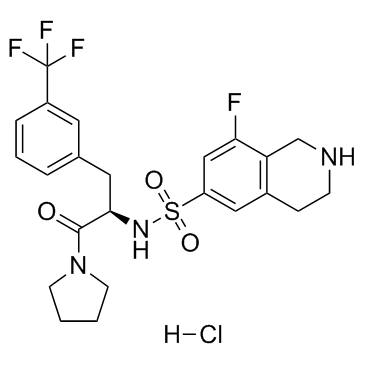
PFI-2 HCl, the hydrochloride salt of PFI-2, is a selective, and cell-active lysine methyltransferase SETD7 inhibitor with potential antitumor activity. It inhibits SETD7 with Ki (app) and IC50 of 0.33 nM and 2 nM, 1000-fold selectivity over other methyltransferases and other non-epigenetic targets. In HEK293 cells, (R)-PFI-2 (10 µM) bound to and stabilized SETD7. In Setd7+/+ murine embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs), (R)-PFI-2 increased nuclear localization of Yes-associated protein (YAP) and the expression of YAP target genes Ctgf, Gli2 and Cdc20.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C23H25F4N3O3S.HCL | |
| Molecular Weight | 535.98 | |
| Exact Mass | 535.131 | |
| CAS # | 1627607-87-7 | |
| Related CAS # | PFI-2;1627676-59-8 | |
| PubChem CID | 78243738 | |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid powder | |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 | |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 9 | |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 6 | |
| Heavy Atom Count | 35 | |
| Complexity | 813 | |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 | |
| SMILES | C1CCN(C1)C(=O)[C@@H](CC2=CC(=CC=C2)C(F)(F)F)NS(=O)(=O)C3=CC4=C(CNCC4)C(=C3)F.Cl |
|
| InChi Key | ZADKZNVAJGEFLC-ZMBIFBSDSA-N | |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C23H25F4N3O3S.ClH/c24-20-13-18(12-16-6-7-28-14-19(16)20)34(32,33)29-21(22(31)30-8-1-2-9-30)11-15-4-3-5-17(10-15)23(25,26)27;/h3-5,10,12-13,21,28-29H,1-2,6-9,11,14H2;1H/t21-;/m1./s1 | |
| Chemical Name | (R)-8-fluoro-N-(1-oxo-1-(pyrrolidin-1-yl)-3-(3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)propan-2-yl)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinoline-6-sulfonamide hydrochloride | |
| Synonyms |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 | |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month Note: Please store this product in a sealed and protected environment, avoid exposure to moisture. |
|
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| ln Vitro | (R)-PFI-2 hydrochloride inhibits with a high IC50 of 2.0 nM, while (S)-PFI-2 hydrochloride has an IC50 of 1.0 μM [1]. |
| ln Vivo | PFI-2 hydrochloride (ip, 200 μM, twice weekly) reduces the progression of renal fibrosis and protects renal function in FA nephropathy [2]. PFI-2 hydrochloride (ip, 200 μM, twice weekly) decreases ECM buildup and fibroblast activation following FA damage [2]. PFI-2 hydrochloride (ip, 200 μM, twice weekly) suppresses Th2 cytokine signaling activation and M2 macrophage polarization [2]. PFI-2 hydrochloride (ip, 200 μM, twice weekly) reduces M2 macrophage-myofibroblast transition and bone marrow myofibroblast accumulation in FA-treated kidneys [2]. PFI-2 hydrochloride (ip, 200 μM, twice weekly) attenuates macrophage M2 polarization and M2 macrophage to myofibroblast transition in obstructed kidneys [2]. PFI-2 hydrochloride (ip, 200 μM, twice weekly) reduces myeloid myofibroblast aggregation and renal fibrosis after UUO damage [2]. PFI-2 hydrochloride (ip, 200 μM, twice weekly) decreases inflammatory cell infiltration, inflammatory chemical synthesis, and NF-κB activation in FA nephropathy [2]. |
| Animal Protocol |
Animal/Disease Models: Male C57BL/6 mice (8-10-week old, 20-25 g)[2] Doses: 200 μM (PFI-2 is diluted in 100 μL 0.1% (v/v) DMSO to a concentration of 200 μM/100 μL) Route of Administration: intraperitoneal (ip)injection, twice a week Experimental Results: Presented less bone marrow-derived myofibroblasts, fewer CD206+/α-smooth muscle actin + cells and developed less renal fibrosis (P<0.01). decreased the infiltration of inflammatory cells and diminished the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines in the kidneys after folic acid treatment (P<0.01). Suppressed the accumulation of NF-κB p65+ cells in folic acid nephropathy (P<0.01). |
| References |
[1]. Revealing inhibition difference between PFI-2 enantiomers against SETD7 by molecular dynamics simulations, binding free energy calculations and unbinding pathway analysis. Sci Rep. 2017 Apr 18;7:46547. [2]. Pharmacological inhibition of SETD7 by PFI-2 attenuates renal fibrosis following folic acid and obstruction injury. Eur J Pharmacol. 2021 Jun 15;901:174097. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
|
|||
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (4.66 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (4.66 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (4.66 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. Solubility in Formulation 4: 1 mg/mL (1.87 mM) in PBS (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution; with ultrasonication. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.8657 mL | 9.3287 mL | 18.6574 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3731 mL | 1.8657 mL | 3.7315 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1866 mL | 0.9329 mL | 1.8657 mL |