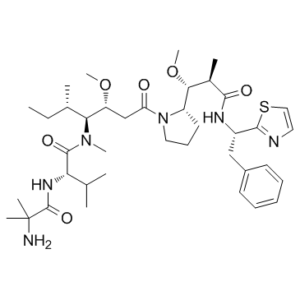
PF-06380101 (Auristatin 0101; PF06380101; AUR-0101) is a novel and ultra-potent cytotoxic Dolastatin 10 analogue and a tubulin inhibitor with excellent anticancer activity. It exhibits differential ADME properties and high potencies in tumor cell proliferation assays when compared to other synthetic auristatin analogues used in ADC preparation. Clinically employed as payloads in antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs), auristatins are synthetic analogues of the naturally occurring antitumor compound Dolastatin 10. They are extremely potent cytotoxic microtubule inhibitors. Our lead auristatin, PF-06380101, is discovered and the design and synthesis of several new auristatin analogues with N-terminal modifications, including amino acids with α,α-disubstituted carbon atoms, are described. Comparing these novel peptide structure modifications to other synthetic auristatin analogues used in the creation of ADCs, the results were analogues with superior potencies in tumor cell proliferation assays and distinct ADME characteristics. Furthermore, tubulin and auristatin cocrystal structures that enable a thorough analysis of their binding mechanisms are presented. Surprisingly, in their functionally relevant tubulin bound state, all the analyzed analogues have a cis-configuration at the Val-Dil amide bond, whereas in solution this bond is exclusively in the trans-configuration. This astounding finding provides insight into the preferred binding mode of auristatins and is a useful resource for structure-based drug design.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C39H62N6O6S |
| Molecular Weight | 743.0112 |
| Exact Mass | 742.445 |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 63.04; H, 8.41; N, 11.31; O, 12.92; S, 4.31 |
| CAS # | 1436391-86-4 |
| Related CAS # | PF-06380101-d8 |
| PubChem CID | 71569947 |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid powder |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 903.1±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Flash Point | 500.0±34.3 °C |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.3 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.546 |
| LogP | 5.05 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 9 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 19 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 52 |
| Complexity | 1170 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 8 |
| SMILES | S1C([H])=C([H])N=C1[C@]([H])(C([H])([H])C1C([H])=C([H])C([H])=C([H])C=1[H])N([H])C([C@]([H])(C([H])([H])[H])[C@]([H])([C@]1([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])N1C(C([H])([H])[C@]([H])([C@]([H])([C@@]([H])(C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])[H])N(C([H])([H])[H])C([C@]([H])(C([H])(C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])[H])N([H])C(C(C([H])([H])[H])(C([H])([H])[H])N([H])[H])=O)=O)OC([H])([H])[H])=O)OC([H])([H])[H])=O |
| InChi Key | QAAFNSMAIAVCHE-BZLYQNAUSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C39H62N6O6S/c1-11-25(4)33(44(8)37(48)32(24(2)3)43-38(49)39(6,7)40)30(50-9)23-31(46)45-20-15-18-29(45)34(51-10)26(5)35(47)42-28(36-41-19-21-52-36)22-27-16-13-12-14-17-27/h12-14,16-17,19,21,24-26,28-30,32-34H,11,15,18,20,22-23,40H2,1-10H3,(H,42,47)(H,43,49)/t25-,26+,28-,29-,30+,32-,33-,34+/m0/s1 |
| Chemical Name | (2S)-2-[(2-amino-2-methylpropanoyl)amino]-N-[(3R,4S,5S)-3-methoxy-1-[(2S)-2-[(1R,2R)-1-methoxy-2-methyl-3-oxo-3-[[(1S)-2-phenyl-1-(1,3-thiazol-2-yl)ethyl]amino]propyl]pyrrolidin-1-yl]-5-methyl-1-oxoheptan-4-yl]-N,3-dimethylbutanamide |
| Synonyms | AUR-0101; PF06380101; Auristatin 0101; AUR 0101; PF-06380101; AUR0101; PF 06380101 |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.03.00 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | Auristatin |
| ln Vitro | PF-06380101 demonstrated a mean systemic clearance (Cl) of 70 mL/min/kg and a volume of distribution (Vss) of 14.70 L/kg following an IV dose of 20a at 20 μg/kg to Wistar Han rats. This led to an approximate 6-hour terminal elimination half-life (t1/2). PF-06380101 is a P-glycoprotein (P-gp) substrate that preferentially distributes into human plasma as opposed to whole blood. It is expected that PF-06380101 will not cause pharmacokinetic drug interactions with substances whose main mechanism of clearance is mediated by CYP1A2, CYP2B6, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, and/or CYP3A4/5. Reports regarding the effectiveness of the newly developed auristatin analogues as ADC payloads, along with the creation of the lead analogue 20a (PF-06380101), will be provided eventually. |
| ln Vivo | The average systemic clearance (Cl) of PF-06380101 was 70 mL/min/kg, the volume of distribution (Vss) was 14.70 L/kg, and the terminal elimination half-life (t1/2) was approximately 6 hours following an intravenous injection of 20 μg/kg into Wistar Han rats for a period of 20 years. As a P-glycoprotein (P-gp) substrate, PF-06380101 distributes preferentially into human plasma as opposed to whole blood. PF-06380101 is anticipated to exhibit minimal pharmacokinetic drug interaction risk with substances whose principal clearance mechanism is metabolism mediated by CYP1A2, CYP2B6, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, and/or CYP3A4/5. We will report on the creation of lead analog 20a (PF-06380101) and the use of novel aristatin analogs as ADC payloads in due time. |
| References |
[1]. Discovery of cytotoxic dolastatin 10 analogues with N-terminal modifications. J Med Chem. 2014 Dec 26;57(24):10527-43. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | DMSO: ≥ 65 mg/mL (~87.5 mM) |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (3.36 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: 2.5 mg/mL (3.36 mM) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), suspension solution; with ultrasonication. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (3.36 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.3459 mL | 6.7294 mL | 13.4588 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.2692 mL | 1.3459 mL | 2.6918 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1346 mL | 0.6729 mL | 1.3459 mL |