Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C17H17CLN4O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 376.79 |
| Exact Mass | 376.09383 |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 54.19; H, 4.55; Cl, 9.41; N, 14.87; O, 16.98 |
| CAS # | 1989620-03-2 |
| PubChem CID | 122497020 |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid powder |
| Density | 1.73±0.1 g/cm3(Temp: 20 °C; Press: 760 Torr)(Predicted) |
| Boiling Point | 713.3±60.0 °C(Predicted) |
| LogP | 0.8 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 7 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 3 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 26 |
| Complexity | 495 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 5 |
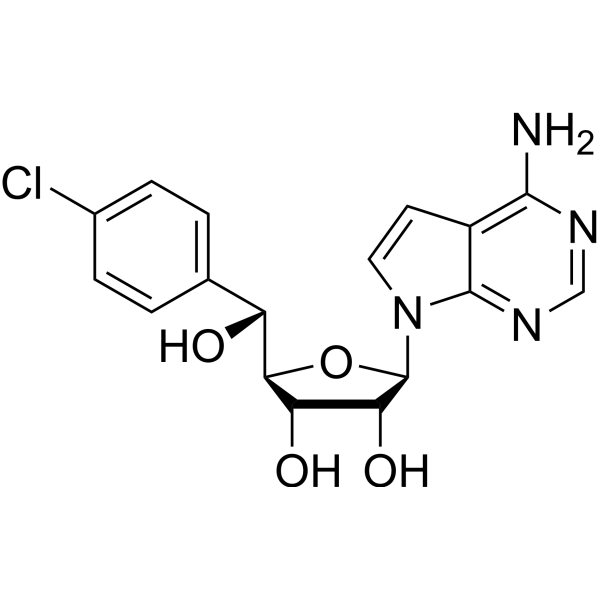
| SMILES | O[C@@H]1[C@@H]([C@@]([H])([C@@H](C2C=CC(Cl)=CC=2)O)O[C@H]1N1C=CC2=C(N=CN=C12)N)O |
| InChi Key | ITEKIFMGFZAFPM-QFRSUPTLSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C17H17ClN4O4/c18-9-3-1-8(2-4-9)11(23)14-12(24)13(25)17(26-14)22-6-5-10-15(19)20-7-21-16(10)22/h1-7,11-14,17,23-25H,(H2,19,20,21)/t11-,12+,13-,14-,17-/m1/s1 |
| Chemical Name | (2R,3R,4S,5R)-2-(4-aminopyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidin-7-yl)-5-[(R)-(4-chlorophenyl)-hydroxymethyl]oxolane-3,4-diol |
| Synonyms | PRT543; CHEMBL4585781; SCHEMBL18026293; SCHEMBL22508993; PRT-543; BDBM415556; |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | PRMT5 (IC50 = 1 nM) |
| ln Vitro | PRT543 is a potent, selective, oral PRMT5 inhibitor with robust preclinical efficacy. As an orally available small molecule inhibitor of protein arginine methyltransferase 5 (PRMT5), PRT543 shows potent antiproliferative and antineoplastic activities. Although the exact mechanism of action has not been completely determined, it is reported that PRMT5 inhibitor PRT543 selectively binds to the substrate recognition site of PRMT5 and inhibits its methyltransferase activity. This decreases the levels of both monomethylated and dimethylated arginine residues in histones H2A, H3 and H4 and modulates the expression of genes involved in several cellular processes, including cellular proliferation. As a result, PRT543 may increase the expression of antiproliferative genes and/or decrease the expression of genes that promote cell proliferation, which may lead to decreased growth of rapidly proliferating cells, including cancer cells. PRTM5, an arginine methyltransferase that catalyzes the formation of both omega-N monomethylarginine (MMA) and symmetric dimethylarginine (sDMA) on histones and a variety of other protein substrates, is overexpressed in several neoplasms[2]. |
| ln Vivo | As of 18 June 2021, 49 unselected pts with measurable disease refractory to established therapies had enrolled (17 pts BIW, 11 pts 5x/week [wk], 21 pts QD). Median number of prior lines of systemic therapies was 3. Six of 21 pts dosed at 25-50 mg QD experienced dose limiting toxicity (DLT) of thrombocytopenia, and 1 pt of 6 dosed at 45 mg 5x/wk had DLT of fatigue. The 45 mg 5x/wk regimen was selected as the expansion dose. Increased intron retention was seen in peripheral blood mononuclear cells. A complete response (CR) has been maintained for >1 yr in a pt with homologous recombination deficiency-positive (HRD+) ovarian cancer who remains on study therapy. An additional 5 pts exhibited stable disease ≥6 mo. Dose-dependent inhibition of target engagement and functional activity of PRMT5 were observed. PRT543 demonstrated encouraging clinical activity with a CR in HRD+ ovarian cancer and prolonged stable disease in multiple pts. An expansion phase in biomarker-selected solid tumor cohorts is ongoing [1]. |
| Animal Protocol | This study assesses safety, pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and preliminary tumor response (REClST v1.1) of PRT543 administered at varying schedules beginning with twice weekly (BIW) and increasing to once daily (QD) with doses ranging from 5-50 mg in 28-day cycles. Dose escalation followed a 3+3 design. Serum symmetric dimethylarginine (sDMA) and intron retention, a marker of PRMT5-mediated mRNA splicing fidelity, were assessed as measures of PRMT5 target engagement and function, respectively.[1] |
| ADME/Pharmacokinetics | PRT543 demonstrated dose-dependent increases of Cmax (nM) and AUC (nM.hr). At the expansion dose, T½ was 15 hrs, and plasma drug exposures (Cmax, 2142 nM; AUC, 26,293 nM.hr) exceeded those for preclinical efficacy models. Serum sDMA decreased in a dose-dependent manner reaching 77% reduction with 50 mg QD and 69% reduction with the expansion dose.[1] |
| Toxicity/Toxicokinetics | PRT543 was well tolerated with a favorable safety profile. Most frequent treatment-related adverse events (TRAEs), any grade, in all regimens were fatigue (n=20, 41%), nausea (n=14, 29%), thrombocytopenia (n=13, 27%), and anemia (n=12, 24%). Grade ≥3 TRAEs in all regimens occurring in ≥5 pts included thrombocytopenia (n=10, 20%) and anemia (n=6, 12%). Cytopenias were reversible and managed with dose modifications. 44 pts discontinued treatment, mainly due to disease progression, with 2 due to AEs (Grade 3 thrombocytopenia and Grade 4 cholangitis).[1] |
| References |
[1]. Abstract P039: A phase 1 dose escalation study of protein arginine methyltransferase 5 (PRMT5) inhibitor PRT543 in patients with advanced solid tumors and lymphMol Cancer Ther (2021) 20 (12_Supplement): P039. https://doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.TARG-21-P039 [2]. protein arginine methyltransferase 5 inhibitor PRT543. https://www.cancer.gov/publications/dictionaries/cancer-drug/def/protein-arginine-methyltransferase-5-inhibitor-prt543 [3]. US20160244475. |
| Additional Infomation | PRMT5 catalyzes symmetric arginine dimethylation of protein substrates with important roles in cancer cell growth/survival. PRT543 is a potent, selective, oral PRMT5 inhibitor with robust preclinical efficacy (Bhagwat AACR 2020). An open-label Phase I study of PRT543 in unselected patients (pts) with advanced solid tumors and hematologic malignancies (NCT03886831) is ongoing. Dose escalation results from pts with solid tumors and lymphoma are presented herein. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Note: Listed below are some common formulations that may be used to formulate products with low water solubility (e.g. < 1 mg/mL), you may test these formulations using a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples. Injection Formulations (e.g. IP/IV/IM/SC) Injection Formulation 1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO stock solution → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline) *Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH ₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) Example: Take the Injection Formulation 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) as an example, if 1 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can take 100 μL 25 mg/mL DMSO stock solution and add to 900 μL corn oil, mix well to obtain a clear or suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Injection Formulation 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in saline = 10 : 90 [i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in saline)] *Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 5: 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin : Saline = 50 : 50 (i.e. 500 μL 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin → 500 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 6: DMSO : PEG300 : castor oil : Saline = 5 : 10 : 20 : 65 (i.e. 50 μL DMSO → 100 μLPEG300 → 200 μL castor oil → 650 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 7: Ethanol : Cremophor : Saline = 10: 10 : 80 (i.e. 100 μL Ethanol → 100 μL Cremophor → 800 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 8: Dissolve in Cremophor/Ethanol (50 : 50), then diluted by Saline Injection Formulation 9: EtOH : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 900 μL Corn oil) Injection Formulation 10: EtOH : PEG300:Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Oral Formulations Oral Formulation 1: Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na (carboxymethylcellulose sodium) Oral Formulation 2: Suspend in 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Example: Take the Oral Formulation 1 (Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na) as an example, if 100 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can first prepare 0.5% CMC Na solution by measuring 0.5 g CMC Na and dissolve it in 100 mL ddH2O to obtain a clear solution; then add 250 mg of the product to 100 mL 0.5% CMC Na solution, to make the suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Oral Formulation 3: Dissolved in PEG400 Oral Formulation 4: Suspend in 0.2% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 5: Dissolve in 0.25% Tween 80 and 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 6: Mixing with food powders Note: Please be aware that the above formulations are for reference only. InvivoChem strongly recommends customers to read literature methods/protocols carefully before determining which formulation you should use for in vivo studies, as different compounds have different solubility properties and have to be formulated differently. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.6540 mL | 13.2700 mL | 26.5400 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5308 mL | 2.6540 mL | 5.3080 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2654 mL | 1.3270 mL | 2.6540 mL |