PF-1355 (also known as PF-06281355), a 2-thiouracil analog, is a novel, potent, selective and orally bioavailable mechanism-based MPO inhibitor used for treatment of vasculitic diseases. MPO is a critical mediator of vasculitis in mouse disease models. MPO has been associated with vasculitis, disseminated vascular inflammation typically involving pulmonary and renal microvasculature and often resulting in critical consequences. MPO contributes to vascular injury by 1) catabolizing nitric oxide, impairing vasomotor function; 2) causing oxidative damage to lipoproteins and endothelial cells, leading to atherosclerosis; and 3) stimulating formation of neutrophil extracellular traps, resulting in vessel occlusion and thrombosis. A pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic response model of PF-1355 exposure in relation with MPO activity was derived from mouse peritonitis. The contribution of MPO activity to vasculitis was then examined in an immune complex model of pulmonary disease. Oral administration of PF-1355 reduced plasma MPO activity, vascular edema, neutrophil recruitment, and elevated circulating cytokines. In a model of anti-glomerular basement membrane disease, formerly known as Goodpasture disease, albuminuria and chronic renal dysfunction were completely suppressed by PF-1355treatment. This study shows that MPO activity is critical in driving immune complex vasculitis and provides confidence in testing the hypothesis that MPO inhibition will provide benefit in treating human vasculitic diseases.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C14H15N3O4S |
| Molecular Weight | 321.3516 |
| Exact Mass | 321.078 |
| CAS # | 1435467-38-1 |
| PubChem CID | 71568997 |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid powder |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.666 |
| LogP | 0.64 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 5 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 5 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 22 |
| Complexity | 508 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| InChi Key | LJBUZOGABRDGBR-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C14H15N3O4S/c1-20-8-3-4-11(21-2)9(5-8)10-6-13(19)16-14(22)17(10)7-12(15)18/h3-6H,7H2,1-2H3,(H2,15,18)(H,16,19,22) |
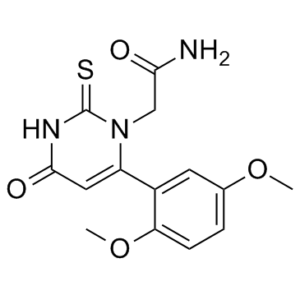
| Chemical Name | 2-(6-(2,5-Dimethoxyphenyl)-4-oxo-2-thioxo-3,4-dihydropyrimidin-1(2H)-yl)acetamide |
| Synonyms | PF-1355; PF 1355; PF1355; PF-06281355; PF 06281355; PF06281355; |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| ln Vitro | PF-1355 demonstrated a dose-dependent reduction in MPO activity in human neutrophils activated with phorbol ester (EC50 = 1.47 μM) and in residual MPO activity in human blood treated with lipopolysaccharide (EC50 = 2.03 μM) [1]. |
| ln Vivo | By reducing plasma MPO activity, angioedema, neutrophil recruitment, and increasing circulating cytokines, PF-1355 is administered orally. Treatment with PF-1355 completely suppressed proteinuria and chronic renal impairment in a model of glomerular basement membrane disease (previously known as Goodpasture's disease) [1]. |
| References |
[1]. PF-1355, a mechanism-based myeloperoxidase inhibitor, prevents immune complex vasculitis and anti-glomerular basement membrane glomerulonephritis. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2015 May;353(2):288-98. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | DMSO : ~50 mg/mL (~155.59 mM) |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (6.47 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 20.8 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (6.47 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 20.8 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (6.47 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 20.8 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.1119 mL | 15.5594 mL | 31.1187 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.6224 mL | 3.1119 mL | 6.2237 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3112 mL | 1.5559 mL | 3.1119 mL |