is also used in pediatric patients aged two months to less than 18 years. Decrease of elevated intraocular pressure in adult patients with ocular hypertension or open-angle glaucoma (see section 5. 1). Decrease of elevated intraocular pressure in paediatric patients aged 2 months to < 18 years with ocular hypertension or paediatric glaucoma (see section 5. 1). Decrease of elevated intraocular pressure in adult patients with ocular hypertension or open-angle glaucoma (see section 5. 1). Decrease of elevated intraocular pressure in paediatric patients aged 3 years to < 18 years with ocular hypertension or paediatric glaucoma. Treatment of glaucoma Mechanism of Action Travoprost is a prodrug. Upon administration, travoprost is absorbed through the cornea and hydrolyzed to its active metabolite, travoprost free acid. The ester moiety of the free acid allows for enhanced penetration into the aqueous humour. While the exact mechanism of travoprost is largely unknown, it is believed to be related to its full agonist activity for the prostaglandin FP receptor. By binding to the FP receptor, travoprost free acid increases the outflow of aqueous humour via the trabecular meshwork and uveoscleral pathways, thereby reducing the intraocular pressure. Pharmacodynamics Travoprost demonstrates preferential affinity and full agonist activity for the prostaglandin FP receptor in the nanomolar range. Travoprost shows no significant affinity for other prostanoid or non-prostanoid receptors. Travoprost-induced reduction of intraocular pressure is observed about two hours after administration, and the maximum effect is reached after 12 hours. Significant lowering of intraocular pressure can be maintained for periods exceeding 24 hours with a single dose. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
Ethanol: ~60 mg/mL (~119.9 mM) DMSO: ≥ 41.67 mg/mL (~83.3 mM) |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (4.16 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 20.8 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (4.16 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 20.8 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (4.16 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 20.8 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.9978 mL | 9.9890 mL | 19.9780 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3996 mL | 1.9978 mL | 3.9956 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1998 mL | 0.9989 mL | 1.9978 mL |