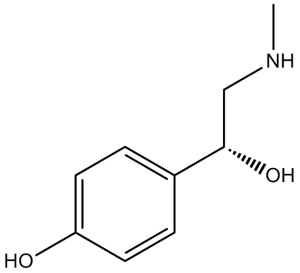
Synephrine [Synephrine (+/-); (+/-)-Synephrine; Oxedrine], a naturally occurring protoalkaloid found in and extracted from bitter orange and other citrus species, is commonly used for weight loss. Ephedrine has been substituted with synephrine. Adverse cardiovascular reactions are suspected in products containing synephrine or bitter orange. In L6 skeletal muscle cells, synephrine can promote glucose consumption (Glut4-dependent glucose uptake) by upregulating AMPK activity, independent of insulin-stimulated PI3 kinase-Akt activity.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C9H13NO2 | |
| Molecular Weight | 167.21 | |
| Exact Mass | 167.094 | |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 64.65; H, 7.84; N, 8.38; O, 19.14 | |
| CAS # | 94-07-5 | |
| Related CAS # | Synephrine hydrochloride; 5985-28-4; Synephrine hemitartrate; 16589-24-5; 614-35-7 (R-isomer) | |
| PubChem CID | 7172 | |
| Appearance | Off-white to light brown solid powder | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | |
| Boiling Point | 341.1±27.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Melting Point | 187 °C (dec.)(lit.) | |
| Flash Point | 163.4±14.3 °C | |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.8 mmHg at 25°C | |
| Index of Refraction | 1.572 | |
| LogP | -0.03 | |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 | |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 3 | |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 3 | |
| Heavy Atom Count | 12 | |
| Complexity | 122 | |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 | |
| SMILES | OC1C=CC(C(CNC)O)=CC=1 |
|
| InChi Key | YRCWQPVGYLYSOX-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C9H13NO2/c1-10-6-9(12)7-2-4-8(11)5-3-7/h2-5,9-12H,6H2,1H3 | |
| Chemical Name | 4-[1-hydroxy-2-(methylamino)ethyl]phenol | |
| Synonyms |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.03.00 | |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | β adrenergic receptor | |
| ln Vitro |
|
|
| ln Vivo |
|
|
| Animal Protocol |
Portal vein ligation (PVL) or bile duct ligation (BDL) rats 1 mg/kg per 12 hours Oral gavage; for 8 days |
|
| References |
[1]. Int J Med Sci . 2012;9(7):527-38. [2]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun . 2012 Feb 24;418(4):720-4. |
|
| Additional Infomation |
Synephrine is a phenethylamine alkaloid that is 4-(2-aminoethyl)phenol substituted by a hydroxy group at position 1 and a methyl group at the amino nitrogen. It has a role as a plant metabolite and an alpha-adrenergic agonist. It is a phenethylamine alkaloid, a member of phenols and a member of ethanolamines. It is a conjugate base of a synephrinium. Synephrine, also referred to as, p-synephrine, is naturally occurring alkaloid. It is present in approved drug products as neo-synephrine, its m-substituted analog. p-synephrine and m-synephrine are known for their longer acting adrenergic effects compared to norepinephrine. The similarity of naming between m-synephrine and the unsubstituted form, synephrine, is a source of some confusion however m-synephrine refers to a related drug more commonly known as phenylephrine. While the compounds share some chemical and pharmacological similarities, they are in fact distinct chemical entities. Synephrine has been reported in Citrus reticulata, Citrus hassaku, and other organisms with data available. Sympathetic alpha-adrenergic agonist with actions like PHENYLEPHRINE. It is used as a vasoconstrictor in circulatory failure, asthma, nasal congestion, and glaucoma. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
|
|||
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (12.44 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 20.8 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (12.44 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 20.8 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (12.44 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 20.8 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 5.9805 mL | 29.9025 mL | 59.8050 mL | |
| 5 mM | 1.1961 mL | 5.9805 mL | 11.9610 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.5981 mL | 2.9903 mL | 5.9805 mL |