PD318088 (PD-318088), an analog of PD184352, is a novel, potent and non-ATP competitive (allosteric) MEK1/2 inhibitor with potential anticancer activity. Against different cancer cells, PD318088 exhibits strong anti-proliferative activity.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C16H13BRF3IN2O4 | |
| Molecular Weight | 561.09 | |
| Exact Mass | 559.905 | |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 34.25; H, 2.34; Br, 14.24; F, 10.16; I, 22.62; N, 4.99; O, 11.41 | |
| CAS # | 391210-00-7 | |
| Related CAS # |
|
|
| PubChem CID | 10231331 | |
| Appearance | Light yellow to yellow solid powder | |
| Density | 2.0±0.1 g/cm3 | |
| Index of Refraction | 1.660 | |
| LogP | 7.43 | |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 4 | |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 8 | |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 7 | |
| Heavy Atom Count | 27 | |
| Complexity | 499 | |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 | |
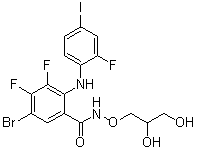
| SMILES | BrC1=CC(C(NOCC(CO)O)=O)=C(C(F)=C1F)NC2=CC=C(C=C2F)I |
|
| InChi Key | XXSSGBYXSKOLAM-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C16H13BrF3IN2O4/c17-10-4-9(16(26)23-27-6-8(25)5-24)15(14(20)13(10)19)22-12-2-1-7(21)3-11(12)18/h1-4,8,22,24-25H,5-6H2,(H,23,26) | |
| Chemical Name | 5-bromo-N-(2,3-dihydroxypropoxy)-3,4-difluoro-2-(2-fluoro-4-iodoanilino)benzamide | |
| Synonyms |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 | |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | MEK1; MEK2 | ||
| ln Vitro | PD318088 is a small-molecule MEK1/2 inhibitor, an analog of PD184352, suggesting it might have significant anti-proliferative activity against cancer cells, even though there isn't a functional study of PD318088 available at this time. In an area of the MEK1 active site close to the ATP-binding site, PD318088 and ATP bind simultaneously. The Kd monomer-dimer for both MEK1 and MEK2 is moderately increased (to 140 nM) by the ternary complexes formed with PD318088 and MgATP. Tetramers and higher-order aggregates cannot form when PD318088 and MgATP are bound to MEK1. Together, PD318088 and MgATP slightly raise the dimerization disassociation constant for MEK1 and MEK2 from ~75 nM to ~140, indicating that the mechanism of PD318088 inhibition is likely the result of localized conformational changes in the active site rather than a general change in the structure. [1] | ||
| ln Vivo |
|
||
| Enzyme Assay | PD318088 and MgATP, the Kd monomer-dimer for MEK1 and MEK2 increases moderately (to 140 nM). The dimerization disassociation constant for MEK1 and MEK2 increases slightly from ~75 nM to ~140 nM when PD318088 and MgATP are combined. | ||
| Animal Protocol |
|
||
| References |
[1]. Nat Struct Mol Biol . 2004 Dec;11(12):1192-7. |
||
| Additional Infomation | MEK1 and MEK2 are closely related, dual-specificity tyrosine/threonine protein kinases found in the Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathway. Approximately 30% of all human cancers have a constitutively activated MAPK pathway, and constitutive activation of MEK1 results in cellular transformation. Here we present the X-ray structures of human MEK1 and MEK2, each determined as a ternary complex with MgATP and an inhibitor to a resolution of 2.4 A and 3.2 A, respectively. The structures reveal that MEK1 and MEK2 each have a unique inhibitor-binding pocket adjacent to the MgATP-binding site. The presence of the potent inhibitor induces several conformational changes in the unphosphorylated MEK1 and MEK2 enzymes that lock them into a closed but catalytically inactive species. Thus, the structures reported here reveal a novel, noncompetitive mechanism for protein kinase inhibition.[1] |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
|
|||
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.75 mg/mL (4.90 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 27.5 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 2.75 mg/mL (4.90 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 27.5 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 2.75 mg/mL (4.90 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 27.5 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.7822 mL | 8.9112 mL | 17.8225 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3564 mL | 1.7822 mL | 3.5645 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1782 mL | 0.8911 mL | 1.7822 mL |