PFI-2 (PFI2) is a novel, potent and selective inhibitor of lysine methyltransferase SETD7 [SET domain containing (lysine methyltransferase) 7] with anticancer activity. It inhibits SETD7 with a Ki (app) and IC50 of 0.33 nM and 2 nM, respectively, and shows >1000-fold selectivity for SETD7 over other methyltransferases and other non-epigenetic targets. In HEK293 cells, (R)-PFI-2 (10 µM) bound to and stabilized SETD7. In Setd7+/+ murine embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs), (R)-PFI-2 increased nuclear localization of Yes-associated protein (YAP) and the expression of YAP target genes Ctgf, Gli2 and Cdc20.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C23H25F4N3O3S | |
| Molecular Weight | 499.52 | |
| Exact Mass | 499.155 | |
| CAS # | 1627676-59-8 | |
| Related CAS # | PFI-2 hydrochloride;1627607-87-7 | |
| PubChem CID | 71300326 | |
| Appearance | Typically exists as solid at room temperature | |
| Density | 1.371±0.06 g/cm3 | |
| Boiling Point | 642.7±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Flash Point | 342.5±34.3 °C | |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.9 mmHg at 25°C | |
| Index of Refraction | 1.566 | |
| LogP | 3.55 | |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 | |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 9 | |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 6 | |
| Heavy Atom Count | 34 | |
| Complexity | 813 | |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 | |
| SMILES | O=S(C1=CC2=C(CNCC2)C(F)=C1)(N[C@H](CC3=CC=CC(C(F)(F)F)=C3)C(N4CCCC4)=O)=O |
|
| InChi Key | ZADKZNVAJGEFLC-ZMBIFBSDSA-N | |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C23H25F4N3O3S.ClH/c24-20-13-18(12-16-6-7-28-14-19(16)20)34(32,33)29-21(22(31)30-8-1-2-9-30)11-15-4-3-5-17(10-15)23(25,26)27;/h3-5,10,12-13,21,28-29H,1-2,6-9,11,14H2;1H/t21-;/m1./s1 | |
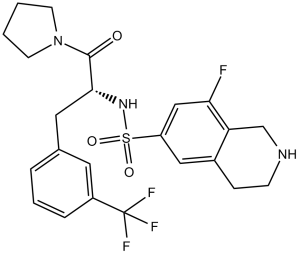
| Chemical Name | (R)-8-fluoro-N-(1-oxo-1-(pyrrolidin-1-yl)-3-(3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)propan-2-yl)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinoline-6-sulfonamide hydrochloride | |
| Synonyms |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 | |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| ln Vitro | (R)-PFI-2 demonstrates strong inhibitory action with an IC50 value of 2.0 nM, while (S)-PFI-2 exhibits inhibiting activity with a 1.0 μM IC50 value[1]. |
| ln Vivo | PFI-2 (ip, 200 μM, twice weekly) in FA nephropathy slows the advancement of renal fibrosis while maintaining renal function[2]. Following FA damage, PFI-2 (ip, 200 μM, twice weekly) decreased ECM buildup and fibroblast activation[2]. PFI-2 (ip, 200 μM, twice weekly) inhibited the activation of Th2 cytokine signaling and the polarization of M2 macrophages[2]. PFI-2 (ip, 200 μM, twice weekly) inhibited the formation of myeloid myofibroblasts and the transition between M2 macrophages and myofibroblasts in the kidneys treated with FA[2]. In obstructed kidneys, PFI-2 (ip, 200 μM, twice a week) reduced the M2 macrophages' polarization and the M2 macrophages' transition to myofibroblasts[2]. Following UUO damage, PFI-2 (ip, 200 μM, twice weekly) reduced the formation of myeloid myofibroblasts and renal fibrosis[2]. PFI-2 (ip, 200 μM, twice weekly) decreased inflammatory cell infiltration, inflammatory chemical synthesis, and activation of NF-κB in FA nephropathy. |
| Animal Protocol |
Animal/Disease Models: Male C57BL/6 mice (8-10 week old, 20-25 g)[2] Doses: 200 μM (PFI-2 is diluted in 100 μL 0.1% (v/ v) DMSO to a concentration of 200 μM/100 μL) Route of Administration: intraperitoneal (ip)injection, twice a week Experimental Results: Presented less bone marrow-derived myofibroblasts, fewer CD206+/α-smooth muscle actin + cells and developed less renal fibrosis (P<0.01 ). decreased the infiltration of inflammatory cells and diminished the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines in the kidneys after folic acid treatment (P<0.01). Suppressed the accumulation of NF-κB p65+ cells in folic acid nephropathy (P<0.01) . |
| References |
[1]. Revealing inhibition difference between PFI-2 enantiomers against SETD7 by molecular dynamics simulations, binding free energy calculations and unbinding pathway analysis. Sci Rep. 2017 Apr 18;7:46547. [2]. Pharmacological inhibition of SETD7 by PFI-2 attenuates renal fibrosis following folic acid and obstruction injury. Eur J Pharmacol. 2021 Jun 15;901:174097. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
|
|||
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Note: Listed below are some common formulations that may be used to formulate products with low water solubility (e.g. < 1 mg/mL), you may test these formulations using a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples. Injection Formulations (e.g. IP/IV/IM/SC) Injection Formulation 1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO stock solution → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline) *Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH ₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) Example: Take the Injection Formulation 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) as an example, if 1 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can take 100 μL 25 mg/mL DMSO stock solution and add to 900 μL corn oil, mix well to obtain a clear or suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Injection Formulation 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in saline = 10 : 90 [i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in saline)] *Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 5: 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin : Saline = 50 : 50 (i.e. 500 μL 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin → 500 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 6: DMSO : PEG300 : castor oil : Saline = 5 : 10 : 20 : 65 (i.e. 50 μL DMSO → 100 μLPEG300 → 200 μL castor oil → 650 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 7: Ethanol : Cremophor : Saline = 10: 10 : 80 (i.e. 100 μL Ethanol → 100 μL Cremophor → 800 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 8: Dissolve in Cremophor/Ethanol (50 : 50), then diluted by Saline Injection Formulation 9: EtOH : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 900 μL Corn oil) Injection Formulation 10: EtOH : PEG300:Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Oral Formulations Oral Formulation 1: Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na (carboxymethylcellulose sodium) Oral Formulation 2: Suspend in 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Example: Take the Oral Formulation 1 (Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na) as an example, if 100 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can first prepare 0.5% CMC Na solution by measuring 0.5 g CMC Na and dissolve it in 100 mL ddH2O to obtain a clear solution; then add 250 mg of the product to 100 mL 0.5% CMC Na solution, to make the suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Oral Formulation 3: Dissolved in PEG400 Oral Formulation 4: Suspend in 0.2% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 5: Dissolve in 0.25% Tween 80 and 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 6: Mixing with food powders Note: Please be aware that the above formulations are for reference only. InvivoChem strongly recommends customers to read literature methods/protocols carefully before determining which formulation you should use for in vivo studies, as different compounds have different solubility properties and have to be formulated differently. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.0019 mL | 10.0096 mL | 20.0192 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4004 mL | 2.0019 mL | 4.0038 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2002 mL | 1.0010 mL | 2.0019 mL |