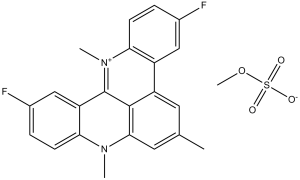
RHPS4 methosulfate (also known as NSC714187) is a potent inhibitor of telomerase with submicromolar activity. RHPS4 treatment of UXF1138L cells resulted in chromosome fusions, telomere-initiated DNA damage signaling, and the removal of the telomerase catalytic subunit (hTERT) from the nucleus. It was also reported that RHPS4 exhibited greater potency against cancer cells growing as colonies as opposed to monolayers.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C23H20F2N2O4S | |
| Molecular Weight | 458.48 | |
| Exact Mass | 458.11 | |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 60.25; H, 4.40; F, 8.29; N, 6.11; O, 13.96; S, 6.99 | |
| CAS # | 390362-78-4 | |
| Related CAS # |
|
|
| PubChem CID | 9804187 | |
| Appearance | Brown to reddish brown solid powder | |
| Melting Point | 256-258 ºC | |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 | |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 7 | |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 0 | |
| Heavy Atom Count | 32 | |
| Complexity | 633 | |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 | |
| SMILES | C1C(F)=CC=C2N(C)C3=CC(C)=CC4=C5C=C(F)C=CC5=[N+](C)C(=C34)C=12.S(=O)([O-])(=O)OC |
|
| InChi Key | VRWGYMXWYZBBGF-UHFFFAOYSA-M | |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C22H17F2N2.CH4O4S/c1-12-8-16-15-10-13(23)4-6-18(15)26(3)22-17-11-14(24)5-7-19(17)25(2)20(9-12)21(16)22;1-5-6(2,3)4/h4-11H,1-3H3;1H3,(H,2,3,4)/q+1;/p-1 | |
| Chemical Name | 4,16-difluoro-8,11,20-trimethyl-8-aza-20-azoniapentacyclo[11.7.1.02,7.09,21.014,19]henicosa-1(20),2(7),3,5,9,11,13(21),14(19),15,17-decaene;methyl sulfate | |
| Synonyms |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 | |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month Note: Please store this product in a sealed and protected environment, avoid exposure to moisture. |
|
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | telomerase in the TRAP assay ( IC50 = 0.33 μM ) | ||
| ln Vitro |
|
||
| ln Vivo |
|
||
| Cell Assay | Twenty-four hours after plating, RHPS4 is added to the cells at different times and at a concentration of 1 μM. Every experiment counts the number of cells and determines their viability (trypan blue dye exclusion). For 24 hours, caffeine at a dose of 10 mM—which has no harmful effects on cell viability—is added to the medium. For thirty minutes, bleomycin is used at a concentration of 30 mM. | ||
| Animal Protocol |
|
||
| References |
[1]. Br J Cancer . 2007 Apr 23;96(8):1223-33. [2]. J Clin Invest . 2007 Nov;117(11):3236-47. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
|
|||
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Note: Listed below are some common formulations that may be used to formulate products with low water solubility (e.g. < 1 mg/mL), you may test these formulations using a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples. Injection Formulations (e.g. IP/IV/IM/SC) Injection Formulation 1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO stock solution → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline) *Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH ₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) Example: Take the Injection Formulation 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) as an example, if 1 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can take 100 μL 25 mg/mL DMSO stock solution and add to 900 μL corn oil, mix well to obtain a clear or suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Injection Formulation 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in saline = 10 : 90 [i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in saline)] *Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 5: 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin : Saline = 50 : 50 (i.e. 500 μL 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin → 500 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 6: DMSO : PEG300 : castor oil : Saline = 5 : 10 : 20 : 65 (i.e. 50 μL DMSO → 100 μLPEG300 → 200 μL castor oil → 650 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 7: Ethanol : Cremophor : Saline = 10: 10 : 80 (i.e. 100 μL Ethanol → 100 μL Cremophor → 800 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 8: Dissolve in Cremophor/Ethanol (50 : 50), then diluted by Saline Injection Formulation 9: EtOH : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 900 μL Corn oil) Injection Formulation 10: EtOH : PEG300:Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Oral Formulations Oral Formulation 1: Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na (carboxymethylcellulose sodium) Oral Formulation 2: Suspend in 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Example: Take the Oral Formulation 1 (Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na) as an example, if 100 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can first prepare 0.5% CMC Na solution by measuring 0.5 g CMC Na and dissolve it in 100 mL ddH2O to obtain a clear solution; then add 250 mg of the product to 100 mL 0.5% CMC Na solution, to make the suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Oral Formulation 3: Dissolved in PEG400 Oral Formulation 4: Suspend in 0.2% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 5: Dissolve in 0.25% Tween 80 and 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 6: Mixing with food powders Note: Please be aware that the above formulations are for reference only. InvivoChem strongly recommends customers to read literature methods/protocols carefully before determining which formulation you should use for in vivo studies, as different compounds have different solubility properties and have to be formulated differently. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.1811 mL | 10.9056 mL | 21.8112 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4362 mL | 2.1811 mL | 4.3622 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2181 mL | 1.0906 mL | 2.1811 mL |