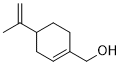
Perillyl alcohol (POH) is a natural monocyclic terpene found in lavender with anti-cancer activity. Acts by preventing the farnesylation of Ras, stimulating the mannose-6-phosphate receptor, and inducing apoptosis.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C10H16O |
| Molecular Weight | 152.237 |
| Exact Mass | 152.12 |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 78.90; H, 10.59; O, 10.51 |
| CAS # | 18457-55-1 |
| Related CAS # | Perillyl alcohol;536-59-4 |
| PubChem CID | 369312 |
| Appearance | Colorless to Pale Yellow liquid |
| Density | 0.9±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 241.2±19.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Flash Point | 99.6±17.8 °C |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.1 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.491 |
| LogP | 3.3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 1 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 2 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 11 |
| Complexity | 179 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
| SMILES | C=C(C)[C@@H]1CC=C(CC1)CO |
| InChi Key | NDTYTMIUWGWIMO-SNVBAGLBSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C10H16O/c1-8(2)10-5-3-9(7-11)4-6-10/h3,10-11H,1,4-7H2,2H3/t10-/m1/s1 |
| Chemical Name | [(4S)-4-prop-1-en-2-ylcyclohexen-1-yl]methanol |
| Synonyms | Perillyl alcohol; perillic alcohol; Perilla alcohol; POH; perillol; Perycorolle |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month Note: Please store this product in a sealed and protected environment (e.g. under nitrogen), avoid exposure to moisture. |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| ln Vitro | Perillyl alcohol inhibits the isoprenylation of small G proteins (21-26 kDa) involved in signal transduction, induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis, and affects differential gene regulation in vitro[1]. In all of the cell lines examined (KPL-1, MCF-7, MKL-F, and MDA-MB-231) perillyl alcohol (POH) inhibits cell proliferation in a dose-dependent manner. POH has a cytostatic effect at a dose of 500 M, wherein growth inhibition is caused by an accumulation of cells in G1 phase. G1 cyclin levels (cyclin D1 and E) drop prior to cell cycle progression, which is then followed by an increase in p21Cip1/Waf1 and a decrease in proliferating cell nuclear antigen levels[2]. |
| ln Vivo | In a nude mouse system, orthotopically transplanted KPL-1 tumor cell growth and regional lymph node metastasis are suppressed by perillyl alcohol (POH) at a dose of 75mg/kg given intraperitoneally three times a week for the entire 6-week experimental period. POH suppresses growth and metastasis in vivo and inhibits the growth of ER-positive and ER-negative human breast cancer cells in vitro[2]. |
| Cell Assay | Colony formation assay is used to gauge the toxicity of the compounds on treated cells. 6-well plates are used for cell plating (200 cells/well). Cells are exposed to perillyl alcohol (POH) or perillaldehyde (PALD) for 12 or 24 hours after the culture medium is replaced with medium containing varying concentrations of the chemicals. The cells are then washed twice with sterile PBS and once with the proper medium after the treatment medium has been removed and the cells have been exposed. The cells are incubated for a further 12–14 days at 37 °C with the addition of fresh medium to each well. Every other day, microscope views of plates are performed. The culture medium is removed from the cells at the end, and PBS is then rinsed through them. Following the fixation and crystal violet staining step, the dye is gently rinsed off the cells for 5 minutes. In order to count colonies, they must have at least 50 cells. |
| ADME/Pharmacokinetics |
Metabolism / Metabolites Perillyl alcohol is a known human metabolite of (-)-limonene. |
| References |
[1]. Life Sci . 2003 Oct 17;73(22):2831-40. [2]. Breast Cancer Res Treat . 2004 Apr;84(3):251-60. |
| Additional Infomation |
(S)-(-)-perillyl alcohol is a perillyl alcohol in which the chiral centre has S configuration. It is an enantiomer of a (R)-(+)-perillyl alcohol. (-)-Perillyl alcohol has been reported in Perilla frutescens, Citrus iyo, and other organisms with data available. See also: Paeonia lactiflora root (part of). |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | DMSO: ≥250 mg/mL (~1642.3 mM) |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (13.66 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 20.8 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (13.66 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 20.8 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (13.66 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 20.8 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 6.5686 mL | 32.8429 mL | 65.6858 mL | |
| 5 mM | 1.3137 mL | 6.5686 mL | 13.1372 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.6569 mL | 3.2843 mL | 6.5686 mL |