Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C21H28O5 |
| Molecular Weight | 360.444026947021 |
| Exact Mass | 360.193 |
| CAS # | 1011528-58-7 |
| PubChem CID | 24854205 |
| Appearance | Typically exists as solid at room temperature |
| LogP | 3.2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 5 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 2 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 26 |
| Complexity | 593 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 7 |
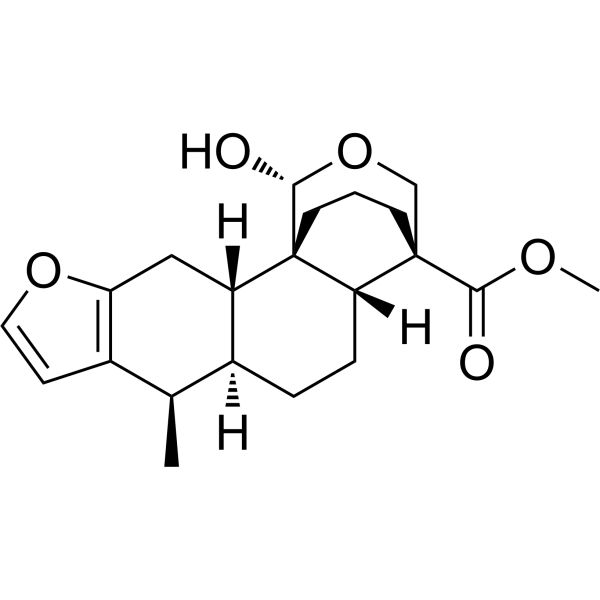
| SMILES | C[C@@H]1[C@@H]2CC[C@H]3[C@@]4(CCC[C@@]3([C@H]2CC5=C1C=CO5)[C@@H](OC4)O)C(=O)OC |
| InChi Key | FBOCRPKLWNKMFW-YCBSRJOKSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C21H28O5/c1-12-13-4-5-17-20(18(22)24-2)7-3-8-21(17,19(23)26-11-20)15(13)10-16-14(12)6-9-25-16/h6,9,12-13,15,17,19,23H,3-5,7-8,10-11H2,1-2H3/t12-,13+,15+,17+,19-,20+,21+/m1/s1 |
| Chemical Name | methyl (1S,2S,9R,10S,13R,14R,17R)-17-hydroxy-9-methyl-5,16-dioxapentacyclo[12.3.3.01,13.02,10.04,8]icosa-4(8),6-diene-14-carboxylate |
| Synonyms | Phanginin A; 1011528-58-7; orb1744452; HY-N9539; EX-A12305; CS-0198836; methyl (1S,2S,9R,10S,13R,14R,17R)-17-hydroxy-9-methyl-5,16-dioxapentacyclo[12.3.3.01,13.02,10.04,8]icosa-4(8),6-diene-14-carboxylate |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets |
- Salt-inducible kinase 1 (SIK1) [1] - Phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE4) [1] |
| ln Vitro |
Phanginin A deters gluconeogenesis in primary mouse hepatocytes in a dose-dependent manner at 2.5, 5, and 10 µM [1]. Phanginin A (5, 10 µM) decreases intracellular cAMP buildup and the mRNA expression of G6P and PEPCK [1]. In primary mouse hepatocytes, Phanginin A (5, 10 µM; 0-120 min) decreases the expression of CREB phosphorylation in a time- and dose-dependent way [1]. In primary murine hepatocytes, Phanginin A (2.5, 5, 10 µM; 0-120 min) enhances p-SIK1 expression in a dose- and time-dependent manner [1]. PDE4 activity is increased by phanginin A (5, 10 µM) [1].
- Primary mouse hepatocytes: Treatment with Phanginin A (concentration not specified) significantly increased SIK1 phosphorylation through LKB1 activation, leading to suppression of gluconeogenic genes (e.g., PEPCK and G6PC) and reduced glucose production. This effect was blocked by pan-SIK inhibitor HG-9-91-01 or siRNA-mediated SIK1 knockdown [1] - PDE4 activity: Phanginin A enhanced PDE4 activity, resulting in decreased intracellular cAMP levels and subsequent inhibition of the cAMP/PKA/CREB pathway in hepatocytes [1] - SIK1 overexpression: Overexpression of SIK1 in hepatocytes mimicked the effects of Phanginin A, increasing PDE4 activity, reducing cAMP accumulation, and inhibiting gluconeogenesis [1] |
| ln Vivo |
In type 2 diabetes ob/ob mice, phanginin A (100 mg/kg; po; once) shows antigluconone action[1]. For 26 days, ob/ob mice treated with phanginin A (100 mg/kg; po; once daily) show improvements in metabolic abnormalities[1].
- ob/ob mice: Oral administration of Phanginin A (100 mg/kg) for 26 days significantly reduced random and fasting blood glucose levels by 29% and 32%, respectively, comparable to metformin (250 mg/kg). Glucose tolerance and dyslipidemia were also improved [1] - Acute treatment: Single-dose Phanginin A (100 mg/kg, oral) reduced hepatic gluconeogenesis in vivo, accompanied by increased SIK1 phosphorylation and PDE4 activity in the liver [1] |
| Enzyme Assay |
PDE4 activity assay: PDE4 activity was measured using cAMP as a substrate. Recombinant PDE4 enzyme was incubated with Phanginin A and cAMP under specific conditions, and the hydrolysis of cAMP was quantified to determine PDE4 activity [1] |
| Cell Assay |
RT-PCR[1] Cell Types: Primary mouse hepatocytes Tested Concentrations: 5, 10 µM Incubation Duration: Experimental Results: Dramatically diminished PEPCK mRNA expression by 25% and 43% under basal conditions and 45% and 67% under forskolin-stimulated conditions, The G6P mRNA expression was also Dramatically decreased, with 5 and 10 μM of phanginin A resulting in a decrease of 30% and 46% under basal conditions and 38% and 57% under forskolin-stimulated conditions, respectively. Western Blot Analysis[1] Cell Types: Primary mouse hepatocytes Tested Concentrations: 0-120 min Incubation Duration: Experimental Results: Inhibited CREB phosphorylation in a time and dose-dependent manner. Primary mouse hepatocytes: Hepatocytes were isolated and treated with Phanginin A. Glucose production was measured using a glucose assay kit. SIK1 phosphorylation and cAMP levels were detected by Western blot and ELISA, respectively. Gene expression of gluconeogenic enzymes was analyzed by qPCR [1] |
| Animal Protocol |
Animal/Disease Models: Type 2 diabetic ob/ob mice[1] Doses: 100 mg/kg Route of Administration: Po; once Experimental Results: Dramatically decreased the blood glucose, increased the phosphorylation of SIK1 in the liver by 119%, PDE4 activity in the liver was elevated by 74%, diminished in the cAMP concentration along with a 46% decrease in the CREB phosphorylation level in the liver, diminished the mRNA levels of PEPCK and G6P. Animal/Disease Models: Male ob/ob mice[1] Doses: 100 mg/ kg Route of Administration: Po; one time/day for 26 days Experimental Results: demonstrated an average reduction rate of 29% and 32% in random and fast blood glucose, demonstrated a marked improvement in glucose tolerance, Dramatically decreased by 20% in HbA1c level, demonstrated no effect on food intake and body weight. ob/ob mice: Phanginin A was dissolved in DMSO/PBS and administered orally at 100 mg/kg daily for 26 days. Blood glucose levels were monitored weekly, and glucose tolerance tests were performed after 23 days of treatment [1] |
| References | [1]. Activation of SIK1 by phanginin A inhibits hepatic gluconeogenesis by increasing PDE4 activity and suppressing the cAMP signaling pathway. Mol Metab. 2020 Nov;41:101045. |
| Additional Infomation |
- Mechanism: Phanginin A activates SIK1, which phosphorylates and activates PDE4, leading to cAMP degradation. Reduced cAMP levels inhibit the PKA/CREB pathway, thereby suppressing hepatic gluconeogenesis [1] - Therapeutic potential: Phanginin A shows promise as a lead compound for treating type 2 diabetes due to its ability to improve glucose homeostasis and lipid metabolism [1] methyl (1S,2S,9R,10S,13R,14R,17R)-17-hydroxy-9-methyl-5,16-dioxapentacyclo[12.3.3.01,13.02,10.04,8]icosa-4(8),6-diene-14-carboxylate has been reported in Biancaea sappan with data available. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Note: Listed below are some common formulations that may be used to formulate products with low water solubility (e.g. < 1 mg/mL), you may test these formulations using a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples. Injection Formulations (e.g. IP/IV/IM/SC) Injection Formulation 1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO stock solution → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline) *Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH ₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) Example: Take the Injection Formulation 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) as an example, if 1 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can take 100 μL 25 mg/mL DMSO stock solution and add to 900 μL corn oil, mix well to obtain a clear or suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Injection Formulation 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in saline = 10 : 90 [i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in saline)] *Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 5: 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin : Saline = 50 : 50 (i.e. 500 μL 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin → 500 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 6: DMSO : PEG300 : castor oil : Saline = 5 : 10 : 20 : 65 (i.e. 50 μL DMSO → 100 μLPEG300 → 200 μL castor oil → 650 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 7: Ethanol : Cremophor : Saline = 10: 10 : 80 (i.e. 100 μL Ethanol → 100 μL Cremophor → 800 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 8: Dissolve in Cremophor/Ethanol (50 : 50), then diluted by Saline Injection Formulation 9: EtOH : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 900 μL Corn oil) Injection Formulation 10: EtOH : PEG300:Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Oral Formulations Oral Formulation 1: Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na (carboxymethylcellulose sodium) Oral Formulation 2: Suspend in 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Example: Take the Oral Formulation 1 (Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na) as an example, if 100 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can first prepare 0.5% CMC Na solution by measuring 0.5 g CMC Na and dissolve it in 100 mL ddH2O to obtain a clear solution; then add 250 mg of the product to 100 mL 0.5% CMC Na solution, to make the suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Oral Formulation 3: Dissolved in PEG400 Oral Formulation 4: Suspend in 0.2% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 5: Dissolve in 0.25% Tween 80 and 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 6: Mixing with food powders Note: Please be aware that the above formulations are for reference only. InvivoChem strongly recommends customers to read literature methods/protocols carefully before determining which formulation you should use for in vivo studies, as different compounds have different solubility properties and have to be formulated differently. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.7744 mL | 13.8719 mL | 27.7439 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5549 mL | 2.7744 mL | 5.5488 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2774 mL | 1.3872 mL | 2.7744 mL |