Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C34H35CL2N7O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 660.592805147171 |
| Exact Mass | 659.217 |
| CAS # | 2831230-38-5 |
| PubChem CID | 165412812 |
| Appearance | Typically exists as solid at room temperature |
| LogP | 4.6 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 5 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 8 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 10 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 46 |
| Complexity | 1010 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
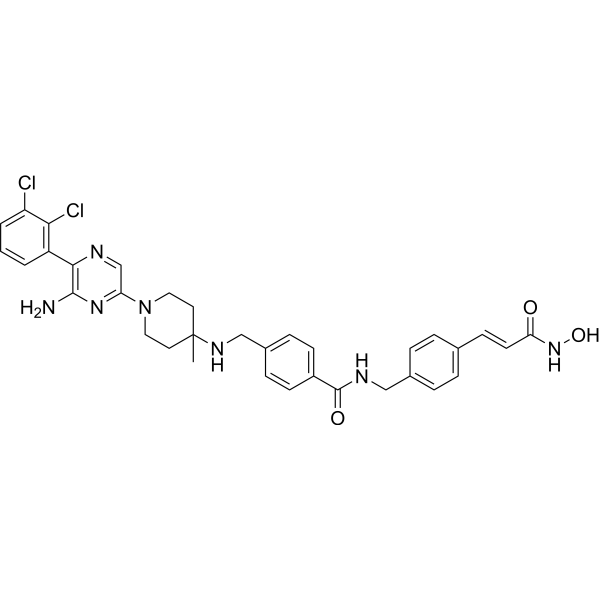
| SMILES | CC1(CCN(CC1)C2=CN=C(C(=N2)N)C3=C(C(=CC=C3)Cl)Cl)NCC4=CC=C(C=C4)C(=O)NCC5=CC=C(C=C5)/C=C/C(=O)NO |
| InChi Key | CJJLAWVMRURPRM-SDNWHVSQSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C34H35Cl2N7O3/c1-34(15-17-43(18-16-34)28-21-38-31(32(37)41-28)26-3-2-4-27(35)30(26)36)40-20-24-9-12-25(13-10-24)33(45)39-19-23-7-5-22(6-8-23)11-14-29(44)42-46/h2-14,21,40,46H,15-20H2,1H3,(H2,37,41)(H,39,45)(H,42,44)/b14-11+ |
| Chemical Name | 4-[[[1-[6-amino-5-(2,3-dichlorophenyl)pyrazin-2-yl]-4-methylpiperidin-4-yl]amino]methyl]-N-[[4-[(E)-3-(hydroxyamino)-3-oxoprop-1-enyl]phenyl]methyl]benzamide |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | HDAC1 25 nM (IC50) HDAC2 79 nM (IC50) HDAC3 233 nM (IC50) HDAC6 27 nM (IC50) SHP2 20.4 nM (IC50) |
| ln Vitro | Compound 8t (approximately 0-10 μM, 72 hours) of SHP2/HDAC-IN-1 suppresses the growth of BxPC-3, SW1990, AsPC-1, and MV4-11 cells[1]. In MV4-11 cells, SHP2/HDAC-IN-1 (0.25 -1 μM, 24 h) increases the acetylation of histone H3 and α-tubulin[1]. In the G1 phase of MV4-11 cells, SHP2/HDAC-IN-1 (0.25 μM, 24 h) inhibits cell cycle progression[1]. SHP2/HDAC-IN-1 (0.25 and 0.5 μM, 24 h) activates caspase-3 and reduces the potential of the mitochondrial membrane[1]. Good stability is demonstrated by SHP2/HDAC-IN-1 (2 h) in mouse liver microsomes[1]. |
| ln Vivo | In MV4-11 and 4T1 tumor-bearing xenograft mice, SHP2/HDAC-IN-1 (compound 8t, 40 mg/kg, po) reduces tumor growth[1]. Rats with good maximal plasma concentrations of SHP2/HDAC-IN-1 (20 mg/kg po, 1 mg/kg iv) are used[1]. |
| Cell Assay |
Cell Proliferation Assay[1] Cell Types: Pancreatic carcinoma (BxPC -3, SW1990, and AsPC-1), acute monocytic leukemia (MV4-11) Tested Concentrations: 0-10 μM approximately Incubation Duration: 72 h Experimental Results: Inhibited cell proliferation with IC50s range of 0.07 μM-3.92 μM. Western Blot Analysis[1] Cell Types: MV4-11 cells Tested Concentrations: 0.25, 0.5, 1 μM Incubation Duration: 24 h Experimental Results: Increased the acetylation of α-tubulin and histone H3. Inhibited the phosphorylation level of ERK. |
| Animal Protocol |
Animal/Disease Models: MV4-11 tumor-bearing xenograft mice[1] Doses: 40 mg/kg Route of Administration: Oral adminstration (po), every day for 20 days. Experimental Results: Delayed tumor progression with a tumor growth inhibition rate (TGI %) value of 64.0%, with no obvious signs of toxicity. Animal/Disease Models: 4T1 murine breast cancer model[1] Doses: 40 mg/kg Route of Administration: Oral adminstration (po), every day for 12 days. Experimental Results: Dramatically diminished tumor burden with a TGI value of 72%. Increased the proportions of CD4+ T cells and CD8+ T cells in the spleen. Enhanced the proportion of mDCs in lymph nodes. Animal/Disease Models: Male SD (Sprague-Dawley) rats (pharmacokinetic/PK assay)[1] Doses: 20 mg/kg po, 1 mg/kg iv Route of Administration: Oral adminstration (po) or intravenous (iv)injection Experimental Results: pharmacokinetic/PK profile of SHP2/HDAC-IN-1 (compound 8t). dose (mg/kg) T1/2 (h) Cmax (ng/mL) Cl (mL/h /kg) F (%) 20 (po) 5.32 1835 21.42 1 (iv) 6.15 3517 326 |
| References |
[1]. Discovery of Novel Src Homology-2 Domain-Containing Phosphatase 2 and Histone Deacetylase Dual Inhibitors with Potent Antitumor Efficacy and Enhanced Antitumor Immunity. J Med Chem. 2022 Sep 22;65(18):12200-12218. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Note: Listed below are some common formulations that may be used to formulate products with low water solubility (e.g. < 1 mg/mL), you may test these formulations using a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples. Injection Formulations (e.g. IP/IV/IM/SC) Injection Formulation 1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO stock solution → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline) *Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH ₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) Example: Take the Injection Formulation 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) as an example, if 1 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can take 100 μL 25 mg/mL DMSO stock solution and add to 900 μL corn oil, mix well to obtain a clear or suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Injection Formulation 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in saline = 10 : 90 [i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in saline)] *Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 5: 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin : Saline = 50 : 50 (i.e. 500 μL 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin → 500 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 6: DMSO : PEG300 : castor oil : Saline = 5 : 10 : 20 : 65 (i.e. 50 μL DMSO → 100 μLPEG300 → 200 μL castor oil → 650 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 7: Ethanol : Cremophor : Saline = 10: 10 : 80 (i.e. 100 μL Ethanol → 100 μL Cremophor → 800 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 8: Dissolve in Cremophor/Ethanol (50 : 50), then diluted by Saline Injection Formulation 9: EtOH : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 900 μL Corn oil) Injection Formulation 10: EtOH : PEG300:Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Oral Formulations Oral Formulation 1: Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na (carboxymethylcellulose sodium) Oral Formulation 2: Suspend in 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Example: Take the Oral Formulation 1 (Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na) as an example, if 100 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can first prepare 0.5% CMC Na solution by measuring 0.5 g CMC Na and dissolve it in 100 mL ddH2O to obtain a clear solution; then add 250 mg of the product to 100 mL 0.5% CMC Na solution, to make the suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Oral Formulation 3: Dissolved in PEG400 Oral Formulation 4: Suspend in 0.2% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 5: Dissolve in 0.25% Tween 80 and 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 6: Mixing with food powders Note: Please be aware that the above formulations are for reference only. InvivoChem strongly recommends customers to read literature methods/protocols carefully before determining which formulation you should use for in vivo studies, as different compounds have different solubility properties and have to be formulated differently. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.5138 mL | 7.5690 mL | 15.1380 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3028 mL | 1.5138 mL | 3.0276 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1514 mL | 0.7569 mL | 1.5138 mL |