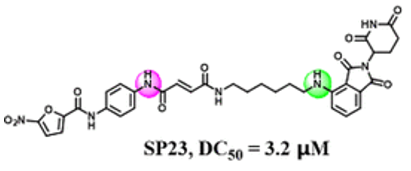
SP-23 (SP23) is a novel, first-in-class and potent STING-targeting PROTAC degrader based on C-170 (STING inhibitor) with anti-inflammatory effects. In degrades STING with a DC50 of 3.2 μM. SP23 exerted high anti-inflammatory efficacy in a cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury mouse model by modulating the STING signaling pathway. Taken together, SP23 represents the first PROTAC degrader of STING deserving further investigation as a new anti-inflammatory agent.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C34H33N7O10 |
| Molecular Weight | 699.666727781296 |
| Exact Mass | 699.23 |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 58.37; H, 4.75; N, 14.01; O, 22.87 |
| CAS # | 2762552-74-7 |
| PubChem CID | 164886634 |
| Appearance | Light yellow solid |
| LogP | 2.9 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 5 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 11 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 14 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 51 |
| Complexity | 1390 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| SMILES | C1CC(=O)NC(=O)C1N2C(=O)C3=C(C2=O)C(=CC=C3)NCCCCCCNC(=O)/C=C/C(=O)NC4=CC=C(C=C4)NC(=O)C5=CC=C(O5)[N+](=O)[O-] |
| InChi Key | TXNQXRGOKABDOB-FOCLMDBBSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C34H33N7O10/c42-26(15-16-27(43)37-20-8-10-21(11-9-20)38-32(46)25-13-17-29(51-25)41(49)50)36-19-4-2-1-3-18-35-23-7-5-6-22-30(23)34(48)40(33(22)47)24-12-14-28(44)39-31(24)45/h5-11,13,15-17,24,35H,1-4,12,14,18-19H2,(H,36,42)(H,37,43)(H,38,46)(H,39,44,45)/b16-15+ |
| Chemical Name | (E)-N-[6-[[2-(2,6-dioxopiperidin-3-yl)-1,3-dioxoisoindol-4-yl]amino]hexyl]-N'-[4-[(5-nitrofuran-2-carbonyl)amino]phenyl]but-2-enediamide |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | STING |
| ln Vitro | SP23 demonstrated the highest STING-degrading effect with a DC50 of 3.2 μM. Western blot analysis confirmed that SP23 induced the degradation of STING via the PROTAC mechanism, which is the proteasome-dependent pathway.In addition, the STING/TBK1/NF-κB signaling pathway was downregulated in THP-1 cells.[1] |
| ln Vivo | SP23 exhibited high in vivo anti-inflammatory efficacy in a cisplatin- AKI mouse model and effectively protected mouse kidneys from cisplatininduced injury in vivo. Mechanistically, SP23 inhibited the downstream signals of the STING signaling pathway in vivo, which is consistent with the results from in vitro experiments.SP23 also demonstrated benign toxicity profiles in the AKI mouse model.[1] |
| Enzyme Assay | Enzyme-linked Immunosorbent Assay. Culture medium supernatant and serum from mouse eyeball blood samples were collected. Levels of mouse and human IFN-β, CXCL10 and IL-6 were determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay kits (B Neobioscience) according to the product manual.[1] |
| Cell Assay | Cytotoxicity (MTT) Assay. The newly synthesized compounds SP21-23 were assessed for their cytotoxicity against various normal cell lines, including human normal hepatocyte (LO2), human embryonic kidney cells (HEK293A) and mouse neural stem cells (C17.2), using the MTT assay. Cells were seeded into 96-well plates at a density of 5000 cells/well. After treatment with compounds SP21-23 at the indicated concentration, MTT (5 mg/mL in PBS) was added and the cells were incubated for another 4 h. Cell viability was detected with a microplate reader at a wavelength of 570 nm.[1] |
| Animal Protocol |
In Vivo Anti-inflammatory Efficacy Study. Eight-week-old C57BL/6J male mice were purchased from Guangzhou Southern Medical University Experimental Animal Technology Development Co, certificate number: 110324201104674226. All experimental procedures were approved by Ethical Committee at SMU (Southern Medical University) and implemented accordingly. After 24 h of diurnal circulation and free diet and water, mice were randomly assigned to the following four groups: control group and cisplatin induction model group (25 mg/kg), low-dose treatment group (SP23, 30 mg/kg), and high-dose treatment group (SP23, 60 mg/kg). Mice were pretreated with SP23 administered intraperitoneally 1 h prior to cisplatin injection and administered continuously at the same time each day. Seventy-two hours after cisplatin treatment, all mice were euthanized, blood samples and heart, liver, and kidney tissues were collected. One sample from each tissue in each group was randomly selected and fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde for histological examination, and the remaining tissues were immediately frozen in liquid nitrogen and stored at -80°C. Urea nitrogen (BUN) and creatinine concentrations were determined at the Guangzhou Huayin Medical Laboratory Center using a serum biochemical auto-analyzer. Renal imaging was monitored by the Small Animal Magnetic Resonance Imaging System (PharmaScan70/16, USA) at the Southern Medical University Experimental Center.[1] Pharmacokinetic Study in Male SD Rats. Male SD rats (300-360 g) were purchased from Liaoning Changsheng Biotechnology Co., Ltd. Diet was prohibited for 12 h before the experiment but water was freely available. Blood samples (0.5 mL) were collected from the tail vein into heparinized 1.5 mL polythene tubes at 0.0833, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 12, 24, 36, and 48 h after oral (20 mg/kg) or intravenous (2 mg/kg) administration of compound SP23. Waters Acquity UPLC (Waters Corp., Milford, MA, USA) was used for the separation of SP23 and internal standard compound. The effective separation of SP23 and internal standard compound was achieved on Acquity UPLC BEH C18 column (50 × 2.1 mm, 1.7 μm, Waters Corporation, Milford, MA, USA) used at a column temperature of 40 °C. The mobile phase consisted of a mixture of solvent A (acetonitrile) and solvent B (formic acid/ ultrapure water, 1:1000, v/v). The linear gradient program for the mobile phase was set as follows: 0 min 10% A; 0.5 min 30% A; 1 min 95% A; 2 min 95% A; 2.3 min 10% A. The flow rate of the mobile phase was 0.4 mL/min and the injection volume was 2 μL. The XEVO TQD triple quadrupole mass spectrometer was equipped with an electrospray ionization (ESI) source; multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) mode was selected for quantitation. The Mass Lynx 4.1 software (Waters Corp.) was used for data acquisition. Mass spectral data were obtained in positive electrospray mode (ESI+) in MRM mode. |
| References |
[1]. Novel CRBN-Recruiting Proteolysis-Targeting Chimeras as Degraders of Stimulator of Interferon Genes with In Vivo Anti-Inflammatory Efficacy. J Med Chem. 2022 May 12;65(9):6593-6611. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | DMSO : ~100 mg/mL (~142.92 mM) |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Note: Listed below are some common formulations that may be used to formulate products with low water solubility (e.g. < 1 mg/mL), you may test these formulations using a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples. Injection Formulations (e.g. IP/IV/IM/SC) Injection Formulation 1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO stock solution → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline) *Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH ₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) Example: Take the Injection Formulation 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) as an example, if 1 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can take 100 μL 25 mg/mL DMSO stock solution and add to 900 μL corn oil, mix well to obtain a clear or suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Injection Formulation 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in saline = 10 : 90 [i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in saline)] *Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 5: 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin : Saline = 50 : 50 (i.e. 500 μL 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin → 500 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 6: DMSO : PEG300 : castor oil : Saline = 5 : 10 : 20 : 65 (i.e. 50 μL DMSO → 100 μLPEG300 → 200 μL castor oil → 650 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 7: Ethanol : Cremophor : Saline = 10: 10 : 80 (i.e. 100 μL Ethanol → 100 μL Cremophor → 800 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 8: Dissolve in Cremophor/Ethanol (50 : 50), then diluted by Saline Injection Formulation 9: EtOH : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 900 μL Corn oil) Injection Formulation 10: EtOH : PEG300:Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Oral Formulations Oral Formulation 1: Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na (carboxymethylcellulose sodium) Oral Formulation 2: Suspend in 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Example: Take the Oral Formulation 1 (Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na) as an example, if 100 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can first prepare 0.5% CMC Na solution by measuring 0.5 g CMC Na and dissolve it in 100 mL ddH2O to obtain a clear solution; then add 250 mg of the product to 100 mL 0.5% CMC Na solution, to make the suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Oral Formulation 3: Dissolved in PEG400 Oral Formulation 4: Suspend in 0.2% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 5: Dissolve in 0.25% Tween 80 and 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 6: Mixing with food powders Note: Please be aware that the above formulations are for reference only. InvivoChem strongly recommends customers to read literature methods/protocols carefully before determining which formulation you should use for in vivo studies, as different compounds have different solubility properties and have to be formulated differently. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.4292 mL | 7.1462 mL | 14.2925 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.2858 mL | 1.4292 mL | 2.8585 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1429 mL | 0.7146 mL | 1.4292 mL |