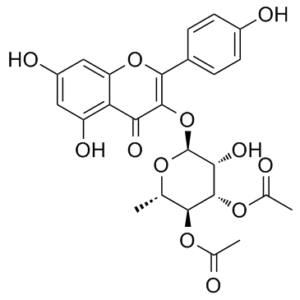
SL0101 (SL 0101-1) a kaempferol glycoside isolated from the tropical plant F. refracta, is a novel, potent, cell-permeable, selective, reversible, ATP-competitive p90 Ribosomal S6 Kinase (RSK) inhibitor, with an IC50 of 89 nM. It causes a cell cycle block in the G1 phase and inhibits proliferation in the human breast cancer cell line MCF-7. While maintaining RSK specificity, SL0101 demonstrated improved in vitro biological stability. The creation of RSK inhibitors derived from SL0101 as anticancer agents ought to be made easier as a result of these findings.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C25H24O12 |
| Molecular Weight | 516.45086 |
| Exact Mass | 516.126 |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 58.14; H, 4.68; O, 37.18 |
| CAS # | 77307-50-7 |
| Related CAS # | 77307-50-7 |
| PubChem CID | 10459196 |
| Appearance | White to yellow solid powder |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 753.0±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 128-132ºC |
| Flash Point | 255.6±26.4 °C |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.6 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.666 |
| LogP | 2.75 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 12 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 7 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 37 |
| Complexity | 909 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 5 |
| SMILES | OC1=CC(O)=C(C(C(O[C@@H]2O[C@@H](C)[C@H](OC(C)=O)[C@@H](OC(C)=O)[C@H]2O)=C(C3=CC=C(O)C=C3)O4)=O)C4=C1 |
| InChi Key | SXOZSDJHGMAEGZ-IGKKHSBFSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C25H24O12/c1-10-21(34-11(2)26)24(35-12(3)27)20(32)25(33-10)37-23-19(31)18-16(30)8-15(29)9-17(18)36-22(23)13-4-6-14(28)7-5-13/h4-10,20-21,24-25,28-30,32H,1-3H3/t10-,20+,21-,24-,25-/m0/s1 |
| Chemical Name | [(2S,3S,4S,5R,6S)-4-acetyloxy-6-[5,7-dihydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-4-oxochromen-3-yl]oxy-5-hydroxy-2-methyloxan-3-yl] acetate |
| Synonyms | SL0101; SL0101; SL 0101; SL 0101-1; CHEMBL240954; 5,7-Dihydroxy-2-(4-Hydroxyphenyl)-4-Oxo-4h-Chromen-3-Yl 3,4-Di-O-Acetyl-6-Deoxy-Alpha-L-Mannopyranoside; 3ubd; SL-0101-1; SL0101-1 |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | RSK1/Ribosomal S6 Kinase 1 |
| ln Vitro | SL 0101-1 (SL0101) shows inhibition of proliferation in the human breast cancer cell line MCF-7 and results in a block in the G1 phase of the cell cycle[1]. |
| Enzyme Assay |
RSK2 in vitro kinase assay [2] IC50 determination was performed as previously described1 . Briefly, a fusion protein consisting of glutathione Stransferase and the amino acid sequence RRRLASTNDKG (1 µg/well) was adsorbed to MaxiSorp-treated LumiNunc 96-well white polystyrene plates. The wells were blocked with 3% tryptone in phosphate-buffered saline. Kinase (0.3 nM) in kinase buffer (25 mM HEPES pH 7.4), 150 mM NaCl, 5 mM -glycerophosphate, 1.5 mM DTT, 30 mM MgCl2, 1% BSA) was added. Reactions were incubated with or without inhibitor. Reactions were initiated by the addition of ATP (10 uM) for 15 min, which is in the linear range of the assay. The reactions were terminated by addition of EDTA (500 mM, pH 8.0). The plates were washed and phosphorylation was measured using rabbit polyclonal anti- LApSTND1 and horseradish peroxidase (HRP)-conjugated donkey anti-rabbit antibodies. Western Lightning Enhanced Chemiluminescent Reagent Plus was used to measure HRP activity. To determine IC50 values, non-linear regression analysis was performed using GraphPad Prism version 6.0a. Further validation of inhibitor activity for RSK2 was determined using the LanthaScreen Eu kinase binding assay for according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Inhibitors were pre-incubated with purified kinase before addition of kinase tracer 236 for two h. Excitation fluorescence was 330 nm, background emission from Eu tag 620 nm and fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) emission 665 nm. Fluorescence was measured using a Synergy Neo. FRET was calculated as the ratio of emission at 665 divided by emission at 620. |
| Cell Assay |
p90 ribosomal S6 kinase (RSK) is an important downstream effector of mitogen-activated protein kinase, but its biological functions are not well understood. We have now identified the first small-molecule, RSK-specific inhibitor, which we isolated from the tropical plant Forsteronia refracta. We have named this novel inhibitor SL0101. SL0101 shows remarkable specificity for RSK. The major determinant of SL0101-binding specificity is the unique ATP-interacting sequence in the amino-terminal kinase domain of RSK. SL0101 inhibits proliferation of the human breast cancer cell line MCF-7, producing a cell cycle block in G(1) phase with an efficacy paralleling its ability to inhibit RSK in intact cells. RNA interference of RSK expression confirmed that RSK regulates MCF-7 proliferation. Interestingly, SL0101 does not alter proliferation of a normal human breast cell line MCF-10A, although SL0101 inhibits RSK in these cells. We show that RSK is overexpressed in approximately 50% of human breast cancer tissue samples, suggesting that regulation of RSK has been compromised. Thus, we show that RSK has an unexpected role in proliferation of transformed cells and may be a useful new target for chemotherapeutic agents. SL0101 will provide a powerful new tool to dissect the molecular functions of RSK in cancer cells[1].
Cell proliferation assay [2] The MCF-7 line was obtained and cultured as direct by ATCC. Stocks were authenticated based on growth rate, morphology, molecular markers and absence of mycoplasma. For proliferation assays 103 cells/well were plated in a 96-well. Inhibitor or vehicle was added, and luciferase measured at 42 h using CellTiterGlo reagent with a GLoMax Discover luminometer. |
| References |
[1]. Identification of the first specific inhibitor of p90 ribosomal S6 kinase (RSK) reveals an unexpected role for RSK in cancer cell proliferation. Cancer Res. 2005 Feb 1;65(3):1027-34. [2]. The Affinity of RSK for Cylitol Analogues of SL0101 Is Critically Dependent on the B-ring C-4'-hydroxy. Chem Commun (Camb). 2020 Mar 10;56(20):3058-3060. |
| Additional Infomation |
5,7-Dihydroxy-2-(4-Hydroxyphenyl)-4-Oxo-4h-Chromen-3-Yl 3,4-Di-O-Acetyl-6-Deoxy-Alpha-L-Mannopyranoside has been reported in Zingiber officinale, Zingiber spectabile, and Zingiber zerumbet with data available. Five cyclitol analogues of SL0101 with variable substitution at the C-4' position (i.e., OH, Cl, F, H, OMe) were synthesized. The series of analogues were evaluated for their ability to inhibit p90 ribosomal S6 kinase (RSK) activity. The study demonstrated the importance of the B-ring C-4' hydroxy group for RSK1/2 inhibition.[2] |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Note: Listed below are some common formulations that may be used to formulate products with low water solubility (e.g. < 1 mg/mL), you may test these formulations using a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples. Injection Formulations (e.g. IP/IV/IM/SC) Injection Formulation 1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO stock solution → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline) *Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH ₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) Example: Take the Injection Formulation 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) as an example, if 1 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can take 100 μL 25 mg/mL DMSO stock solution and add to 900 μL corn oil, mix well to obtain a clear or suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Injection Formulation 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in saline = 10 : 90 [i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in saline)] *Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 5: 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin : Saline = 50 : 50 (i.e. 500 μL 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin → 500 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 6: DMSO : PEG300 : castor oil : Saline = 5 : 10 : 20 : 65 (i.e. 50 μL DMSO → 100 μLPEG300 → 200 μL castor oil → 650 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 7: Ethanol : Cremophor : Saline = 10: 10 : 80 (i.e. 100 μL Ethanol → 100 μL Cremophor → 800 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 8: Dissolve in Cremophor/Ethanol (50 : 50), then diluted by Saline Injection Formulation 9: EtOH : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 900 μL Corn oil) Injection Formulation 10: EtOH : PEG300:Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Oral Formulations Oral Formulation 1: Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na (carboxymethylcellulose sodium) Oral Formulation 2: Suspend in 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Example: Take the Oral Formulation 1 (Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na) as an example, if 100 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can first prepare 0.5% CMC Na solution by measuring 0.5 g CMC Na and dissolve it in 100 mL ddH2O to obtain a clear solution; then add 250 mg of the product to 100 mL 0.5% CMC Na solution, to make the suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Oral Formulation 3: Dissolved in PEG400 Oral Formulation 4: Suspend in 0.2% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 5: Dissolve in 0.25% Tween 80 and 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 6: Mixing with food powders Note: Please be aware that the above formulations are for reference only. InvivoChem strongly recommends customers to read literature methods/protocols carefully before determining which formulation you should use for in vivo studies, as different compounds have different solubility properties and have to be formulated differently. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.9363 mL | 9.6815 mL | 19.3630 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3873 mL | 1.9363 mL | 3.8726 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1936 mL | 0.9681 mL | 1.9363 mL |