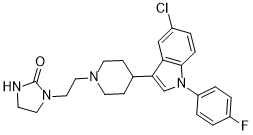
Sertindole (Sertindolum; Lu 23-174) is a potent antipsychotic medication and a neuroleptic drug. Sertindole exerts a potent antagonism at serotonin 5-HT2A, 5-HT2C, dopamine D2, and αl adrenergic receptors. Sertindole strongly binds to the αl adrenergic, dopamine D2, serotonin 5-HT2A, and 5-HT2C receptors. With a favorable metabolic profile, good EPS profile, and efficacy comparable to risperidone, sertindole presents a viable alternative for treating patients who are not responding to other treatment options. For patients who are intolerant to other antipsychotic medications, sertindole is an option as a second-line treatment due to concerns about cardiovascular safety. Sertindole is anticipated to be a highly beneficial supplement to the current therapeutic options for the management of psychotic disorders. Sertindole improves negative symptoms, and is also effective for the treatment of neuroleptic-resistant schizophrenia. Sertindole has a low incidence of extrapyramidal symptoms (EPS) and is generally well tolerated. Consequently, sertindole is a helpful option for treating schizophrenia in patients.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C24H26CLFN4O |
| Molecular Weight | 440.94 |
| Exact Mass | 440.177 |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 65.37; H, 5.94; Cl, 8.04; F, 4.31; N, 12.71; O, 3.63 |
| CAS # | 106516-24-9 |
| Related CAS # | Sertindole-d4; 1794737-42-0 |
| PubChem CID | 60149 |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid powder |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 592.1±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 95-100ºC |
| Flash Point | 311.9±30.1 °C |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.7 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.671 |
| LogP | 5.26 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 3 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 5 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 31 |
| Complexity | 623 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| SMILES | ClC1C([H])=C([H])C2=C(C=1[H])C(=C([H])N2C1C([H])=C([H])C(=C([H])C=1[H])F)C1([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])N(C([H])([H])C([H])([H])N2C(N([H])C([H])([H])C2([H])[H])=O)C([H])([H])C1([H])[H] |
| InChi Key | GZKLJWGUPQBVJQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C24H26ClFN4O/c25-18-1-6-23-21(15-18)22(16-30(23)20-4-2-19(26)3-5-20)17-7-10-28(11-8-17)13-14-29-12-9-27-24(29)31/h1-6,15-17H,7-14H2,(H,27,31) |
| Chemical Name | 1-[2-[4-[5-chloro-1-(4-fluorophenyl)indol-3-yl]piperidin-1-yl]ethyl]imidazolidin-2-one |
| Synonyms | Sertindolum; Serdolect; SerLect; Serdolect; Serlect; sertindole; Lu 23-174; Sertindole; Sertindol; Lu-23-174; sertindole hydrochloride |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | 5-HT2A Receptor; 5-HT2C Receptor |
| ln Vitro |
Sertindole (0-100 μM; 48 h) reduces the growth of breast cancer cells[2]. Sertindole (0.8-27.6 μM; 48 h) inhibits the proliferation of numerous cancers in vitro[2]. Sertindole (5 μΜ and 10 μΜ; 24 h) inhibits breast cancer cell migration[2]. |
| ln Vivo | Sertindole (10 mg/kg; once daily; 12 d) exhibits anti-tumor activity in vivo[2]. |
| Cell Assay |
Cell Line: SUM159 and MCF-10A cells Concentration: 0-100 μM Incubation Time: 48 hours Result: Showed IC50s of 9.2 µM and 27.6 µM for SUM159 and MCF-10A cells, respectively. |
| Animal Protocol |
Immune-deficient Balb/c mice implanted MDA-MB-231 human TNBC cells 10 mg/kg Oral gavage; 10 mg/kg; once daily; 12 days |
| ADME/Pharmacokinetics |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion Orally available. Metabolism / Metabolites Hepatic. Sertindole is metabolized by cytochrome P450 isoenzymes CYP 2D6 and CYP 3A4. Sertindole has known human metabolites that include 5-Chloro-1-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-(piperidin-4-yl)-1H-indole and 1-[2-[4-[5-Chloro-1-(4-fluorophenyl)indol-3-yl]piperidin-1-yl]ethyl]-4-hydroxyimidazolidin-2-one. Biological Half-Life 3 days |
| References |
[1]. Sertindole : a review of its use in schizophrenia. CNS Drugs. 2006;20(3):233-55. [2]. Antiproliferative activities of the second-generation antipsychotic drug sertindole against breast cancers with a potential application for treatment of breast-to-brain metastases. Sci Rep. 2018 Oct 25;8(1):15753. [3]. Sertindole in the management of schizophrenia. J Cent Nerv Syst Dis. 2011 May 17;3:75-85. |
| Additional Infomation |
Sertindole is a phenylindole that is 1H-indole which is substituted on the nitrogen by a p-chlorophenyl group, at position 5 by chlorine, and at position 3 by a piperidin-4-yl group, which is itself substituted on the nitrogen by a 2-(2-oxoimidazolidin-1-yl)ethyl group. It has a role as a serotonergic antagonist, an alpha-adrenergic antagonist, a H1-receptor antagonist and a second generation antipsychotic. It is a phenylindole, an organofluorine compound, an organochlorine compound, a heteroarylpiperidine and an imidazolidinone. Sertindole, a neuroleptic, is one of the newer antipsychotic medications available. Serdolect is developed by the Danish pharmaceutical company H. Lundbeck. It is a phenylindole derivative used in the treatment of schizophrenia. It was first marketed in 1996 in several European countries before being withdrawn two years later because of numerous cardiac adverse effects. It has once again been approved and should soon be available on the French and Australian market. Drug Indication Used in the treatment of schizophrenia. Mechanism of Action Sertindole is an antipsychotic drug with affinity for dopamine D2, serotonin 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C, and alpha1-adrenoreceptors. Preclinical studies suggest that sertindole acts preferentially on limbic and cortical dopaminergic neurons and clinical trials have confirmed that sertindole is effective at a low dopamine D2 occupancy level. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | DMSO: ~25 mg/mL (~56.7 mM) |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.67 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.67 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.67 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.2679 mL | 11.3394 mL | 22.6788 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4536 mL | 2.2679 mL | 4.5358 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2268 mL | 1.1339 mL | 2.2679 mL |