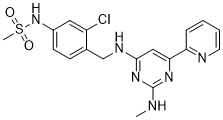
TC-G-1008, formerly known as GPR39-C3, is a GPR39 (zinc receptor) agonist (EC50 are 0.4 and 0.8 nM for rat and human receptors respectively).
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C18H19CLN6O2S |
| Molecular Weight | 418.9 |
| Exact Mass | 418.097 |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 51.61; H, 4.57; Cl, 8.46; N, 20.06; O, 7.64; S, 7.65 |
| CAS # | 1621175-65-2 |
| Related CAS # | 1621175-65-2 |
| PubChem CID | 91826086 |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid powder |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 662.1±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Flash Point | 354.2±34.3 °C |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.0 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.678 |
| LogP | 1.14 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 8 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 7 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 28 |
| Complexity | 589 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| SMILES | ClC1C([H])=C(C([H])=C([H])C=1C([H])([H])N([H])C1C([H])=C(C2=C([H])C([H])=C([H])C([H])=N2)N=C(N([H])C([H])([H])[H])N=1)N([H])S(C([H])([H])[H])(=O)=O |
| InChi Key | DRSZMILOMUPIBJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C18H19ClN6O2S/c1-20-18-23-16(15-5-3-4-8-21-15)10-17(24-18)22-11-12-6-7-13(9-14(12)19)25-28(2,26)27/h3-10,25H,11H2,1-2H3,(H2,20,22,23,24) |
| Chemical Name | N-[3-chloro-4-[[[2-(methylamino)-6-pyridin-2-ylpyrimidin-4-yl]amino]methyl]phenyl]methanesulfonamide |
| Synonyms | GPR39-C3; GPR39C3; GPR39 C3; TC-G-1008; TC-G1008; TC-G 1008; TCG-1008; TCG1008; TCG 1008 |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | GPR39 ( IC50 = 0.4 nM ); GPR39 ( IC50 = 0.8 nM ) |
| ln Vitro | TC-G-1008 demonstrates selectivity towards a range of kinases (IC50s>10 μM) and lacks significant binding affinity towards the associated ghrelin and neurotensin-1 receptors (IC50s>30 μM)[1]. GPR39-C3, a positive allosteric modulator, stimulates the production of cAMP (downstream of Gs), IP1 accumulation (downstream of Gq), SRF-RE-dependent transcription (downstream of G12/13), and β-arrestin recruitment in HEK293-GPR39 cells. By introducing the compound again, GPR39-C3 causes a dose- and time-dependent loss of response in the synthesis of cAMP[2]. |
| ln Vivo | For TC-G-1008, the measured levels of rat and mouse plasma protein binding are 99.3% and 99.1%, respectively. In mice, TC-G-1008 is orally bioavailable and effectively raises acute GLP-1 levels. After taking 10, 30, and 100 mg/kg of aqueous suspensions in 0.5% methylcellulose/0.1% Tween 80 orally, TC-G-1008 reaches maximal exposures of 1.4, 6.1, and 25.3 μM in 1 to 1.5 hours, respectively[1]. |
| Enzyme Assay | HEK293-GPR39 cells are plated and grown in the growth medium for an entire night at 37°C with 5% CO2 in white, 384-well plates coated with poly-d-lysine (4000 cells/well). The culture medium is removed before the cells are stimulated with GPR39 ligands in assay buffer for the specified amount of time at 37°C. This is done for pretreatment of the cells with GPR39 ligands (TC-G-1008) or vehicle control (DMSO). After that, the compound solution is taken out and twice cleaned using PBS that has 0.1% BSA added. The cells are stimulated with drugs in stimulation buffer for 30 minutes at 37°C in order to measure the amount of intracellular cAMP. The HTRF cAMP dynamic 2 kit is used to measure the intracellular cAMP level[2]. |
| Animal Protocol | Mice: Single oral doses of TC-G-1008 at 10, 30, and 100 mg/kg are administered to mice[1]. |
| References |
[1]. Discovery of 2-Pyridylpyrimidines as the First Orally Bioavailable GPR39 Agonists. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2014 Aug 4;5(10):1114-8. [2]. Rho kinase-dependent desensitization of GPR39; a unique mechanism of GPCR downregulation. Biochem Pharmacol. 2017 Sep 15;140:105-114. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
DMSO: ~84 mg/mL (~200.5 mM) Ethanol: ~2 mg/mL |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.97 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.97 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.97 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.3872 mL | 11.9360 mL | 23.8720 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4774 mL | 2.3872 mL | 4.7744 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2387 mL | 1.1936 mL | 2.3872 mL |