Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C20H13FN4O2 | |
| Molecular Weight | 360.34 | |
| Exact Mass | 360.102 | |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 66.66; H, 3.64; F, 5.27; N, 15.55; O, 8.88 | |
| CAS # | 152121-53-4 | |
| Related CAS # |
|
|
| PubChem CID | 4712 | |
| Appearance | white solid powder | |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | |
| Boiling Point | 583.1±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Flash Point | 306.4±30.1 °C | |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.6 mmHg at 25°C | |
| Index of Refraction | 1.651 | |
| LogP | 5.32 | |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 | |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 5 | |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 3 | |
| Heavy Atom Count | 27 | |
| Complexity | 495 | |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 | |
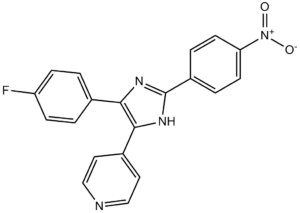
| SMILES | FC(C=C1)=CC=C1C2=C(C3=CC=NC=C3)NC(C4=CC=C([N+]([O-])=O)C=C4)=N2 |
|
| InChi Key | BGIYKDUASORTBB-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C20H13FN4O2/c21-16-5-1-13(2-6-16)18-19(14-9-11-22-12-10-14)24-20(23-18)15-3-7-17(8-4-15)25(26)27/h1-12H,(H,23,24) | |
| Chemical Name | 4-[4-(4-fluorophenyl)-2-(4-nitrophenyl)-1H-imidazol-5-yl]pyridine | |
| Synonyms |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 | |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | p38 MAPK (IC50 = 89 nM); TGF-β; Activin A; Enterovirus71 |
| ln Vitro | PD169316 (10 μM) inhibits TGFβ and Activin A signaling but not BMP4 signaling in CaOV3 cells. In CaOV3 cells, PD169316 (0.2–20 μM) inhibits TGFβ-induced Smad2 nuclear translocation, Smad7 mRNA induction, and reporter gene activity[1]. In Nestin knockdown cells, PD169316 (10 μM) exhibits a noticeably higher rate of proliferation, and it can reverse the effect of Nestin knockdown on cell viability in the absence of EGF[2]. In PC12 cells, PD169316 significantly reduces p38 MAP kinase activity while having no effect on ERK activity. In differentiated PC12 cells, PD169316 (10 μM) inhibits the apoptosis that is brought on by the removal of trophic factors[3]. Without preventing upstream kinases from phosphorylating p38, PD169316 (10 μM, 30 min) selectively inhibits the kinase activity of the phosphorylated p38. Increased phospho p-38 levels in the presence of PD169316 are most likely caused by MAPK phosphatases blocking the negative feedback loop of p38 MAPK dephosphorylation[4]. |
| ln Vivo | PD169316 PD169316 (1 mg/kg, intramuscular injection every day for 14 days straight) exhibits antiviral activity in a suckling mouse model[5]. |
| Enzyme Assay | The cells are incubated in the absence or presence of insulin (50 ng/mL) for 15 min at 37°C sixteen hours after the removal of serum from Rat-1 fibroblasts or NGF from differentiated PC12 cells. The cells are then solubilized in 400 μL of ice-cold immunoprecipitation buffer, which contains 10 mM Tris, pH 7.4, 1% Triton X-100, 0.5% Nonidet P-40, 150 mM NaCl, 1 mM EDTA, 1 mM EGTA, 0.2 mM sodium orthovanadate, and 0.2 mM phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride. The cell lysates are centrifuged to remove insoluble material, and 200 g of the supernatant protein (400 μL, total volume) is incubated with 1 μg of anti-p38 antibodies for 1 h at 4°C before being incubated with 30 μL of Protein G Plus/Protein A-agarose for an additional hour. The immunocomplexes are pelleted, washed three times in immunoprecipitation buffer, and then once in kinase ish buffer (50 mM β-glycerolphosphate, 1 mM EGTA, 20 mM MgCl2, and 100 μM sodium orthovanadate). The protein kinase assay is initiated by the addition of 20 μL of 2× reaction buffer (50 mMβ-glycerolphosphate, 1 mM EGTA, 20 mM MgCl2, 100 μM sodium orthovanadate, 0.1 mg/mL ATF-2 (N-terminal half), 50 μg/mL IP20, a peptide inhibitor of c-AMP dependent protein kinase, 200 μM ATP, and 0.9 mCi/mL [32P]ATP) to 20 μL of immune complex. The reaction is allowed to run for 10 minutes at 30 degrees Celsius before being stopped by adding 2× LaemmLi sample buffer. This reaction is then examined using 12% acrylamide gels and SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. The gels are dried and then put through phosphoimaging after electrophoresis. |
| Cell Assay | KBU cells are subjected to 12 ppm G. pps either alone or in combination with 1 hour of pre-exposure to the P38 inhibitor PD169316, and their proliferation (MTT), apoptosis (Ann V), and changes in the degree of protein modifications in the SAPK/JNK and P38 signaling pathways are assessed. |
| Animal Protocol |
EV71-challenged suckling mouse model (7-day-old Kunming mice)[5]. 1 mg/kg. Intramuscular injection every day for 14 consecutive days. |
| References |
[1]. The p38 MAPK inhibitor, PD169316, inhibits transforming growth factor beta-induced Smad signaling in human ovarian cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2003 Oct 17;310(2):391-7. [2]. Suppression of Nestin reveals a critical role for p38-EGFR pathway in neural progenitor cell proliferation. Oncotarget. 2016 Dec 27;7(52):87052-87063. [3]. Apoptosis induced by withdrawal of trophic factors is mediated by p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1997 Aug 15;272(33):20490-4. [4]. p38 and p42/44 MAPKs differentially regulate progesterone receptor A and B isoform stabilization. Mol Endocrinol. 2011 Oct;25(10):1710-24. [5]. PD169316, a specific p38 inhibitor, shows antiviral activity against Enterovirus71. Virology. 2017 Aug;508:150-158. |
| Additional Infomation |
4-[4-(4-fluorophenyl)-2-(4-nitrophenyl)-1H-imidazol-5-yl]pyridine is a member of imidazoles. PD-169316 is a p38 MAP kinase inhibitor. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
DMSO: ~14 mg/mL ( ~38.6 mM) Water: Insoluble Ethanol: Insoluble |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: 1.25 mg/mL (3.47 mM) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), suspension solution; with sonication. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 12.5 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: 1.25 mg/mL (3.47 mM) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), suspension solution; with ultrasonication. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 12.5 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 1.25 mg/mL (3.47 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 12.5 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. Solubility in Formulation 4: 5%DMSO+40%PEG300+5%Tween 80+ 50%ddH2O: 0.7mg/ml (1.94mM) Solubility in Formulation 5: 5 mg/mL (13.88 mM) in 50% PEG300 50% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), suspension solution; with ultrasonication. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.7752 mL | 13.8758 mL | 27.7516 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5550 mL | 2.7752 mL | 5.5503 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2775 mL | 1.3876 mL | 2.7752 mL |